SLVS996D September 2009 – September 2015 TPS54262-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Unregulated Input Voltage
- 7.3.2 Regulated Output Voltage
- 7.3.3 Regulation and Feedback Voltage
- 7.3.4 Enable and Shutdown
- 7.3.5 Soft Start
- 7.3.6 Oscillator Frequency
- 7.3.7 Slew Rate Control
- 7.3.8 Reset
- 7.3.9 Reset Delay
- 7.3.10 Reset Threshold and Undervoltage Threshold
- 7.3.11 Overvoltage Supervisor
- 7.3.12 Noise Filter on RST_TH and OV_TH Terminals
- 7.3.13 Boot Capacitor
- 7.3.14 Short Circuit Protection
- 7.3.15 Overcurrent Protection
- 7.3.16 Internal Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO)
- 7.3.17 Thermal Shutdown (TSD)
- 7.3.18 Loop Control Frequency Compensation - Type 3
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1
Component Selection
- 8.2.2.1.1 Input Capacitors (C1, C11)
- 8.2.2.1.2 Output Capacitor (C4, C12)
- 8.2.2.1.3 Soft-Start Capacitor (C6)
- 8.2.2.1.4 Bootstrap Capacitor (C3)
- 8.2.2.1.5 Power-On Reset Delay (PORdly) Capacitor (C2)
- 8.2.2.1.6 Output Inductor (L1)
- 8.2.2.1.7 Flyback Schottky Diode (D2)
- 8.2.2.1.8 Resistor to Set Slew Rate (R7)
- 8.2.2.1.9 Resistor to Select Switching Frequency (R8)
- 8.2.2.1.10 Resistors to Select Output Voltage (R4, R5)
- 8.2.2.1.11 Resistors to Set Undervoltage, Overvoltage, and Reset Thresholds (R1, R2, R3)
- 8.2.2.1.12 Low-Power Mode (LPM) Threshold
- 8.2.2.1.13 Enable Pin Pull-Up Resistor (R11) and Voltage Divider Resistor (R10)
- 8.2.2.1.14 Pull-Up Resistor (R12) at RST Pin
- 8.2.2.1.15 Type 3 Compensation Components (R5, R6, R9, C5, C7, C8)
- 8.2.2.1.16 Noise Filter on RST_TH and OV_TH Terminals (C9, C10)
- 8.2.2.2
Design Example 1
- 8.2.2.2.1 Calculate the Switching Frequency (fsw)
- 8.2.2.2.2 Calculate the Ripple Current (IRipple)
- 8.2.2.2.3 Calculate the Inductor Value (L1)
- 8.2.2.2.4 Calculate the Output Capacitor and ESR (C4)
- 8.2.2.2.5 Calculate the Feedback Resistors (R4, R5)
- 8.2.2.2.6 Calculate Type 3 Compensation Components
- 8.2.2.2.7 Calculate Soft-Start Capacitor (C6)
- 8.2.2.2.8 Calculate Bootstrap Capacitor (C3)
- 8.2.2.2.9 Calculate Power-On Reset Delay Capacitor (C2)
- 8.2.2.2.10 Calculate Input Capacitor (C1, C11)
- 8.2.2.2.11 Calculate Resistors to Control Slew Rate (R7)
- 8.2.2.2.12 Resistors to Select Undervoltage, Overvoltage and Reset Threshold Values (R1, R2, R3)
- 8.2.2.2.13 Diode D1 and D2 Selection
- 8.2.2.2.14 Noise Filter on RST_TH and OV_TH Terminals (C9 and C10)
- 8.2.2.2.15 Power Budget and Temperature Estimation
- 8.2.2.3
Design Example 2
- 8.2.2.3.1 Calculate the Switching Frequency (fsw)
- 8.2.2.3.2 Calculate the Ripple Current (IRipple)
- 8.2.2.3.3 Calculate the Inductor Value (L1)
- 8.2.2.3.4 Calculate the Output Capacitor and ESR (C4, C12)
- 8.2.2.3.5 Calculate the Feedback Resistors (R4, R5)
- 8.2.2.3.6 Calculate Type 3 Compensation Components
- 8.2.2.3.7 Calculate Soft-Start Capacitor (C6)
- 8.2.2.3.8 Calculate Bootstrap Capacitor (C3)
- 8.2.2.3.9 Calculate Power-On Reset Delay Capacitor (C2)
- 8.2.2.3.10 Calculate Input Capacitor (C1, C11)
- 8.2.2.3.11 Calculate Resistors to Control Slew Rate (R7)
- 8.2.2.3.12 Resistors to Select Undervoltage, Overvoltage and Reset Threshold Values (R1, R2, R3)
