SLVSHH5B August 2023 – December 2024 TPS25983
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Device Comparison Table
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Undervoltage Protection (UVLO and UVP)
- 7.3.2 Overvoltage Protection (OVP)
- 7.3.3 Inrush Current, Overcurrent, and Short-Circuit Protection
- 7.3.4 Overtemperature Protection (OTP)
- 7.3.5 Analog Load Current Monitor (IMON)
- 7.3.6 Power Good (PG)
- 7.3.7 Reverse Current Blocking FET Driver
- 7.3.8 Fault Response
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application: Standby Power Rail Protection in Datacenter Servers
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Device Selection
- 8.2.2.2 Setting the Current Limit Threshold: RILIM Selection
- 8.2.2.3 Setting the Undervoltage and Overvoltage Lockout Set Point
- 8.2.2.4 Choosing the Current Monitoring Resistor: RIMON
- 8.2.2.5 Setting the Output Voltage Ramp Time (TdVdt)
- 8.2.2.6 Setting the Transient Overcurrent Blanking Interval (tITIMER)
- 8.2.2.7 Setting the Auto-Retry Delay and Number of Retries
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 8.3 System Examples
- 8.4 Power Supply Recommendations
- 8.5 Layout
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Revision History
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RGE|24
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RGE|24
Orderable Information
8.3.3 Priority Power MUXing
Applications having two energy sources such as PCIe cards, tablets, and portable battery powered equipment require preference of one source to another. For example, mains power (wall-adapter) has the priority over the internal battery back-up power. These applications demand for switchover from mains power to backup power only when main input voltage falls below a user-defined threshold. The TPS25983 devices provide a simple design for priority power multiplexing needs.
Figure 8-17 shows a typical priority power multiplexing implementation using TPS25983 devices. When the primary (priority) power source (IN1) is present and above the undervoltage (UVLO) threshold, the primary path device path powers the OUT bus irrespective of which auxiliary supply voltage condition. The device in auxiliary path is held in off condition by forcing the OVLO pin to high using the EN/UVLO signal of the primary path device. Once the primary supply voltage falls below the user-defined undervoltage threshold (UVLO), the primary path device is turned off. At the same the auxiliary, the auxiliary path device turns on and starts delivering power to the load. In this configuration, supply overvoltage protection is not available on both channels.
 Figure 8-17 Two Devices, Priority Power
MUX Configuration
Figure 8-17 Two Devices, Priority Power
MUX ConfigurationThe PG pins of the devices can be used as a digital indication to identify which of the two supplies is active and delivering power to the load.
A key consideration in power MUXing applications is the minimum voltage the output bus droops to during the switchover from one supply to another. This in turn depends on multiple factors including the output load current (ILOAD), output bus hold-up capacitance (COUT) and switchover time (tSW).
While switching from primary supply (VIN1) to auxiliary supply (VIN2) or vice versa, the minimum bus voltage can be calculated using Equation 30. Here, the maximum switchover time (tSW) is the time taken by the device to turn on and start delivering power to the load, which is equal to the device turn on time (tON), which includes the turn on delay (tD,ON) and rise time (tR) determined by the dVdt capacitor (CdVdt) and bus voltage.
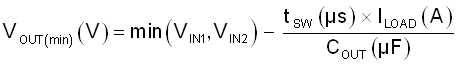
Figure 8-18 and Figure 8-19 illustrate the power MUXing behavior.
 Figure 8-18 TPS25983 Power MUX, Switchover From Primary to Auxiliary Supply
Figure 8-18 TPS25983 Power MUX, Switchover From Primary to Auxiliary Supply Figure 8-19 TPS25983 Power MUX, Switchover From Auxiliary to Primary Supply
Figure 8-19 TPS25983 Power MUX, Switchover From Auxiliary to Primary Supply- Power MUXing can be accomplished either between two similar rails (such as 12-V primary and 12-V auxiliary, 3.3-V primary and 3.3-V auxiliary) or between dissimilar rails (such as 12-V primary and 5-V auxiliary, or vice versa).
- For power MUXing cases with skewed voltage combinations, care must be taken to design circuit components on EN/UVLO, OVLO pins for the lower voltage channel devices such that the absolute-maximum ratings on those pins are not exceeded when higher voltage is present on the other channel. Also, the dVdt pin capacitor rating must be chosen based on the highest of the two supplies. Refer to Recommended Operating Conditions table for more details.
- Using a series resistance between EN/UVLO pin of primary path eFuse and the OVLO pin of the auxiliary path eFuse is recommended. The value of the series resistor must be at least 10 times higher than the bottom resistor of the ladder on the EN/UVLO pin of the primary path eFuse.