SLVSBK0D October 2012 – March 2017 TPS54340
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Fixed Frequency PWM Control
- 7.3.2 Slope Compensation Output Current
- 7.3.3 Pulse Skip Eco-mode
- 7.3.4 Low Dropout Operation and Bootstrap Voltage (BOOT)
- 7.3.5 Error Amplifier
- 7.3.6 Adjusting the Output Voltage
- 7.3.7 Enable and Adjusting Undervoltage Lockout
- 7.3.8 Internal Soft-Start
- 7.3.9 Constant Switching Frequency and Timing Resistor (RT/CLK) Terminal)
- 7.3.10 Accurate Current Limit Operation and Maximum Switching Frequency
- 7.3.11 Synchronization to RT/CLKTerminal
- 7.3.12 Overvoltage Protection
- 7.3.13 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.3.14 Small Signal Model for Loop Response
- 7.3.15 Simple Small Signal Model for Peak Current Mode Control
- 7.3.16 Small Signal Model for Frequency Compensation
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Applications
- 8.2.1
Buck Converter
- 8.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.1.2
Detailed Design Procedures
- 8.2.1.2.1 Custom Design with WEBENCH Tools
- 8.2.1.2.2 Selecting the Switching Frequency
- 8.2.1.2.3 Output Inductor Selection (LO)
- 8.2.1.2.4 Output Capacitor
- 8.2.1.2.5 Catch Diode
- 8.2.1.2.6 Input Capacitor
- 8.2.1.2.7 Bootstrap Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.1.2.8 Undervoltage Lockout Set Point
- 8.2.1.2.9 Output Voltage and Feedback Resistors Selection
- 8.2.1.2.10 Minimum VIN
- 8.2.1.2.11 Compensation
- 8.2.1.2.12 Discontinuous Conduction Mode and Eco-mode Boundary
- 8.2.1.2.13 Power Dissipation
- 8.2.1.3 Application Curves
- 8.2.2 Inverting Power
- 8.2.3 Split Rail Power Supply
- 8.2.1
Buck Converter
- 8.3 WEBENCH Power Designer
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DDA|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DDA|8
Orderable Information
8.2.1.2.11 Compensation
There are several methods to design compensation for DC-DC regulators. The method presented here is easy to calculate and ignores the effects of the slope compensation that is internal to the device. Since the slope compensation is ignored, the actual crossover frequency will be lower than the crossover frequency used in the calculations. This method assumes the crossover frequency is between the modulator pole and the ESR zero and the ESR zero is at least 10 times greater the modulator pole.
To get started, the modulator pole, ƒp(mod), and the ESR zero, ƒz1 must be calculated using Equation 44 and Equation 45. For COUT, use a derated value of 70 μF. Use equations Equation 46 and Equation 47 to estimate a starting point for the crossover frequency, ƒco. For the example design, ƒp(mod) is 2411 Hz and ƒz(mod) is 455 kHz. Equation 45 is the geometric mean of the modulator pole and the ESR zero and Equation 47 is the mean of modulator pole and the switching frequency. Equation 46 yields 33.1 kHz and Equation 47 gives 26.9 kHz. Use the lower value of Equation 46 or Equation 47 for an initial crossover frequency. For this example, the target ƒco is 26.9 kHz.
Next, the compensation components are calculated. A resistor in series with a capacitor is used to create a compensating zero. A capacitor in parallel to these two components forms the compensating pole.




To determine the compensation resistor, R4, use Equation 48. Assume the power stage transconductance, gmps, is 12 A/V. The output voltage, VO, reference voltage, VREF, and amplifier transconductance, gmea, are 5 V, 0.8 V and 350 μA/V, respectively. R4 is calculated to be 11.6 kΩ and a standard value of 11.5 kΩ is selected. Use Equation 49 to set the compensation zero to the modulator pole frequency. Equation 49 yields 5740 pF for compensating capacitor C5. 5600 pF is used for this design.
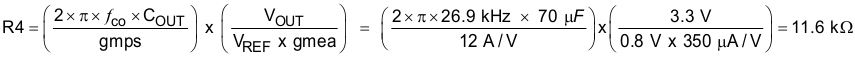

A compensation pole can be implemented if desired by adding capacitor C8 in parallel with the series combination of R4 and C5. Use the larger value calculated from Equation 50 and Equation 51 for C8 to set the compensation pole. The selected value of C8 is 47 pF for this design example.