- 8.2.2.3.13 Diode D1 and D2 Selection
- 8.2.2.3.14 Noise Filter on RST_TH and OV_TH Terminals (C9 and C10)
- 8.2.2.3.15 Power Budget and Temperature Estimation
- 8.2.2.1
Component Selection
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|20
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|20
Orderable Information
6 Specifications
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted) (1)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input voltage | EN | –0.3 | 60 | V | ||
| VIN | –0.3 | 60 | ||||
| VReg | –0.3 | 20 | ||||
| LPM | –0.3 | 5.5 | ||||
| OV_TH | –0.3 | 5.5 | ||||
| RST_TH | –0.3 | 5.5 | ||||
| SYNC | –0.3 | 5.5 | ||||
| VSENSE | –0.3 | 5.5 | ||||
| Output voltage | BOOT | –0.3 | 65 | V | ||
| PH | DC voltage | –0.3 | 60 | |||
| DC voltage, TJ = –40°C | –0.85 | |||||
| DC voltage, TJ = 125°C | –0.5 | |||||
| 30-ns Transient Pulse | –2 | |||||
| 200-ns Transient Pulse | –1 | |||||
| RT | –0.3 | 5.5 | ||||
| RST | –0.3 | 5.5 | ||||
| Cdly | –0.3 | 8 | ||||
| SS | –0.3 | 8 | ||||
| COMP | –0.3 | 7 | ||||
| Temperature | Operating virtual junction temperature, TJ | -40 | 150 | °C | ||
| Storage temperature, Tstg | –55 | 165 | ||||
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, which do not imply functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under Recommended Operating Conditions. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
6.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human body model (HBM), per AEC Q100-002(1)(2) | ±2000 | V | ||
| Charged device model (CDM), per AEC Q100-011 | Corner pins (1, 10, 11, and 20) | ±750 | ||||
| Other pins | ±750 | |||||
(1) AEC Q100-002 indicates HBM stressing is done in accordance with the ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001 specification.
(2) The human body model is a 100-pF capacitor discharged through a 1.5-kΩ resistor into each pin.
6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VI | Unregulated buck supply input voltage (VIN, EN) | 3.6 | 48 | V | ||
| VReg | Regulated output voltage | In continuous conduction mode (CCM) | 0.9 | 18 | V | |
| Power up in low-power mode (LPM) or discontinuous conduction mode (DCM) | 0.9 | 5.5 | V | |||
| Bootstrap capacitor (BOOT) | 3.6 | 56 | V | |||
| Switched outputs (PH) | 3.6 | 48 | V | |||
| Logic levels (RST, VSENSE, OV_TH, RST_TH, Rslew, SYNC, RT) | 0 | 5.25 | V | |||
| Logic levels (SS, Cdly, COMP) | 0 | 6.5 | V | |||
| TA | Operating ambient temperature | –40 | 125 | °C | ||
6.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | TPS54262-Q1 | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PWP (HTSSOP) | |||
| 20 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 36.2 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 20.9 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 17.9 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 0.5 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 17.7 | °C/W |
| RθJC(bot) | Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance | 1.4 | °C/W |
(1) For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see the Semiconductor and IC Package Thermal Metrics application report, SPRA953.
