SLVS932F May 2009 – November 2014 TPS54325
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Simplified Schematic
- 5 Revision History
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|14
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|14
Orderable Information
11 Layout
11.1 Layout Guidelines
- Keep the input switching current loop as small as possible.
- Keep the SW node as physically small and short as possible to minimize parasitic capacitance and inductance and to minimize radiated emissions. Kelvin connections should be brought from the output to the feedback pin of the device.
- Keep analog and non-switching components away from switching components.
- Make a single point connection from the signal ground to power ground.
- Do not allow switching current to flow under the device.
- Keep the pattern lines for VIN and PGND broad.
- Exposed pad of device must be connected to PGND with solder.
- VREG5 capacitor should be placed near the device, and connected PGND.
- Output capacitor should be connected to a broad pattern of the PGND.
- Voltage feedback loop should be as short as possible, and preferably with ground shield.
- Lower resistor of the voltage divider which is connected to the VFB pin should be tied to SGND.
- Providing sufficient via is preferable for VIN, SW and PGND connection.
- PCB pattern for VIN, SW, and PGND should be as broad as possible.
- If VIN and VCC is shorted, VIN and VCC patterns need to be connected with broad pattern lines.
- VIN Capacitor should be placed as near as possible to the device.
11.2 Layout Example
 Figure 13. PCB Layout
Figure 13. PCB Layout
11.3 Thermal Considerations
This PowerPAD™ package incorporates an exposed thermal pad that is designed to be connected to an external heatsink. The thermal pad must be soldered directly to the printed board (PCB). After soldering, the PCB can be used as a heatsink. In addition, through the use of thermal vias, the thermal pad can be attached directly to the appropriate copper plane shown in the electrical schematic for the device, or alternatively, can be attached to a special heatsink structure designed into the PCB. This design optimizes the heat transfer from the integrated circuit (IC).
For additional information on the PowerPAD™ package and how to use the advantage of its heat dissipating abilities, refer to:
The exposed thermal pad dimensions for this package are shown in Figure 14
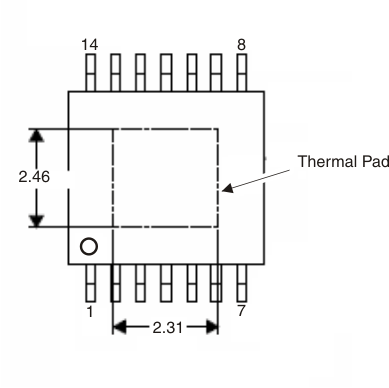 Figure 14. Thermal Pad Dimensions
Figure 14. Thermal Pad Dimensions