SLVSGO0 October 2024 TPS25763-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Device Comparison Table
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Recommended Components
- 6.5 Thermal Information
- 6.6 Buck-Boost Regulator
- 6.7 CC Cable Detection Parameters
- 6.8 CC VCONN Parameters
- 6.9 CC PHY Parameters
- 6.10 Thermal Shutdown Characteristics
- 6.11 Oscillator Characteristics
- 6.12 ADC Characteristics
- 6.13 TVSP Parameters
- 6.14 Input/Output (I/O) Characteristics
- 6.15 BC1.2 Characteristics
- 6.16 I2C Requirements and Characteristics
- 6.17 Typical Characteristics
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Device Power Management and Supervisory Circuitry
- 8.3.2 TVSP Device Configuration and ESD Protection
- 8.3.3 External NFET and LSGD
- 8.3.4
Buck-Boost Regulator
- 8.3.4.1 Buck-Boost Regulator Operation
- 8.3.4.2 Switching Frequency, Frequency Dither, Phase-Shift and Synchronization
- 8.3.4.3 VIN Supply and VIN Over-Voltage Protection
- 8.3.4.4 Feedback Paths and Error Amplifiers
- 8.3.4.5 Transconductors and Compensation
- 8.3.4.6 Output Voltage DAC, Soft-Start and Cable Droop Compensation
- 8.3.4.7 VBUS Overvoltage Protection
- 8.3.4.8 VBUS Undervoltage Protection
- 8.3.4.9 Current Sense Resistor (RSNS) and Current Limit Operation
- 8.3.4.10 Buck-Boost Peak Current Limits
- 8.3.5 USB-PD Physical Layer
- 8.3.6 VCONN
- 8.3.7 Cable Plug and Orientation Detection
- 8.3.8 ADC
- 8.3.9 BC 1.2, Legacy and Fast Charging Modes (Px_DP, Px_DM)
- 8.3.10 DisplayPort Hot-Plug Detect (HPD)
- 8.3.11 USB2.0 Low-Speed Endpoint
- 8.3.12 Digital Interfaces
- 8.3.13 I2C Interface
- 8.3.14 Digital Core
- 8.3.15 NTC Input
- 8.3.16 Thermal Sensors and Thermal Shutdown
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Revision History
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RQL|29
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.3.1.2 Internal LDO Regulators
Three internal LDOs provide regulated supplies for operation of internal circuitry.
- LDO_5V: Supplies buck-boost gate drive circuitry, LDO_3V3, LDO_1V5, and PA and
PB VCONN power paths. External bypass capacitance, CLDO_5V is required for
proper operation. It is highly recommended to include an additional high frequency 0.1
μF capacitor in parallel with CLDO_5V. In the design, place
CLDO_5V and the parallel high frequency capacitor as close to the LDO_5V
pin as possible. This capacitance: 1) provides energy storage for the buck-boost
internal FET gate drivers, and 2) is required to stabilize the internal 5-V LDO in
applications where an external 5-V supply is not connected. The TPS25763-Q1 does not operate (release reset) until VLDO_5V(UVLO_R)
threshold is met. Hard reset occurs when VLDO_5V <
VLDO_5V(UVLO_F) threshold. Current from LDO_5V returns to PGND pin. The
LDO_5V output may be used to supply a small external loads such as indicator LEDs. When
supplying external components, it is recommended that the total external load current
not exceed 25 mA (MAX).
- 0.1W VCONN: when enabled in the application configuration GUI, LDO_5V is capable of sourcing 20 mA each to PA_VCONN and PB_VCONN.
- 1W VCONN: when enabled in the application configuration GUI, this mode of operation requires an external 4.75 - 5.5 V, 500-mA capable supply connected to LDO_5V. Back-feeding of LDO_5V is allowed.
- LDO_3V3: Supplies internal analog circuits, GPIO buffers, USB PD and the USB Endpoint PHYs. External bypass capacitance of CLDO_3V3 is required for proper operation. An additional 0.1 μF capacitor in parallel with CLDO_3V3 is highly recommended to filter high frequency noise from the I/O buffers and PHYs. The LDO_3V3 can supply external circuits at up to 25 mA. Expected loads include: EEPROM (5mA), NTC resistor divider network (< 1 mA). Current may be drawn up to ILDO_3V3(ILIMIT). Note: the USB PD and Endpoint PHYs draw current from LDO_3V3. If a CCx or Dx pin is shorted to GND during a transmission the current drawn may reach the current limit threshold. Similarly, if any GPIO pins are configured as push-pull outputs and a GPIO short to GND event occurs, the LDO_3V3 current limit may be reached. Current returns to AGND pin.
- LDO_1V5: Supplies digital core. External bypass capacitance of CLDO_1V5 is required for proper operation. An additional 0.1 μF capacitor in parallel with CLDO_1V5 is highly recommended to filter noise generated by the digital core. The M0 is held in reset until all three UVLO_R (rising) thresholds are met. Current returns to AGND pin.
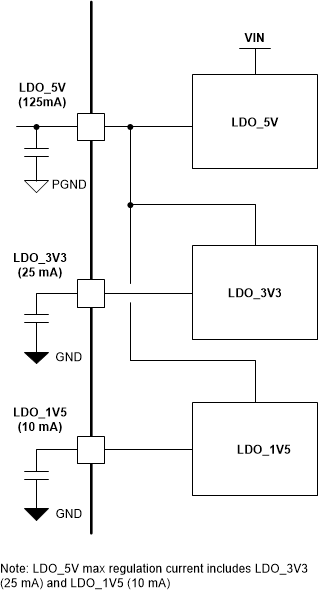 Figure 8-3 Internal LDO Connection
Diagram
Figure 8-3 Internal LDO Connection
Diagram