6.5 DC Electrical Characteristics
VIN = 7 V to 48 V, EN = VIN, TJ = –40°C to 150°C (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | TEST(1) | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| INPUT POWER SUPPLY | ||||||||
| VIN | Supply voltage on VIN | Normal mode: after initial start-up | Info | 3.6 | 48 | V | ||
| Low-power mode | Falling threshold (LPM disabled) | 8 | ||||||
| Rising threshold (LPM activated) | 8.5 | |||||||
| High voltage threshold (LPM disabled) | 29 | 31 | 34 | |||||
| Iq-Normal | Quiescent current, normal mode | Open loop test – maximum duty cycle VIN = 7 V to 48 V |
PT | 5 | 10 | mA | ||
| Iq-LPM | Quiescent current, low-power mode | ILoad < 1 mA, VIN = 12 V | TA = 25°C | PT | 50 | 70 | µA | |
| –40 < TJ < 150°C | 75 | |||||||
| ILoad < 1 mA, VIN = 24 V | TA = 25°C | 75 | ||||||
| –40 < TJ < 150°C | 75 | |||||||
| ISD | Shutdown current | EN = 0 V, device is off | TA = 25°C, VIN = 12 V | PT | 1 | 4 | µA | |
| TRANSITION TIMES (LOW POWER – NORMAL MODES) | ||||||||
| td1 | Transition delay, normal mode to low-power mode | VIN = 12 V, VReg = 5 V, ILoad = 1 A to 1 mA | CT | 100 | µs | |||
| td2 | Transition delay, low-power mode to normal mode | VIN = 12 V, VReg = 5 V ILoad = 1 mA to 1 A | CT | 5 | µs | |||
| SWITCH MODE SUPPLY; VReg | ||||||||
| VReg | Regulator output | VSENSE = 0.8 Vref | Info | 0.9 | 18 | V | ||
| VSENSE | Feedback voltage | VReg = 0.9 V to 18 V (open loop) | CT | 0.788 | 0.8 | 0.812 | V | |
| RDS(ON) | Internal switch resistance | Measured across VIN and PH, ILoad = 500 mA | PT | 500 | mΩ | |||
| ICL | Switch current limit, cycle by cycle | VIN = 12 V | Info | 2.5 | 3.2 | 4.1 | A | |
| tON-Min | Duty cycle pulse width | Bench CHAR only | Info | 50 | 100 | 150 | ns | |
| tOFF-Min | Bench CHAR only | Info | 100 | 200 | 250 | |||
| fsw | Switching frequency | Set using external resistor on RT pin | PT | 0.2 | 2.2 | MHz | ||
| fsw | Internal oscillator frequency tolerance | PT | –10% | 10% | ||||
| ISink | Start-up condition | OV_TH = 0 V, VReg = 10 V | Info | 1 | mA | |||
| ILimit | Prevent overshoot | 0 V < OV_TH < 0.8 V, VReg = 10 V | Info | 80 | mA | |||
(1) PT: Production tested
CT: Characterization tested only, not production tested
Info: User information only, not production tested
CT: Characterization tested only, not production tested
Info: User information only, not production tested
6.6 DC Electrical Characteristics
VIN = 7 V to 48 V, EN = VIN, TJ = –40°C to 150°C (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | TEST(2) | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ENABLE (EN) | |||||||
| VIL | Low input threshold voltage | PT | 0.7 | V | |||
| VIH | High input threshold voltage | PT | 1.7 | V | |||
| Ilkg | Leakage current into EN terminal | EN = 60 V | PT | 100 | 135 | µA | |
| EN = 12 V | 8 | 15 | µA | ||||
| RESET DELAY (Cdly) | |||||||
| IO | External capacitor charge current | EN = high | PT | 1.4 | 2 | 2.6 | µA |
| VThreshold | Switching threshold voltage | Output voltage in regulation | PT | 2 | V | ||
| LOW-POWER MODE (LPM) | |||||||
| VIL | Low input threshold voltage | VIN = 12 V | PT | 0.7 | V | ||
| VIH | High input threshold voltage | VIN = 12 V | PT | 1.7 | V | ||
| Ilkg | Leakage current into LPM terminal | LPM = 5 V | PT | 65 | 95 | µA | |
| RESET OUTPUT (RST) | |||||||
| trdly | POR delay timer | Based on Cdly capacitor | PT | 3.6 | 7 | ms/nF | |
| VReg_RST | Reset threshold voltage for VReg | Check RST output | PT | 0.768 | 0.832 | V | |
| tnRSTdly | Filter time | Delay before RST is asserted low | PT | 10 | 20 | 35 | µs |
| SOFT START (SS) | |||||||
| ISS | Soft-start source current | PT | 40 | 50 | 60 | µA | |
| SYNCHRONIZATION (SYNC) | |||||||
| VIL | Low input threshold voltage | PT | 0.7 | V | |||
| VIH | High input threshold voltage | PT | 1.7 | V | |||
| Ilkg | Leakage current | SYNC = 5 V | PT | 65 | 95 | µA | |
| SYNC (fext) | External input clock frequency | VIN = 12 V, VReg = 5 V, 180 kHz < fsw < fext < 2 × fsw < 2.2 MHz |
CT | 180 | 2200 | kHz | |
| SYNCtrans | External clock to internal clock | No external clock, VIN = 12 V, VReg = 5 V | Info | 32 | µs | ||
| SYNCtrans | Internal clock to external clock | External clock = 1 MHz, VIN = 12 V, VReg = 5 V |
Info | 2.5 | µs | ||
| SYNCCLK | Minimum duty cycle | CT | 30% | ||||
| SYNCCLK | Maximum duty cycle | CT | 70% | ||||
| Rslew | |||||||
| IRslew | Rslew = 50 kΩ | CT | 20 | µA | |||
| IRslew | Rslew = 10 kΩ | CT | 100 | µA | |||
| OVERVOLTAGE SUPERVISORS (OV_TH) | |||||||
| VReg_OV | Threshold voltage for VReg during overvoltage | Internal switch is turned off | PT | 0.768 | 0.832 | V | |
| VReg = 5 V | Internal pulldown on VReg, OV_TH = 1 V | 70(1) | mA | ||||
| THERMAL SHUTDOWN | |||||||
| TSD | Thermal shutdown junction temperature | CT | 175 | °C | |||
| THYS | Hysteresis | CT | 30 | °C | |||
(1) This is the current flowing into the VReg pin when voltage at OV_TH pin is 1 V.
