SLUSED1B May 2020 – June 2021 TPS543820
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 VIN Pins and VIN UVLO
- 7.3.2 Enable and Adjustable UVLO
- 7.3.3 Adjusting the Output Voltage
- 7.3.4 Switching Frequency Selection
- 7.3.5 Switching Frequency Synchronization to an External Clock
- 7.3.6 Ramp Amplitude Selection
- 7.3.7 Soft Start and Prebiased Output Start-up
- 7.3.8 Mode Pin
- 7.3.9 Power Good (PGOOD)
- 7.3.10 Current Protection
- 7.3.11 Output Overvoltage and Undervoltage Protection
- 7.3.12 Overtemperature Protection
- 7.3.13 Output Voltage Discharge
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Applications
- 8.2.1
1.0-V Output, 1-MHz Application
- 8.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.1.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.1.2.1 Switching Frequency
- 8.2.1.2.2 Output Inductor Selection
- 8.2.1.2.3 Output Capacitor
- 8.2.1.2.4 Input Capacitor
- 8.2.1.2.5 Adjustable Undervoltage Lockout
- 8.2.1.2.6 Output Voltage Resistors Selection
- 8.2.1.2.7 Bootstrap Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.1.2.8 BP5 Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.1.2.9 PGOOD Pullup Resistor
- 8.2.1.2.10 Current Limit Selection
- 8.2.1.2.11 Soft-Start Time Selection
- 8.2.1.2.12 Ramp Selection and Control Loop Stability
- 8.2.1.2.13 MODE Pin
- 8.2.1.3 Application Curves
- 8.2.2 1.0-V Output, 1.5-MHz Application
- 8.2.3 3.3-V Output, 1.0-MHz Application
- 8.2.1
1.0-V Output, 1-MHz Application
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RPY|14
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.3.6 Ramp Amplitude Selection
The TPS543820 uses VIN, duty cycle, and low-side FET current information to generate an internal ramp. The ramp amplitude is determined by an internal ramp generation capacitor, CRAMP. Three different values for CRAMP can be selected with a resistor to AGND on the MODE pin (see Section 7.3.8). The capacitor options are 1 pF, 2 pF, and 4 pF. A larger ramp capacitor results in a smaller ramp amplitude, which results in a higher control loop bandwidth. Figure 7-6 and Figure 7-7 show how the loop changes with each ramp setting for the schematic in Section 8.2.3.
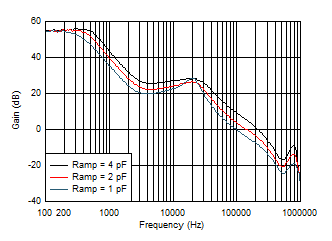 Figure 7-6 Loop Gain vs Ramp
Settings
Figure 7-6 Loop Gain vs Ramp
Settings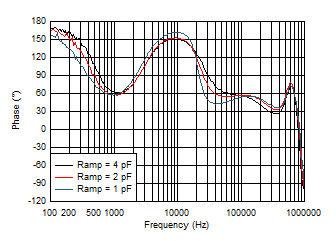 Figure 7-7 Loop Phase vs Ramp
Settings
Figure 7-7 Loop Phase vs Ramp
Settings