SLVS675E August 2006 – January 2024 TPS5410
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
-
6 Detailed Description
- 6.1 Overview
- 6.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 6.3
Feature Description
- 6.3.1 Oscillator Frequency
- 6.3.2 Voltage Reference
- 6.3.3 Enable (ENA) and Internal Slow-Start
- 6.3.4 Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO)
- 6.3.5 Boost Capacitor (BOOT)
- 6.3.6 Output Feedback (VSENSE)
- 6.3.7 Internal Compensation
- 6.3.8 Voltage Feed-Forward
- 6.3.9 Pulse-Width-Modulation (PWM) Control
- 6.3.10 Overcurrent Limiting
- 6.3.11 Overvoltage Protection
- 6.3.12 Thermal Shutdown
- 6.4 Device Functional Modes
-
7 Applications and Implementation
- 7.1 Application Information
- 7.2
Typical Applications
- 7.2.1 Application Circuit
- 7.2.2 Using All Ceramic Capacitors
- 7.3 Power Supply Recommendations
- 7.4 Layout
- 8 Device and Documentation Support
- 9 Revision History
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- D|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.2.1.2.3.1 Inductor Selection
To calculate the minimum value of the output inductor, use Equation 4:
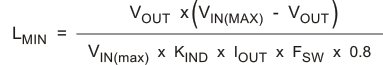
KIND is a coefficient that represents the amount of inductor ripple current relative to the maximum output current. Three things must be considered when determining the amount of ripple current in the inductor: the peak to peak ripple current affects the output ripple voltage amplitude, the ripple current affects the peak switch current, and the amount of ripple current determines at what point the circuit becomes discontinuous. For designs using the TPS5410, KIND of 0.2 to 0.3 yields good results. Low output ripple voltages is obtained when paired with the proper output capacitor, the peak switch current is below the current limit set point, and low load currents can be sourced before discontinuous operation.
For this design example, use KIND = 0.3, and the minimum inductor value is 66 μH. The next highest standard value used in this design is 68 μH.
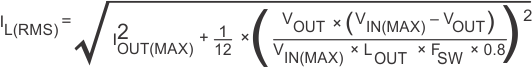
For the output filter inductor, the RMS current and saturation current ratings not being exceeded is important. The RMS inductor current can be found from Equation 5:
and the peak inductor current can be determined using Equation 6:
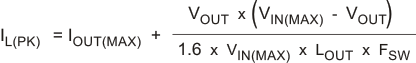
For this design, the RMS inductor current is 1.004 A, and the peak inductor current is 1.147 A. The chosen inductor is a Coilcraft MSS1260-683 type. The nominal inductance is 68μH. It has a saturation current rating of 2.3 A and a RMS current rating of 2.3 A, which meets the requirements. Inductor values for use with the TPS5410 are in the range of 10 μH to 100 μH.