SBVS261C April 2015 – March 2024 TPS3702-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
- 6 Detailed Description
- 7 Application and Implementation
- 8 Device and Documentation Support
- 9 Revision History
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DDC|6
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
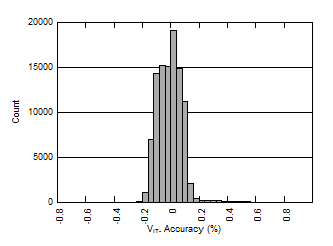
5.7 Typical Characteristics
At TJ = 25°C, VDD = 3V, and RPU = 10kΩ, unless otherwise noted.
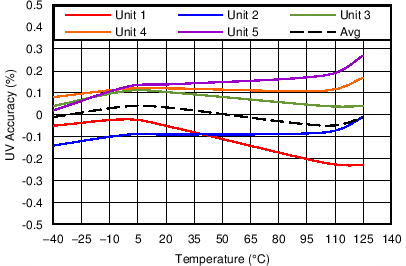
| Performance is across VDD with SET high or low |
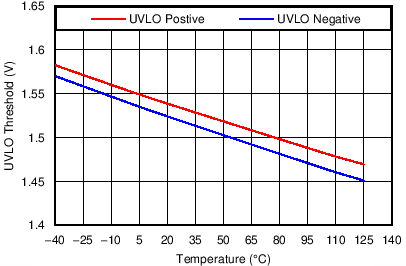
| Performance is across VDD with SET high or low |
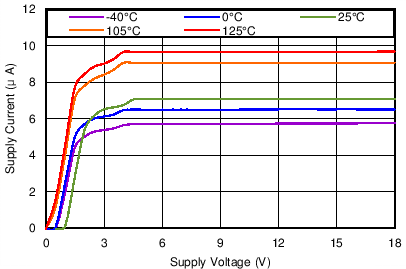
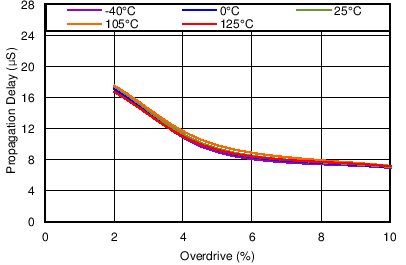
| SENSE transitions from high to low |
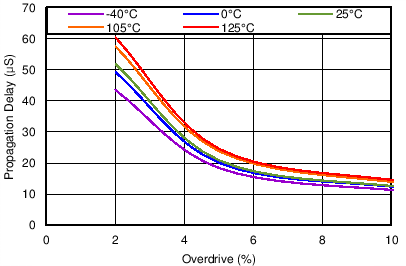
| SENSE transitions from low to high |
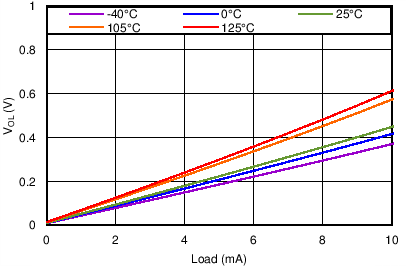
| VDD = 1.8V |
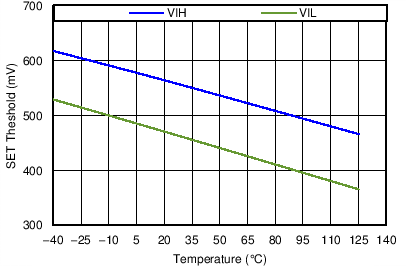
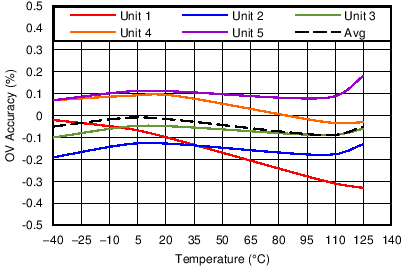
| Performance is across VDD with SET high or low |
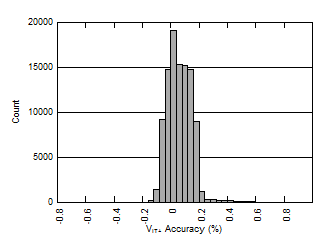
| Performance is across VDD with SET high or low |
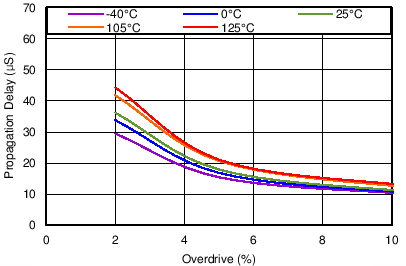
| SENSE transitions from low to high |
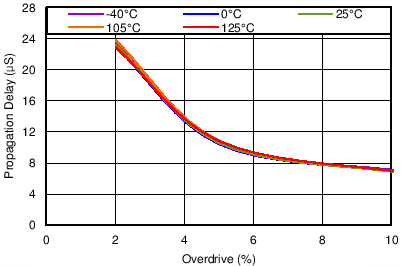
| SENSE transitions from high to low |
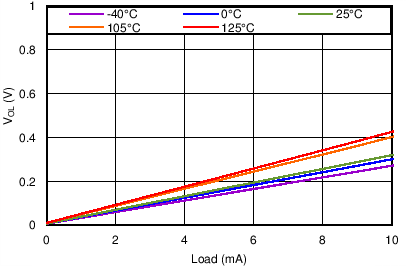
| VDD = 18V |