SLUSF28 November 2023 TPS546A24S
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
-
6 Detailed Description
- 6.1 Overview
- 6.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 6.3
Feature Description
- 6.3.1 Average Current-Mode Control
- 6.3.2 Linear Regulators
- 6.3.3 AVIN and PVIN Pins
- 6.3.4 Input Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO)
- 6.3.5 Start-Up and Shutdown
- 6.3.6 Differential Sense Amplifier and Feedback Divider
- 6.3.7 Set Output Voltage and Adaptive Voltage Scaling (AVS)
- 6.3.8 Prebiased Output Start-Up
- 6.3.9 Soft Stop and (65h) TOFF_FALL Command
- 6.3.10 Power Good (PGOOD)
- 6.3.11 Set Switching Frequency
- 6.3.12 Frequency Synchronization
- 6.3.13 Loop Follower Detection
- 6.3.14 Current Sensing and Sharing
- 6.3.15 Telemetry
- 6.3.16 Overcurrent Protection
- 6.3.17 Overvoltage/Undervoltage Protection
- 6.3.18 Overtemperature Management
- 6.3.19 Fault Management
- 6.3.20 Back-Channel Communication
- 6.3.21 Switching Node (SW)
- 6.3.22 PMBus General Description
- 6.3.23 PMBus Address
- 6.3.24 PMBus Connections
- 6.4 Device Functional Modes
- 6.5 Programming
- 6.6
Register Maps
- 6.6.1 Conventions for Documenting Block Commands
- 6.6.2 (01h) OPERATION
- 6.6.3 (02h) ON_OFF_CONFIG
- 6.6.4 (03h) CLEAR_FAULTS
- 6.6.5 (04h) PHASE
- 6.6.6 (10h) WRITE_PROTECT
- 6.6.7 (15h) STORE_USER_ALL
- 6.6.8 (16h) RESTORE_USER_ALL
- 6.6.9 (19h) CAPABILITY
- 6.6.10 (1Bh) SMBALERT_MASK
- 6.6.11 (1Bh) SMBALERT_MASK_VOUT
- 6.6.12 (1Bh) SMBALERT_MASK_IOUT
- 6.6.13 (1Bh) SMBALERT_MASK_INPUT
- 6.6.14 (1Bh) SMBALERT_MASK_TEMPERATURE
- 6.6.15 (1Bh) SMBALERT_MASK_CML
- 6.6.16 (1Bh) SMBALERT_MASK_OTHER
- 6.6.17 (1Bh) SMBALERT_MASK_MFR
- 6.6.18 (20h) VOUT_MODE
- 6.6.19 (21h) VOUT_COMMAND
- 6.6.20 (22h) VOUT_TRIM
- 6.6.21 (24h) VOUT_MAX
- 6.6.22 (25h) VOUT_MARGIN_HIGH
- 6.6.23 (26h) VOUT_MARGIN_LOW
- 6.6.24 (27h) VOUT_TRANSITION_RATE
- 6.6.25 (29h) VOUT_SCALE_LOOP
- 6.6.26 (2Bh) VOUT_MIN
- 6.6.27 (33h) FREQUENCY_SWITCH
- 6.6.28 (35h) VIN_ON
- 6.6.29 (36h) VIN_OFF
- 6.6.30 (37h) INTERLEAVE
- 6.6.31 (38h) IOUT_CAL_GAIN
- 6.6.32 (39h) IOUT_CAL_OFFSET
- 6.6.33 (40h) VOUT_OV_FAULT_LIMIT
- 6.6.34 (41h) VOUT_OV_FAULT_RESPONSE
- 6.6.35 (42h) VOUT_OV_WARN_LIMIT
- 6.6.36 (43h) VOUT_UV_WARN_LIMIT
- 6.6.37 (44h) VOUT_UV_FAULT_LIMIT
- 6.6.38 (45h) VOUT_UV_FAULT_RESPONSE
- 6.6.39 (46h) IOUT_OC_FAULT_LIMIT
- 6.6.40 (47h) IOUT_OC_FAULT_RESPONSE
- 6.6.41 (4Ah) IOUT_OC_WARN_LIMIT
- 6.6.42 (4Fh) OT_FAULT_LIMIT
- 6.6.43 (50h) OT_FAULT_RESPONSE
- 6.6.44 (51h) OT_WARN_LIMIT
- 6.6.45 (55h) VIN_OV_FAULT_LIMIT
- 6.6.46 (56h) VIN_OV_FAULT_RESPONSE
- 6.6.47 (58h) VIN_UV_WARN_LIMIT
- 6.6.48 (60h) TON_DELAY
- 6.6.49 (61h) TON_RISE
