SLVSD73B December 2015 – March 2018 TPS4H000-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3 Feature Description
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|20
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|20
Orderable Information
9.2.3 Application Curves
Figure 38 shows a test example of soft-start when driving a big capacitive load. Figure 39 shows an expanded waveform of the output current.
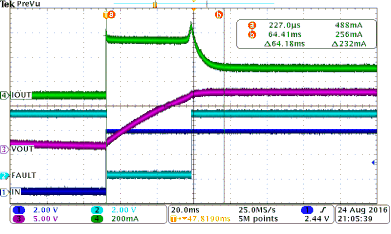
| Load current = 0.2 A | CH2 = FAULT | INx = ↑ |
| Current limit = 0.5 A | CH3 = output voltage | CH1 = INx |
| CL = 2.3 mF | CH4 = output current | VS = 12 V |
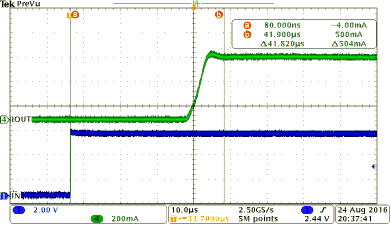
| Load current = 0.2 A | CH2 = FAULT | INx = ↑ |
| Current limit = 0.5 A | CH3 = output voltage | CH1 = INx |
| CL = 2.3 mF | CH4 = output current | VVS = 12 V |
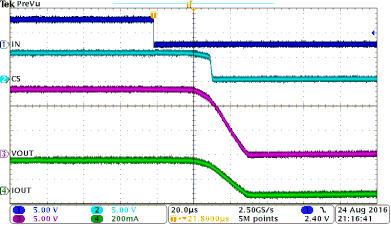
Figure 40 shows a test example of PWM-mode driving. Figure 41 shows the expanded waveform of the rising edge. Figure 42 shows the expanded waveform of the falling edge.
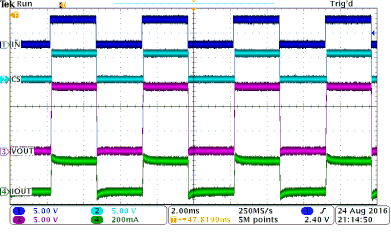
| INx = 200-Hz PWM, 50% duty cycle | CH2 = CS voltage | |
| VVS = 13.5 V | CH3 = output voltage | |
| CH1 = INx signal | CH4 = output current | |
| INx = 200-Hz PWM, 50% duty cycle | CH2 = CS voltage | |||
| VVS = 13.5 V | CH3 = output voltage | |||
| CH1 = INx signal | CH4 = output current | |||
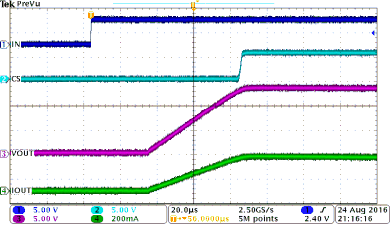
| INx = 200-Hz PWM, 50% duty cycle | CH2 = CS voltage | |
| VVS = 13.5 V | CH3 = output voltage | |
| CH1 = INx signal | CH4 = output current | |