SLVSA70F March 2011 – October 2017 TPS54622
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configurations and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Fixed-Frequency PWM Control
- 7.3.2 Continuous Current Mode Operation (CCM)
- 7.3.3 VIN and Power VIN Pins (VIN and PVIN)
- 7.3.4 Voltage Reference
- 7.3.5 Adjusting the Output Voltage
- 7.3.6 Safe Start-Up Into Prebiased Outputs
- 7.3.7 Error Amplifier
- 7.3.8 Slope Compensation
- 7.3.9 Enable and Adjusting Undervoltage Lockout
- 7.3.10 Adjustable Switching Frequency and Synchronization (RT/CLK)
- 7.3.11 Slow Start (SS/TR)
- 7.3.12 Power Good (PWRGD)
- 7.3.13 Output Overvoltage Protection (OVP)
- 7.3.14 Overcurrent Protection
- 7.3.15 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.3.16 Small Signal Model for Loop Response
- 7.3.17 Simple Small Signal Model for Peak Current Mode Control
- 7.3.18 Small Signal Model for Frequency Compensation
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedures
- 8.2.2.1 Custom Design With WEBENCH® Tools
- 8.2.2.2 Operating Frequency
- 8.2.2.3 Output Inductor Selection
- 8.2.2.4 Output Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.2.5 Input Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.2.6 Slow-Start Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.2.7 Bootstrap Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.2.8 Undervoltage Lockout Setpoint
- 8.2.2.9 Output Voltage Feedback Resistor Selection
- 8.2.2.10 Compensation Component Selection
- 8.2.2.11 Fast Transient Considerations
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RHL|14
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
10 Layout
10.1 Layout Guidelines
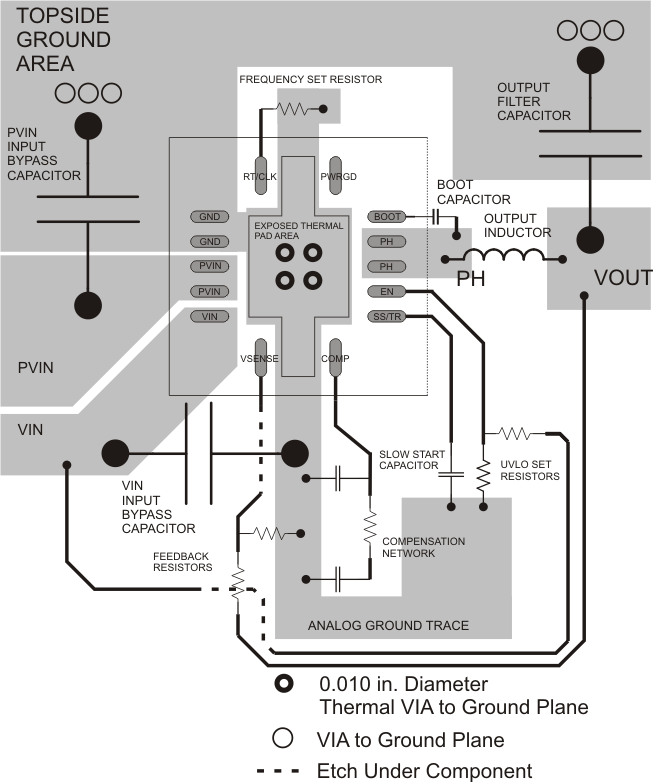
- Layout is a critical portion of good power supply design. See Figure 46 for a PCB layout example.
- The top layer contains the main power traces for VIN, VOUT, and VPHASE. Also on the top layer are connections for the remaining pins of the TPS54622 and a large top-side area filled with ground.
- Connect the top layer ground area to the internal ground layers using vias at the input bypass capacitor, the output filter capacitor, and directly under the TPS54622 device to provide a thermal path from the exposed thermal pad land to ground
- Tie the GND pin directly to the power pad under the IC and the power pad.
- For operation at full rated load, the top side ground area together with the internal ground plane, must provide adequate heat dissipating area.
- There are several signals paths that conduct fast changing currents or voltages that can interact with stray inductance or parasitic capacitance to generate noise or degrade the power supplies performance.
- To help eliminate these problems, the PVIN pin should be bypassed to ground with a low ESR ceramic bypass capacitor with X5R or X7R dielectric.
- Care should be taken to minimize the loop area formed by the bypass capacitor connections, the PVIN pins, and the ground connections.
- The VIN pin must also be bypassed to ground using a low ESR ceramic capacitor with X5R or X7R dielectric.
- Make sure to connect this capacitor to the quite analog ground trace rather than the power ground trace of the PVIn bypass capacitor.
- Since the PH connection is the switching node, the output inductor should be located close to the PH pins, and the area of the PCB conductor minimized to prevent excessive capacitive coupling.
- The output filter capacitor ground should use the same power ground trace as the PVIN input bypass capacitor.
- Try to minimize this conductor length while maintaining adequate width.
- The small signal components should be grounded to the analog ground path as shown.
- The RT/CLK pin is sensitive to noise so the RT resistor must be located as close as possible to the IC and routed with minimal lengths of trace.
- The additional external components can be placed approximately as shown.
- It may be possible to obtain acceptable performance with alternate PCB layouts, however, this layout has been shown to produce good results and is meant as a guideline.
- Land pattern and stencil information is provided in the data sheet addendum.
- The dimension and outline information is for the standard RHL (S-PVQFN-N14) package.
- There may be slight differences between the provided data and actual lead frame used on the TPS54622RHL package.
10.2 Layout Examples
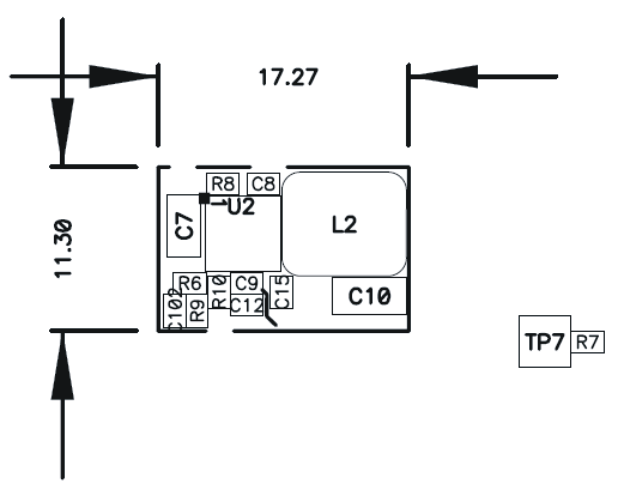 Figure 47. Ultra-Small PCB Layout Using TPS54622 (PMP4854-2)
Figure 47. Ultra-Small PCB Layout Using TPS54622 (PMP4854-2)
10.3 Estimated Circuit Area
The estimated printed-circuit-board area for the components used in the design of Figure 29 is 0.58 in2 (374mm2). This area does not include test points or connectors.