SLVSF00 January 2019 TPS54560B
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Fixed Frequency PWM Control
- 7.3.2 Slope Compensation Output Current
- 7.3.3 Pulse Skip Eco-mode
- 7.3.4 Low Dropout Operation and Bootstrap Voltage (BOOT)
- 7.3.5 Error Amplifier
- 7.3.6 Adjusting the Output Voltage
- 7.3.7 Enable and Adjusting Undervoltage Lockout
- 7.3.8 Internal Soft Start
- 7.3.9 Constant Switching Frequency and Timing Resistor (RT/CLK) pin)
- 7.3.10 Accurate Current-Limit Operation and Maximum Switching Frequency
- 7.3.11 Synchronization to RT/CLK pin
- 7.3.12 Overvoltage Protection
- 7.3.13 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.3.14 Small Signal Model for Loop Response
- 7.3.15 Simple Small Signal Model for Peak-Current-Mode Control
- 7.3.16 Small Signal Model for Frequency Compensation
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Custom Design with WEBENCH® Tools
- 8.2.2.2 Selecting the Switching Frequency
- 8.2.2.3 Output Inductor Selection (LO)
- 8.2.2.4 Output Capacitor
- 8.2.2.5 Catch Diode
- 8.2.2.6 Input Capacitor
- 8.2.2.7 Bootstrap Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.2.8 Undervoltage Lockout Setpoint
- 8.2.2.9 Output Voltage and Feedback Resistors Selection
- 8.2.2.10 Minimum Input Voltage, VIN
- 8.2.2.11 Compensation
- 8.2.2.12 Discontinuous Conduction Mode and Eco-mode Boundary
- 8.2.2.13 Power Dissipation Estimate
- 8.2.2.14 Safe Operating Area
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 8.3 Other System Examples
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DDA|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DDA|8
Orderable Information
8.2.2.13 Power Dissipation Estimate
The following formulas show how to estimate the TPS54560B power dissipation under CCM operation. Do not use these equations if the device is operating in DCM.
The power dissipation of the IC includes conduction loss (PCOND), switching loss (PSW), gate-drive loss (PGD), and supply current (PQ). Example calculations are shown with the 12-V typical input voltage of the design example.
Equation 52. 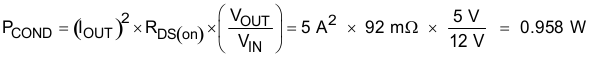
spacer
Equation 53. 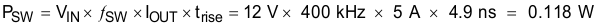
spacer
Equation 54. 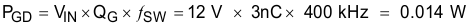
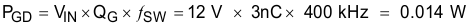
spacer
Equation 55. 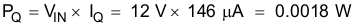
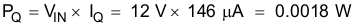
where
- IOUT is the output current (A).
- RDS(on) is the on-resistance of the high-side MOSFET (Ω)
- VOUT is the output voltage (V).
- VIN is the input voltage (V).
- fsw is the switching frequency (Hz)
- trise is the SW pin voltage rise time and can be estimated by trise = VIN x 0.16 ns/V + 3 ns
- QG is the total gate charge of the internal MOSFET
- IQ is the operating nonswitching supply current
Therefore,
Equation 56. 

For given TA,
Equation 57. 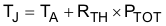
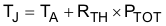
For given TJMAX = 150°C
Equation 58. 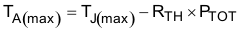
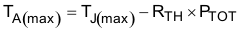
where
- Ptot is the total device power dissipation (W)
- TA is the ambient temperature (°C).
- TJ is the junction temperature (°C).
- RTH is the thermal resistance of the package (°C/W)
- TJMAX is maximum junction temperature (°C)
- TAMAX is maximum ambient temperature (°C).
There will be additional power losses in the regulator circuit due to the inductor ac and dc losses, the catch diode and PCB trace resistance impacting the overall efficiency of the regulator.