SLUS886B NOVEMBER 2008 – June 2019 TPS40197
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description Continued
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RGY|16
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RGY|16
Orderable Information
8.3.6 Voltage Reference and Dynamic VID
To provide optimized voltage for Smart-Reflex™ DSP cores, the TPS40197 is designed to monitor the VID code at all times once soft-start is complete, and actively adjusts its output voltage if the VID code should change during normal operation. A digital-to-analog converter (DAC) generates a reference voltage based on the state of logical signals at pins VID0 through VID3. The DAC decodes the 4-bit logic signal into one of the discrete voltages shown in Table 2. The default setting for the output is 1.2 V (VID code 1111). The output voltage is 1.2 V during initial start or restart after cycling the input, toggling EN pin or recovering from a short circuit at the output.
To ensure that no erroneous output voltage is produced, the TPS40197 VID inputs have internal anti-skew circuit with approximately 550 ns of filtering time. Each VID input is pulled up to an internal 1.68-V source with 80-μA pullup current for use with open-drain outputs.
The output voltage can be programmed from 0.9 V to 1.2 V in 20 mV steps. Smooth upward and downward core voltage transition can be achieved by programming the transition rate with an external capacitor connected from REF pin to GND. The required capacitance can be calculated using Equation 5.
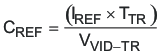
where
- VVID-TR is the total voltage transition through VID
- IREF is the internal reference source/sink current
- TTR is the intended total VID voltage transition time
CREF must be limited to a maximum of 1.5 μF to avoid interfering with the soft start. A capacitor (CREF) with a minimum capacitance of 100-nF is also recommended.
Table 2. Voltage Identification Codes
| VID TERMINALS (0 = LOW, 1 = HIGH) | VREF | |||
| VID3 | VID2 | VID1 | VID0 | (Vdc) |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.90 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.92 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0.94 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0.96 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.98 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1.00 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1.02 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1.04 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.06 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1.08 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1.10 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1.12 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1.14 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1.16 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1.18 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1.20 |