SBVS240C November 2014 – February 2019 TPS3701
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DDC|6
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
6.7 Typical Characteristics
At TJ = 25°C and VDD = 12 V, unless otherwise noted.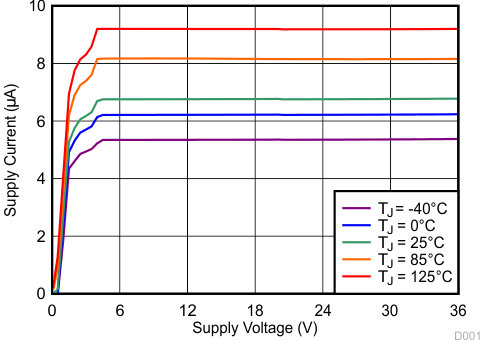
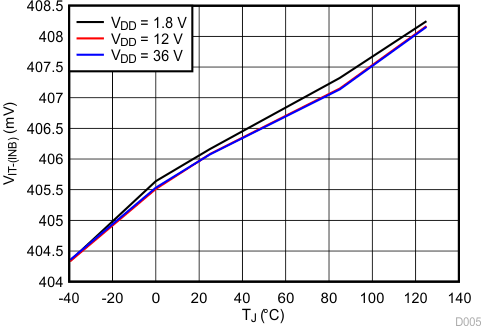 Figure 4. INA Positive Input Threshold Voltage (VIT+(INA)) vs Temperature
Figure 4. INA Positive Input Threshold Voltage (VIT+(INA)) vs Temperature 

| VDD = 1.8 V |

| VDD = 1.8 V |

| Input step ±200 mV |
(High-to-Low Transition at the Inputs)

| VDD = 1.8 V | ||

| VDD = 5 V | ||

| VDD = 5 V, VINA = 410 mV, VINB = 390 mV, VPULL-UP = 3.3 V | ||
 Figure 5. INA Negative Input Threshold Voltage (VIT–(INA)) vs Temperature
Figure 5. INA Negative Input Threshold Voltage (VIT–(INA)) vs Temperature 

| VDD = 1.8 V |
| VDD = 1.8 V |

| Input step ±200 mV |
(Low-to-High Transition at the Inputs)
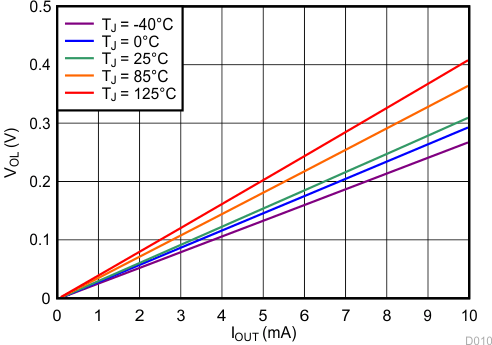
| VDD = 12 V | ||

| VDD = 5 V, VINA = 390 mV, VINB = 410 mV, VPULL-UP = 3.3 V | ||
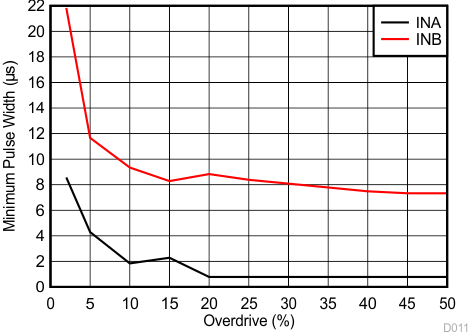
1. Minimum pulse duration required to trigger output high-to-low transition. INA = negative spike below VIT– and INB = positive spike above VIT+.