SLUSCT1B June 2017 – January 2019 TPS53681
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Supply: Currents, UVLO, and Power-On Reset
- 6.6 References: DAC and VREF
- 6.7 Voltage Sense: AVSP and BVSP, AVSN and BVSN
- 6.8 Telemetry
- 6.9 Input Current Sensing
- 6.10 Programmable Loadline Settings
- 6.11 Current Sense and Calibration
- 6.12 Logic Interface Pins: AVR_EN, AVR_RDY, BVR_EN, BVR_RDY, RESET, VR_FAULT, VR_HOT
- 6.13 I/O Timing
- 6.14 PMBus Address Setting
- 6.15 Overcurrent Limit Thresholds
- 6.16 Switching Frequency
- 6.17 Slew Rate Settings
- 6.18 Ramp Selections
- 6.19 Dynamic Integration and Undershoot Reduction
- 6.20 Boot Voltage and TMAX Settings
- 6.21 Protections: OVP and UVP
- 6.22 Protections: ATSEN and BTSEN Pin Voltage Levels and Fault
- 6.23 PWM: I/O Voltage and Current
- 6.24 Dynamic Phase Add and Drop
- 6.25 Typical Characteristics
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5
Programming
- 7.5.1 PMBus Connections
- 7.5.2 PMBus Address Selection
- 7.5.3 Supported Commands
- 7.5.4 Commonly Used PMBus Commands
- 7.5.5 Voltage, Current, Power, and Temperature Readings
- 7.5.6 Input Current Sense and Calibration
- 7.5.7 Output Current Sense and Calibration
- 7.5.8 Output Voltage Margin Testing
- 7.5.9 Loop Compensation
- 7.5.10 Converter Protection and Response
- 7.5.11 Output Overvoltage Protection and Response
- 7.5.12 Maximum Allowed Output Voltage Setting
- 7.5.13 Output Undervoltage Protection and Response
- 7.5.14 Minimum Allowed Output Voltage Setting
- 7.5.15 Output Overcurrent Protection and Response
- 7.5.16 Input Under-Voltage Lockout (UVLO)
- 7.5.17 Input Over-Voltage Protection and Response
- 7.5.18 Input Undervoltage Protection and Response
- 7.5.19 Input Overcurrent Protection and Response
- 7.5.20 Over-Temperature Protection and Response
- 7.5.21 Dynamic Phase Shedding (DPS)
- 7.5.22 NVM Programming
- 7.5.23 NVM Security
- 7.5.24 Black Box Recording
- 7.5.25 Board Identification and Inventory Tracking
- 7.5.26 Status Reporting
-
8 Applications, Implementation, and Layout
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2 Typical Application
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RSB|40
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RSB|40
Orderable Information
7.3.1.4 AutoBalance™ Current Sharing
The basic mechanism for current sharing is to sense the average phase current, then adjust the pulse width of each phase to equalize the current in each phase as shown in Figure 10. The PWM comparator (not shown) starts a pulse when the feedback voltage meets the reference. The VIN voltage charges Ct(on) through Rt(on). The pulse terminates when the voltage at Ct(on) matches the on-time reference, which normally equals the DAC voltage (VDAC).
The circuit operates in the following fashion. First assume that the 1-µs averaged value from each phase current are equal. In this case, the PWM modulator terminates at VDAC, and the normal pulse width is delivered to the system. If instead, I1 > IAVG, then an offset is subtracted from VDAC, and the pulse width for Phase 1 is shortened to reduce the phase current in Phase 1 for balancing. If I1 < IAVG, then a longer pulse is generated to increase the phase current in Phase 1 to achieve current balancing.
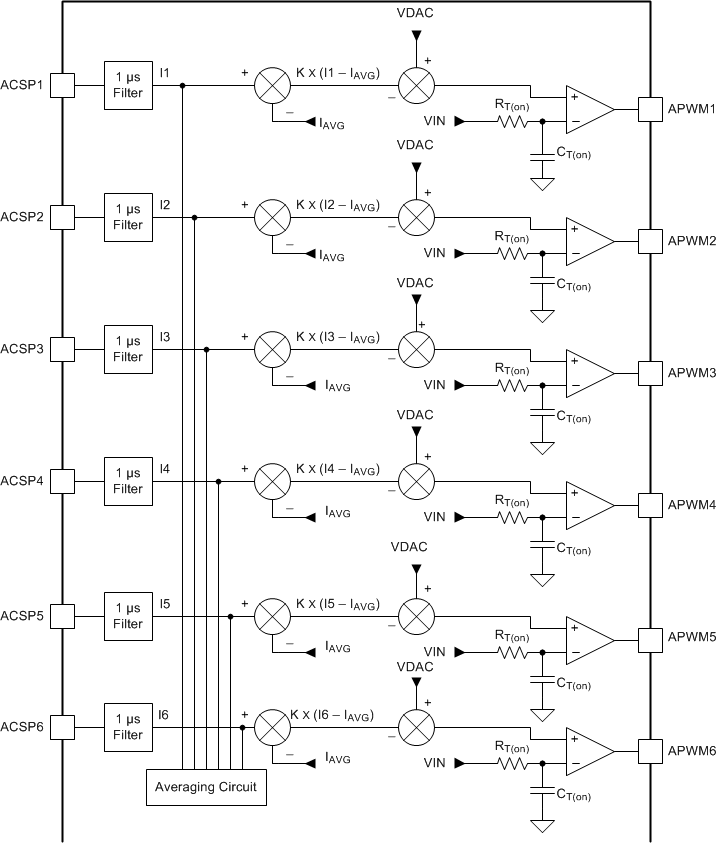 Figure 10. AutoBalance Current Sharing Circuit Detail
Figure 10. AutoBalance Current Sharing Circuit Detail