- 6.6.50 (62h) TON_MAX_FAULT_LIMIT
- 6.6.51 (63h) TON_MAX_FAULT_RESPONSE
- 6.6.52 (64h) TOFF_DELAY
- 6.6.53 (65h) TOFF_FALL
- 6.6.54 (78h) STATUS_BYTE
- 6.6.55 (79h) STATUS_WORD
- 6.6.56 (7Ah) STATUS_VOUT
- 6.6.57 (7Bh) STATUS_IOUT
- 6.6.58 (7Ch) STATUS_INPUT
- 6.6.59 (7Dh) STATUS_TEMPERATURE
- 6.6.60 (7Eh) STATUS_CML
- 6.6.61 (7Fh) STATUS_OTHER
- 6.6.62 (80h) STATUS_MFR_SPECIFIC
- 6.6.63 (88h) READ_VIN
- 6.6.64 (8Bh) READ_VOUT
- 6.6.65 (8Ch) READ_IOUT
- 6.6.66 (8Dh) READ_TEMPERATURE_1
- 6.6.67 (98h) PMBUS_REVISION
- 6.6.68 (99h) MFR_ID
- 6.6.69 (9Ah) MFR_MODEL
- 6.6.70 (9Bh) MFR_REVISION
- 6.6.71 (9Eh) MFR_SERIAL
- 6.6.72 (ADh) IC_DEVICE_ID
- 6.6.73 (AEh) IC_DEVICE_REV
- 6.6.74 (B1h) USER_DATA_01 (COMPENSATION_CONFIG)
- 6.6.75 (B5h) USER_DATA_05 (POWER_STAGE_CONFIG)
- 6.6.76 (D0h) MFR_SPECIFIC_00 (TELEMETRY_CONFIG)
- 6.6.77 (DAh) MFR_SPECIFIC_10 (READ_ALL)
- 6.6.78 (DBh) MFR_SPECIFIC_11 (STATUS_ALL)
- 6.6.79 (DCh) MFR_SPECIFIC_12 (STATUS_PHASE)
- 6.6.80 (E3h) MFR_SPECIFIC_19 (PGOOD_CONFIG)
- 6.6.81 (E4h) MFR_SPECIFIC_20 (SYNC_CONFIG)
- 6.6.82 (ECh) MFR_SPECIFIC_28 (STACK_CONFIG)
- 6.6.83 (EDh) MFR_SPECIFIC_29 (MISC_OPTIONS)
- 6.6.84 (EEh) MFR_SPECIFIC_30 (PIN_DETECT_OVERRIDE)
- 6.6.85 (EFh) MFR_SPECIFIC_31 (DEVICE_ADDRESS)
- 6.6.86 (F0h) MFR_SPECIFIC_32 (NVM_CHECKSUM)
- 6.6.87 (F1h) MFR_SPECIFIC_33 (SIMULATE_FAULT)
- 6.6.88 (FAh) MFR_SPECIFIC_42 (PASSKEY)
- 6.6.89 (FBh) MFR_SPECIFIC_43 (EXT_WRITE_PROTECT)
- 6.6.90 (FCh) MFR_SPECIFIC_44 (FUSION_ID0)
- 6.6.91 (FDh) MFR_SPECIFIC_45 (FUSION_ID1)
-
7 Application and Implementation
- 7.1 Application Information
- 7.2
Typical Application
- 7.2.1 Design Requirements
- 7.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 7.2.2.1 Custom Design With WEBENCH® Tools
- 7.2.2.2 Switching Frequency
- 7.2.2.3 Inductor Selection
- 7.2.2.4 Output Capacitor Selection
- 7.2.2.5 Input Capacitor Selection
- 7.2.2.6 AVIN, BP1V5, VDD5 Bypass Capacitor
- 7.2.2.7 Bootstrap Capacitor Selection
- 7.2.2.8 R-C Snubber
- 7.2.2.9 Output Voltage Setting (VSEL Pin)
- 7.2.2.10 Compensation Selection (MSEL1 Pin)
- 7.2.2.11 Soft Start, Overcurrent Protection, and Stacking Configuration (MSEL2 Pin)
- 7.2.2.12 Enable and UVLO
- 7.2.2.13 ADRSEL
- 7.2.2.14 Pin-Strapping Resistor Selection
- 7.2.2.15 BCX_CLK and BCX_DAT
- 7.2.3 Application Curves
- 7.3 Power Supply Recommendations
- 7.4 Layout
- 8 Device and Documentation Support
- 9 Revision History
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RVF|40
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RVF|40
Orderable Information
7.2.2.10 Compensation Selection (MSEL1 Pin)
