SPRS288H May 2008 – October 2021
PRODMIX
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DBV|6
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.3.1.2 VDD Glitch Immunity
These devices are immune to quick voltage transient or excursion on VDD. Sensitivity to transients depends on both pulse duration (tGI_VIT) found in Section 6.6 and transient overdrive. Overdrive is defined by how much VDD exceeds the specified threshold. Threshold overdrive is calculated as a percent of the threshold in question, as shown in Equation 1.
where
- VIT = VIT– is the threshold voltage
- VIT+ = VIT + VHYS is the rising threshold voltage
- VDD is the input voltage crossing VIT
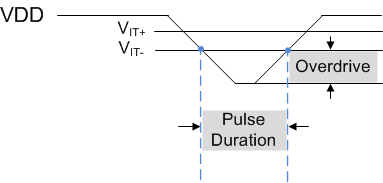 Figure 7-1 Overdrive Versus Pulse Duration
Figure 7-1 Overdrive Versus Pulse DurationTPS3813-Q1 devices have built-in glitch immunity (tGI_VIT-) as shown in Section 6.6. Figure 7-1 shows that VDD must fall below VIT for tGI_VIT, otherwise the faling transistion is ignored. When VDD falls below VIT for tGI_VIT, RESET transitions low to indicate a fault condition after the propagation delay high-to-low (tPHL). When VDD rises above VIT+ = VIT + VHYS, RESET deasserts to a logic high indicating there is no more fault condition only if VDD remains above VIT+ for longer than the reset delay (tD).