(2) PT: Production tested
CT: Characterization tested only, not production tested
CT: Characterization tested only, not production tested
6.7 Typical Characteristics
Table 1. Table of Graphs
| FIGURE | |
|---|---|
| Efficiency vs Load Current for Different Rslew Resistors | Figure 1 |
| Efficiency vs Load Current for Different Vin | Figure 2 |
| LPM, Quiescent Current Variation With Temperature | Figure 3 |
| Shutdown Current Variation With Temperature | Figure 4 |
| Output Voltage vs Input Voltage for Different Load Currents | Figure 5 |
| Input Voltage vs Load Current During Power Up and Power Down | Figure 6 |
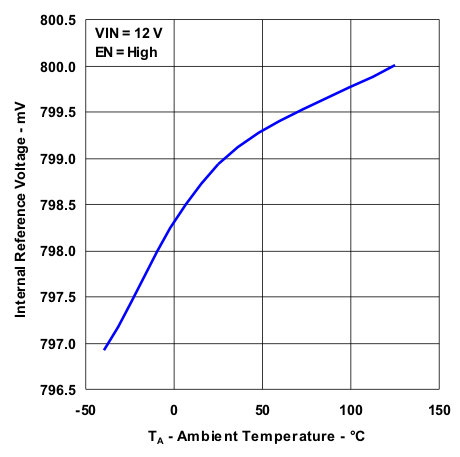
| Internal Reference Voltage | Figure 7 |
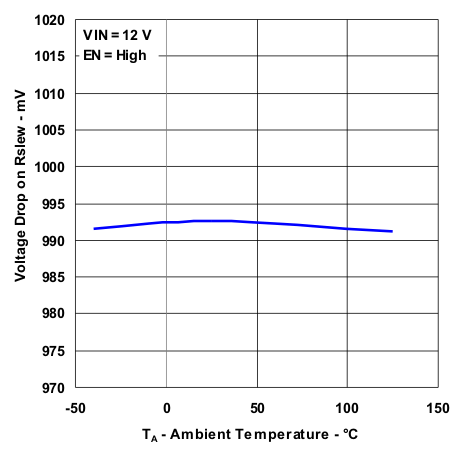
| Voltage Drop ON Rslew For Current Reference (Slew Rate / Rslew) | Figure 8 |
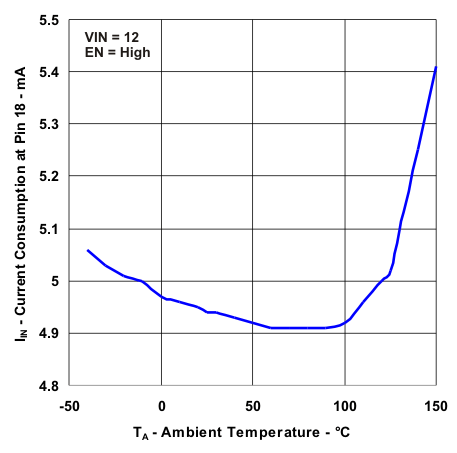
| Current Consumption With Temperature | Figure 9 |
