SLVS996D September 2009 – September 2015 TPS54262-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Unregulated Input Voltage
- 7.3.2 Regulated Output Voltage
- 7.3.3 Regulation and Feedback Voltage
- 7.3.4 Enable and Shutdown
- 7.3.5 Soft Start
- 7.3.6 Oscillator Frequency
- 7.3.7 Slew Rate Control
- 7.3.8 Reset
- 7.3.9 Reset Delay
- 7.3.10 Reset Threshold and Undervoltage Threshold
- 7.3.11 Overvoltage Supervisor
- 7.3.12 Noise Filter on RST_TH and OV_TH Terminals
- 7.3.13 Boot Capacitor
- 7.3.14 Short Circuit Protection
- 7.3.15 Overcurrent Protection
- 7.3.16 Internal Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO)
- 7.3.17 Thermal Shutdown (TSD)
- 7.3.18 Loop Control Frequency Compensation - Type 3
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1
Component Selection
- 8.2.2.1.1 Input Capacitors (C1, C11)
- 8.2.2.1.2 Output Capacitor (C4, C12)
- 8.2.2.1.3 Soft-Start Capacitor (C6)
- 8.2.2.1.4 Bootstrap Capacitor (C3)
- 8.2.2.1.5 Power-On Reset Delay (PORdly) Capacitor (C2)
- 8.2.2.1.6 Output Inductor (L1)
- 8.2.2.1.7 Flyback Schottky Diode (D2)
- 8.2.2.1.8 Resistor to Set Slew Rate (R7)
- 8.2.2.1.9 Resistor to Select Switching Frequency (R8)
- 8.2.2.1.10 Resistors to Select Output Voltage (R4, R5)
- 8.2.2.1.11 Resistors to Set Undervoltage, Overvoltage, and Reset Thresholds (R1, R2, R3)
- 8.2.2.1.12 Low-Power Mode (LPM) Threshold
- 8.2.2.1.13 Enable Pin Pull-Up Resistor (R11) and Voltage Divider Resistor (R10)
- 8.2.2.1.14 Pull-Up Resistor (R12) at RST Pin
- 8.2.2.1.15 Type 3 Compensation Components (R5, R6, R9, C5, C7, C8)
- 8.2.2.1.16 Noise Filter on RST_TH and OV_TH Terminals (C9, C10)
- 8.2.2.2
Design Example 1
- 8.2.2.2.1 Calculate the Switching Frequency (fsw)
- 8.2.2.2.2 Calculate the Ripple Current (IRipple)
- 8.2.2.2.3 Calculate the Inductor Value (L1)
- 8.2.2.2.4 Calculate the Output Capacitor and ESR (C4)
- 8.2.2.2.5 Calculate the Feedback Resistors (R4, R5)
- 8.2.2.2.6 Calculate Type 3 Compensation Components
- 8.2.2.2.7 Calculate Soft-Start Capacitor (C6)
- 8.2.2.2.8 Calculate Bootstrap Capacitor (C3)
- 8.2.2.2.9 Calculate Power-On Reset Delay Capacitor (C2)
- 8.2.2.2.10 Calculate Input Capacitor (C1, C11)
- 8.2.2.2.11 Calculate Resistors to Control Slew Rate (R7)
- 8.2.2.2.12 Resistors to Select Undervoltage, Overvoltage and Reset Threshold Values (R1, R2, R3)
- 8.2.2.2.13 Diode D1 and D2 Selection
- 8.2.2.2.14 Noise Filter on RST_TH and OV_TH Terminals (C9 and C10)
- 8.2.2.2.15 Power Budget and Temperature Estimation
- 8.2.2.3
Design Example 2
- 8.2.2.3.1 Calculate the Switching Frequency (fsw)
- 8.2.2.3.2 Calculate the Ripple Current (IRipple)
- 8.2.2.3.3 Calculate the Inductor Value (L1)
- 8.2.2.3.4 Calculate the Output Capacitor and ESR (C4, C12)
- 8.2.2.3.5 Calculate the Feedback Resistors (R4, R5)
- 8.2.2.3.6 Calculate Type 3 Compensation Components
- 8.2.2.3.7 Calculate Soft-Start Capacitor (C6)
- 8.2.2.3.8 Calculate Bootstrap Capacitor (C3)
- 8.2.2.3.9 Calculate Power-On Reset Delay Capacitor (C2)
- 8.2.2.3.10 Calculate Input Capacitor (C1, C11)
- 8.2.2.3.11 Calculate Resistors to Control Slew Rate (R7)
- 8.2.2.3.12 Resistors to Select Undervoltage, Overvoltage and Reset Threshold Values (R1, R2, R3)
- 8.2.2.3.13 Diode D1 and D2 Selection
- 8.2.2.3.14 Noise Filter on RST_TH and OV_TH Terminals (C9 and C10)
- 8.2.2.3.15 Power Budget and Temperature Estimation
- 8.2.2.1
Component Selection
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|20
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|20
Orderable Information
5 Pin Configuration and Functions
PWP Package
20-Pin HTSSOP
Top View
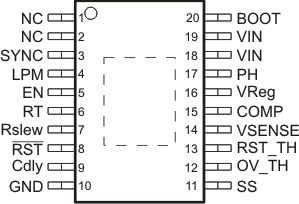
Pin Functions
| PIN | I/O | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||
| NC | 1 | NC | Connect to ground. |
| NC | 2 | NC | Connect to ground. |
| SYNC | 3 | I | External synchronization clock input to override the internal oscillator clock. An internal pulldown resistor of 62 kΩ (typical) is connected to ground. Connect this pin to GND if not used. |
| LPM | 4 | I | Low-power mode control using digital input signal. An internal pulldown resistor of 62 kΩ (typical) is connected to ground. |
| EN | 5 | I | Enable pin, internally pulled up. Must be externally pulled up or down to enable or disable the device. |
| RT | 6 | O | External resistor to ground to program the internal oscillator frequency. |
| Rslew | 7 | O | External resistor to ground to control the slew rate of internal switching FET. |
| RST | 8 | O | Active low, open-drain reset output connected to external bias voltage through a resistor, asserted high after the device starts regulating. |
| Cdly | 9 | O | External capacitor to ground to program power on reset delay. |
| GND | 10 | O | Ground pin, must be electrically connected to the exposed pad on the PCB for proper thermal performance. |
| SS | 11 | O | External capacitor to ground to program soft-start time. |
| OV_TH | 12 | I | Sense input for overvoltage detection on regulated output, an external resistor network is connected between VReg and ground to program the overvoltage threshold. |
| RST_TH | 13 | I | Sense input for undervoltage detection on regulated output, an external resistor network is connected between VReg and ground to program the reset and undervoltage threshold. |
| VSENSE | 14 | I | Inverting node of error amplifier for voltage mode control. |
| COMP | 15 | O | Error amplifier output to connect external compensation components. |
| VReg | 16 | I | Internal low-side FET to load output during start-up or limit overshoot. |
| PH | 17 | O | Source of the internal switching FET. |
| VIN | 18 | I | Unregulated input voltage. Pin 18 and pin 19 must be connected externally. |
| VIN | 19 | I | Unregulated input voltage. Pin 18 and pin 19 must be connected externally. |
| BOOT | 20 | O | External bootstrap capacitor to PH to drive the gate of the internal switching FET. |