The resistor to AGND for MSEL1 selects the (B1h) USER_DATA_01 (COMPENSATION_CONFIG) values to program the following voltage loop and current loop gains. For options other than the EEPROM code (MSEL1 shorted to AGND or MSEL1 to AGND resistor code 0), the current and voltage loop zero and pole frequencies are scaled with the programmed switching frequency.
Based on Current Error Integrator, calculate the mid-band current loop gain with Equation 24.
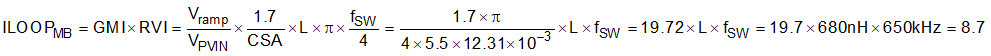
Find the smaller value closest to 8.7 in Table 6-9 and this is .
To calculate the target voltage loop gain, first use Equation 25 to calculate the output impedance. Use Equation 26 to calculate the target voltage loop gain.
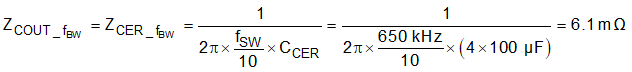 .
.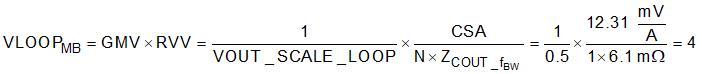
Find the smaller value closest to 4 in Table 6-9 for voltage loop gain and this is 4. This setting gives a stable design but through bench evaluation the voltage loop gain was reduced to 1 to improve the gain and phase margin with the reduced ILOOP gain. The calculated current and voltage loop gain correspond to compensation setting 17. To use this compensation setting resistor to AGND code 1 is needed. With this compensation code the even resistor divider code must be used to set the switching frequency. Divider code 9 sets the fsw to 650 kHz. Resistor to AGND code 1 and resistor divider code is selected using an MSEL1 resistor divider of RTOP = 3.16 kΩ and RBOT = 5.62 kΩ.
The procedure given is meant to give a stable design. Further optimization of the compensation is often possible through testing the design on the bench. Increasing the voltage loop gain increases the loop bandwidth to improve the transient response but make sure to verify there is still sufficient gain and phase margin. The maximum voltage loop bandwidth possible is limited by these stability margins. Decreasing the current loop gain can help to minimize pulse-width jitter but this typically comes with a tradeoff of decreased phase margin. Lastly, the pole and zero locations can also be adjusted through PMBus. For example, it can be beneficial to use the CPV capacitor in the voltage loop to add a pole at the same frequency of the ESR zero when using high ESR output capacitors.
When using a larger inductance, the current loop gain that can be selected through pin strapping can be much lower than the calculated target value. If this happens, the voltage loop gain must also be scaled back by about the same amount to keep sufficient phase margin. For higher voltage loop bandwidth, the inductance can be decreased to reduce the current loop gain needed or higher current loop gain can be programmed through the PMBus command USER_DATA_01 (COMPENSATION_CONFIG).