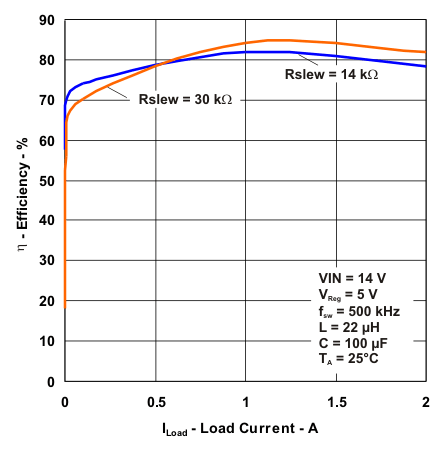
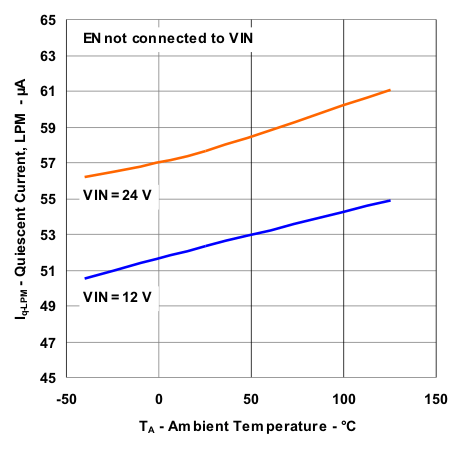
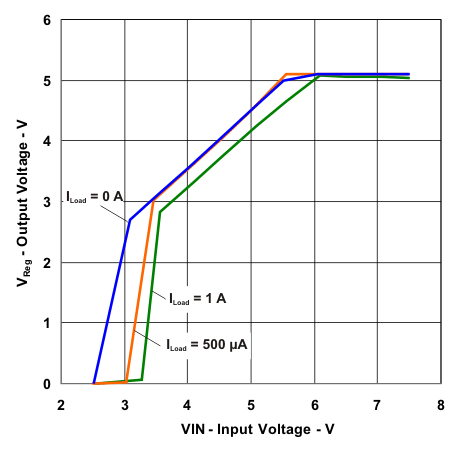 Figure 5. Output Voltage vs Input Voltage for Different Load Currents
Figure 5. Output Voltage vs Input Voltage for Different Load Currents
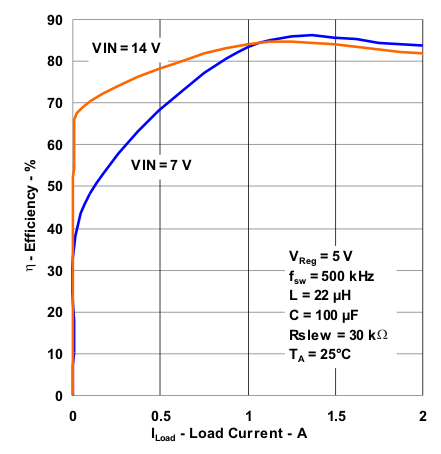
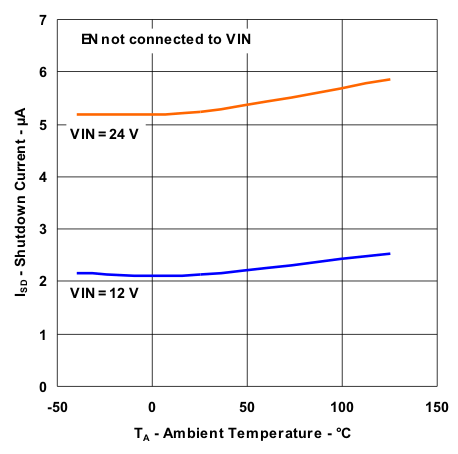
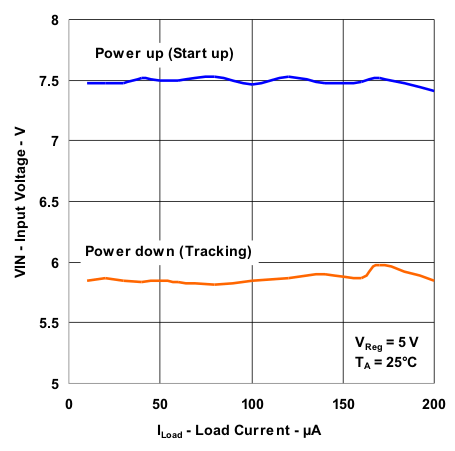 Figure 6. Input Voltage vs Load Current During Power Up and Power Down
Figure 6. Input Voltage vs Load Current During Power Up and Power Down
NOTE
Figure 5 shows the dropout operation during low input conditions
Figure 6 shows the following plots
- Power up (Start-up): Input voltage required to achieve the 5-V regulation during power up over the range of load currents
- Power down (Tracking): Input voltage at which the output voltage drops approximately by 0.7 V from the programmed 5-V regulated voltage