SLUSCO8B November 2016 – June 2018 TPS54200 , TPS54201
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (continued)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3 Feature Description
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DDC|6
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.4.3 Analog Dimming Mode Operation
Once the analog dimming mode is chosen, the internal voltage reference for the FB pin is approximately 200 mV at full scale, and proportional to the PWM duty cycle as shown in Figure 16. LED current is continuous in this mode, and the current magnitude can be adjusted by changing PWM duty cycle, see Figure 18. Because the internal voltage reference is filtered from the PWM signal, a too-low PWM frequency may cause excessive ripple at the voltage reference. To minimize this ripple, the suggested PWM signal frequency is 10 kHz or higher, such as 50 kHz.
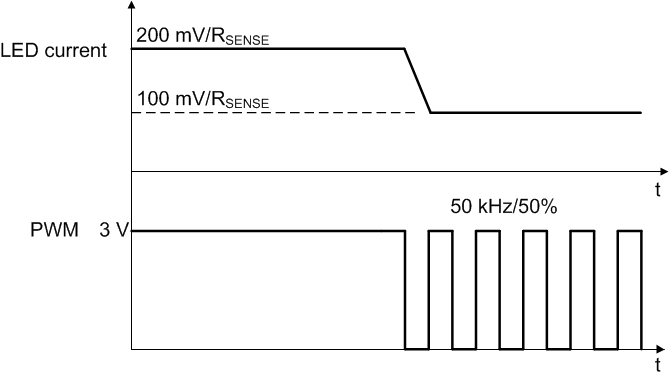 Figure 18. Analog Dimming Operation
Figure 18. Analog Dimming Operation
A comparator with 400-mV hysteresis is used to generate the internal PWM signal, see Figure 17. This internal PWM duty cycle determines the voltage reference. To make sure the PWM pin signal is correctly identified, the high level of the PWM signal should be higher than 1 V, and the low level should be lower than 0.6 V. Figure 19 shows the relationship between the external PWM and internal PWM signals.