SLVSBF3B June 2012 – May 2019 TPS54678
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Fixed Frequency PWM Control
- 7.3.2 Slope Compensation and Output Current
- 7.3.3 Bootstrap Voltage (Boot) and Low Dropout Operation
- 7.3.4 Error Amplifier
- 7.3.5 Voltage Reference
- 7.3.6 Adjusting the Output Voltage
- 7.3.7 Enable and Adjusting Undervoltage Lockout
- 7.3.8 Soft-Start Pin
- 7.3.9 Sequencing
- 7.3.10 Constant Switching Frequency and Timing Resistor (RT/CLK Pin)
- 7.3.11 Overcurrent Protection
- 7.3.12 Safe Start-Up into Prebiased Outputs
- 7.3.13 Synchronize Using the RT/CLK Pin
- 7.3.14 Power Good (PWRGD Pin)
- 7.3.15 Overvoltage Transient Protection
- 7.3.16 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Custom Design With WEBENCH® Tools
- 8.2.2.2 Step One: Select the Switching Frequency
- 8.2.2.3 Step Two: Select the Output Inductor
- 8.2.2.4 Step Three: Choose the Output Capacitor
- 8.2.2.5 Step Four: Select the Input Capacitor
- 8.2.2.6 Step Five: Choose the Soft-Start Capacitor
- 8.2.2.7 Step Six: Select the Bootstrap Capacitor
- 8.2.2.8 Step Eight: Select Output Voltage and Feedback Resistors
- 8.2.2.9 Step Nine: Select Loop Compensation Components
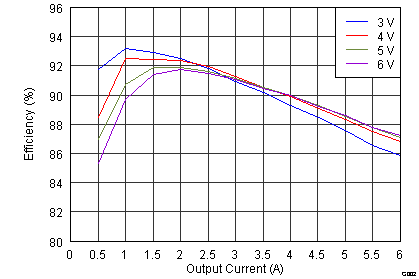
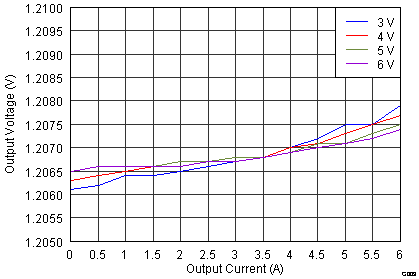
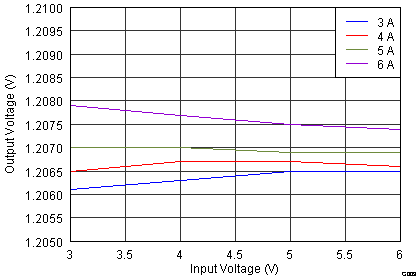
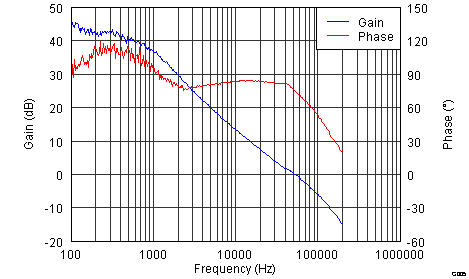
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RTE|16
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RTE|16
Orderable Information
8.2.3.1.4 Hiccup Mode Current Limit
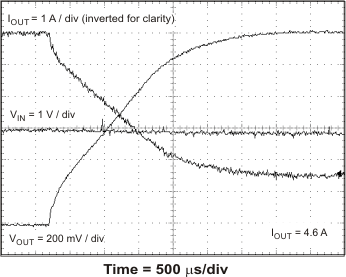
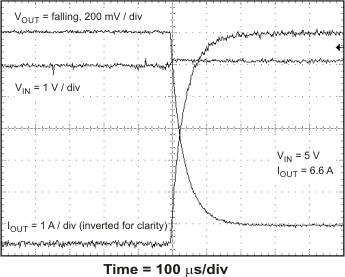
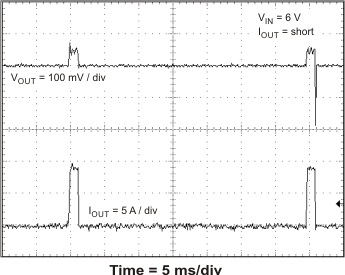
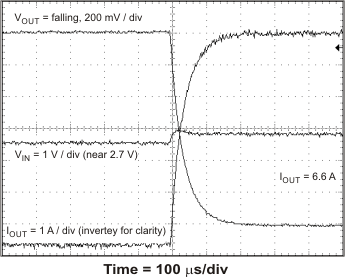
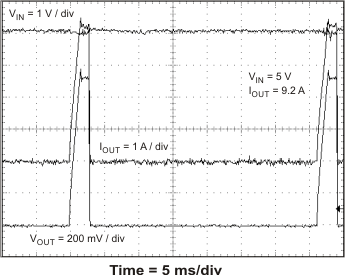
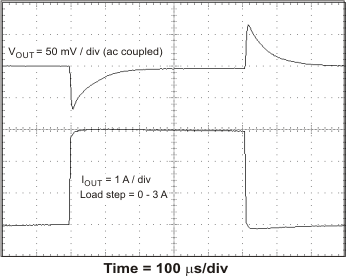
The TPS54678 has hiccup mode current limit. When the peak switch current exceeds the current limit threshold, the device shuts down and restarts. Hiccup mode current limit operation is shown in Figure 46 and Figure 47. Figure 46 shows the hiccup mode current limit with a slight resistive overload. When the peak current limit is exceeded, the output voltage is disabled. Figure 47 shows the operation of the TPS54678 with the output shorted to ground. The device continuously resets until the fault condition is removed.
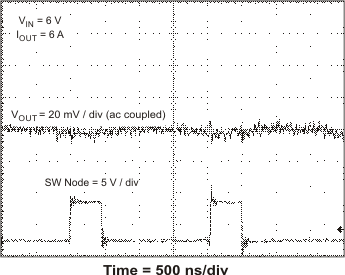
VIN = 6 V, IOUT = 6 A
Figure 38. Output Ripple 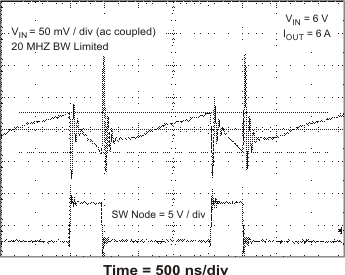
VIN = 6 V, IOUT = 6 A
Figure 40. Input Ripple 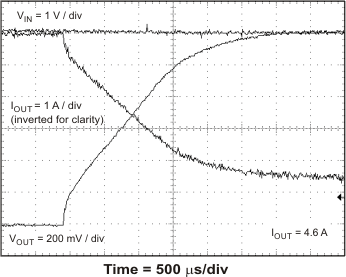
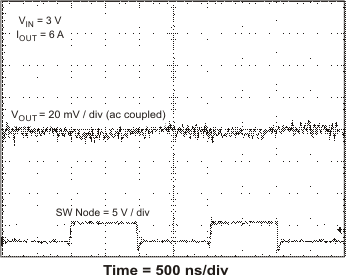
VIN = 3 V, IOUT = 6 A
Figure 37. Output Ripple 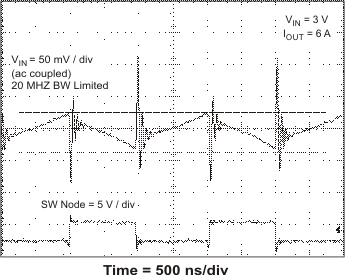
VIN = 3 V, IOUT = 6 A
Figure 39. Input Ripple