SLUSD61A December 2017 – March 2019 TPS53119
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Enable and Soft-Start
- 7.3.2 Adaptive ON-Time D-CAP Control and Frequency Selection
- 7.3.3 Small Signal Model
- 7.3.4 Ramp Signal
- 7.3.5 Adaptive Zero Crossing
- 7.3.6 Output Discharge Control
- 7.3.7 Low-Side Driver
- 7.3.8 High-Side Driver
- 7.3.9 Power Good
- 7.3.10 Current Sense and Overcurrent Protection
- 7.3.11 Overvoltage and Undervoltage Protection
- 7.3.12 UVLO Protection
- 7.3.13 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RGT|16
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RGT|16
Orderable Information
7.3.3 Small Signal Model
From small-signal loop analysis, a buck converter using D-CAP mode can be simplified as shown in Figure 17.
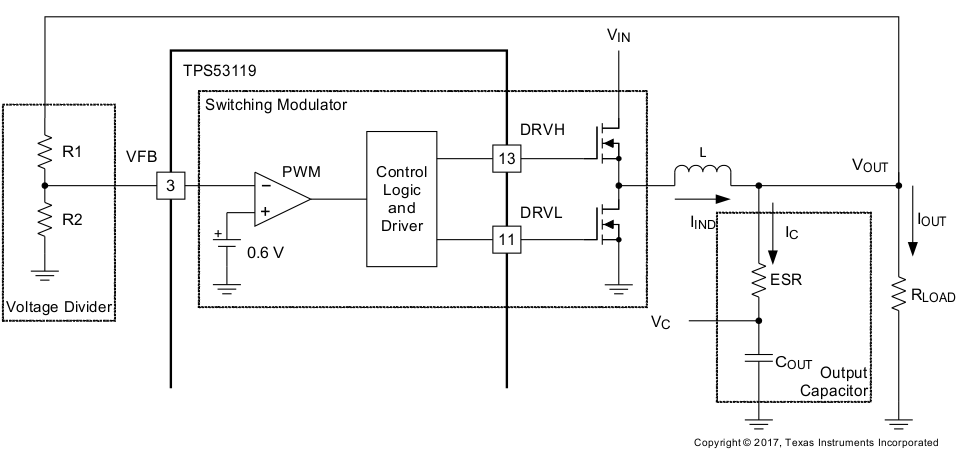 Figure 17. Simplified Modulator Model
Figure 17. Simplified Modulator Model The output voltage is compared with the internal reference voltage (ramp signal is ignored here for simplicity). The PWM comparator determines the timing to turn on the high-side MOSFET. The gain and speed of the comparator can be assumed high enough to keep the voltage at the beginning of each on cycle substantially constant.
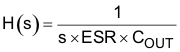
For the loop stability, the 0-dB frequency, f0, defined below must be lower than ¼ of the switching frequency.
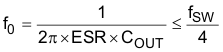
According to Equation 2, the loop stability of D-CAP mode modulator is mainly determined by the capacitor chemistry. For example, specialty polymer capacitors (SP-CAP) have an output capacitance on the order of several 100 µF and ESR in range of 10 mΩ. These yields an f0 on the order of 100 kHz or less and a more stable loop. However, ceramic capacitors have an f0 at more than 700 kHz, and require special care when used with this modulator. An application circuit for ceramic capacitor is described in External Parts Selection With All Ceramic Output Capacitors.