SBVS301B October 2016 – September 2021 TPS3850
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DRC|10
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DRC|10
Orderable Information
8.2.1.2.4 Calculating the RESET and WDO Pullup Resistor
The TPS3850 uses an open-drain configuration for the RESET circuit, as shown in Figure 8-6. When the FET is off, the resistor pulls the drain of the transistor to VDD and when the FET is turned on, the FET attempts to pull the drain to ground, thus creating an effective resistor divider. The resistors in this divider must be chosen to ensure that VOL is below its maximum value. To choose the proper pullup resistor, there are three key specifications to keep in mind: the pullup voltage (VPU), the recommended maximum RESET pin current (IRST), and VOL. The maximum VOL is 0.4 V, meaning that the effective resistor divider created must be able to bring the voltage on the reset pin below 0.4 V with IRST kept below 10 mA. For this example, with a VPU of 1.8 V, a resistor must be chosen to keep IRST below 200 μA because this value is the maximum consumption current allowed. To ensure this specification is met, a pullup resistor value of 10 kΩ was selected, which sinks a maximum of 180 μA when RESET or WDO is asserted. As illustrated in Figure 6-12, the RESET current is at 180 μA and the low-level output voltage is approximately zero.
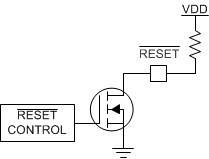 Figure 8-6 Open-Drain
RESET Configuration
Figure 8-6 Open-Drain
RESET Configuration