SLUSDW9A June 2020 – June 2020 TPS51215A
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Switch Mode Power Supply Control
- 7.3.2 VREF, V0, V1, V2, V3 and Output Voltage
- 7.3.3 Soft-Start and Power Good
- 7.3.4 SLEW and VID Function
- 7.3.5 MODE Pin Configuration
- 7.3.6 Light-Load Operation
- 7.3.7 Out-of-Bound Operation
- 7.3.8 Current Sensing and Overcurrent Protection
- 7.3.9 Overvoltage and Undervoltage Protection
- 7.3.10 V5IN Undervoltage Lockout Protection
- 7.3.11 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.4 D-CAP2 Control Mode
- 8 Application and Implementation
-
9 Typical Applications
- 9.1 Design Requirements
- 9.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.1 Step One: Determine the Specifications
- 9.2.2 Step Two: Determine System Parameters
- 9.2.3 Step Three: Determine Inductor Value and Choose Inductor
- 9.2.4 Step Four: Set the Output Voltages
- 9.2.5 Step Five: Calculate SLEW Capacitance
- 9.2.6 Step Six
- 9.2.7 Step Seven: Determine the Output Capacitance
- 9.2.8 Step Eight: Select Decoupling and Peripheral Components
- 9.3 Application Examples
- 9.4 Application Curves of Design 1
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RUK|20
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RUK|20
Orderable Information
9.2.3 Step Three: Determine Inductor Value and Choose Inductor
Smaller values of inductor have better transient performance but higher ripple and lower efficiency. Higher values have the opposite characteristics. It is common practice to limit the ripple current to 25% to 50% of the maximum current. In this example, use 25%:
IP-P = 30 A × 0.4 = 12 A
At fSW = 600 kHz with a 20-V input and a 1.8-V output:
Equation 7. 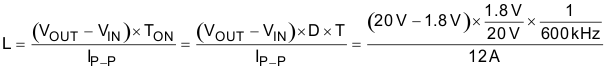
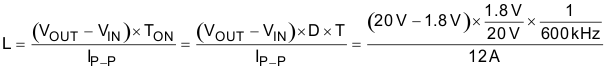
For this application, a 0.22-µH, 1.15-mΩ inductor from Cyntec with part number CMLE063T-R22MS is used.