SLVSGX1A July 2023 – October 2023 TPS25984
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (continued)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Undervoltage Protection
- 8.3.2 Insertion Delay
- 8.3.3 Overvoltage Protection
- 8.3.4 Inrush Current, Overcurrent, and Short-Circuit Protection
- 8.3.5 Analog Load Current Monitor (IMON)
- 8.3.6 Mode Selection (MODE)
- 8.3.7 Parallel Device Synchronization (SWEN)
- 8.3.8 Stacking Multiple eFuses for Unlimited Scalability
- 8.3.9 Analog Junction Temperature Monitor (TEMP)
- 8.3.10 Overtemperature Protection
- 8.3.11 Fault Response and Indication (FLT)
- 8.3.12 Power-Good Indication (PG)
- 8.3.13 Output Discharge
- 8.3.14 FET Health Monitoring
- 8.3.15 Single Point Failure Mitigation
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RZJ|32
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RZJ|32
Orderable Information
9.4.1 Transient Protection
In the case of a short-circuit or circuit-breaker event when the device interrupts current flow, the input inductance generates a positive voltage spike on the input, and the output inductance generates a negative voltage spike on the output. The peak amplitude of voltage spikes (transients) is dependent on the value of inductance in series to the input or output of the device. Such transients can exceed the absolute maximum ratings of the device if steps are not taken to address the issue. Typical methods for addressing transients include:
Minimize lead length and inductance into and out of the device.
Use a large PCB GND plane.
Connect a Schottky diode from the OUT pin ground to absorb negative spikes.
Connect a low ESR capacitor of 2.2 μF or higher at the OUT pin very close to the device.
Connect a ceramic capacitor CIN = 0.1 μF or higher at the IN pin very close to the device to dampen the rise time of input transients. The capacitor voltage rating must be at least twice the input supply voltage to be able to withstand the positive voltage excursion during inductive ringing.
The approximate value of input capacitance can be estimated with Equation 45.
where
VIN is the nominal supply voltage.
ILOAD is the load current.
LIN equals the effective inductance seen looking into the source.
CIN is the capacitance present at the input.
Some applications can require the addition of a Transient Voltage Suppressor (TVS) to prevent transients from exceeding the absolute maximum ratings of the device. In some cases, even if the maximum amplitude of the transients is below the absolute maximum rating of the device, a TVS can help to absorb the excessive energy dump and prevent it from creating very fast transient voltages on the input supply pin of the IC, which can couple to the internal control circuits and cause unexpected behavior.
The circuit implementation with optional protection components is shown in Figure 9-16.
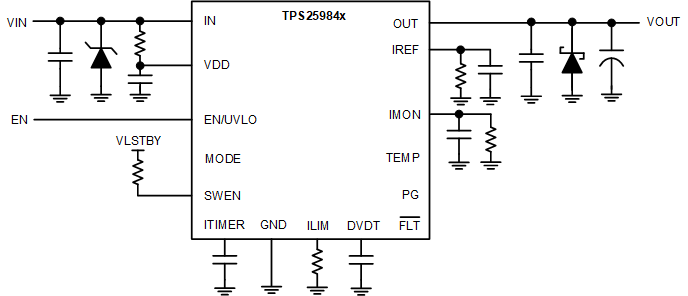 Figure 9-16 Circuit Implementation with
Optional Protection Components
Figure 9-16 Circuit Implementation with
Optional Protection Components