SNVSBM9B July 2020 – November 2020 TPS54JB20
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Internal VCC LDO And Using External Bias On VCC Pin
- 7.3.2 Enable
- 7.3.3 Output Voltage Setting
- 7.3.4 Internal Fixed Soft Start and External Adjustable Soft Start
- 7.3.5 External REFIN For Output Voltage Tracking
- 7.3.6 Frequency and Operation Mode Selection
- 7.3.7 D-CAP3 Control
- 7.3.8 Low-side FET Zero-Crossing
- 7.3.9 Current Sense and Positive Overcurrent Protection
- 7.3.10 Low-side FET Negative Current Limit
- 7.3.11 Power Good
- 7.3.12 Overvoltage and Undervoltage Protection
- 7.3.13 Out-Of-Bounds (OOB) Operation
- 7.3.14 Output Voltage Discharge
- 7.3.15 UVLO Protection
- 7.3.16 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Output Voltage Setting Point
- 8.2.2.2 Choose the Switching Frequency and the Operation Mode
- 8.2.2.3 Choose the Inductor
- 8.2.2.4 Set the Current Limit (TRIP)
- 8.2.2.5 Choose the Output Capacitor
- 8.2.2.6 Choose the Input Capacitors (CIN)
- 8.2.2.7 Soft Start Capacitor (SS/REFIN Pin)
- 8.2.2.8 EN Pin Resistor Divider
- 8.2.2.9 VCC Bypass Capacitor
- 8.2.2.10 BOOT Capacitor
- 8.2.2.11 Series BOOT Resistor and RC Snubber
- 8.2.2.12 PGOOD Pullup Resistor
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RWW|21
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
5 Pin Configuration and Functions
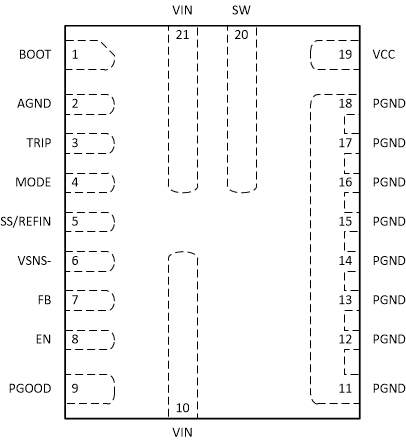 Figure 5-1 RWW Package21-Pin VQFN-HRTop View
Figure 5-1 RWW Package21-Pin VQFN-HRTop View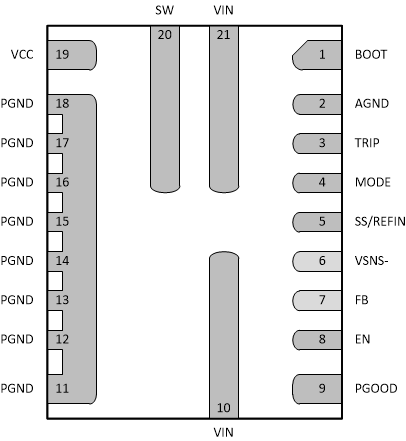 Figure 5-2 RWW Package21-Pin VQFN-HRBottom
View
Figure 5-2 RWW Package21-Pin VQFN-HRBottom
ViewTable 5-1 Pin Functions
| NO. | NAME | I/O(1) | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | BOOT | I/O | Supply rail for the high-side gate driver (boost terminal). Connect the bootstrap capacitor from this pin to SW node. |
| 2 | AGND | G | Ground pin. Reference point for the internal control circuits. |
| 3 | TRIP | I/O | Current limit setting pin. Connect a resistor to AGND to set the current limit trip point. ±1% tolerance resistor is highly recommended. See Section 7.3.9 for details on OCL setting. |
| 4 | MODE | I | The MODE pin sets the forced continuous-conduction mode (FCCM) or skip-mode operation. It also selects the operating frequency by connecting a resistor from MODE pin to AGND pin. ±1% tolerance resistor is recommended. See Table 7-1 for details. |
| 5 | SS/REFIN | I/O | Dual-function pin. Soft-start function: Connecting a capacitor to VSNS– pin programs soft-start time. Minimum soft-start time (1.5 ms) is fixed internally. A minimum 1-nF capacitor is required for this pin to avoid overshoot during the charge of soft-start capacitor. REFIN function: The device always looks at the voltage on this SS/REFIN pin as the reference for the control loop. The internal reference voltage can be overridden by an external DC voltage source on this pin for tracking application. |
| 6 | VSNS– | I | The return connection for a remote voltage sensing configuration. It is also used as ground for the internal reference. Short to AGND for single-end sense configuration. |
| 7 | FB | I | Output voltage feedback input. A resistor divider from the VOUT to VSNS– (tapped to FB pin) sets the output voltage. |
| 8 | EN | I | Enable pin. The enable pin turns the DC/DC switching converter on or off. Floating EN pin before start-up disables the converter. The recommended operating condition for EN pin is maximum 5.5-V. Do not connect EN pin to VIN pin directly. |
| 9 | PGOOD | O | Open-drain power-good status signal. When the FB voltage moves outside the specified limits, PGOOD goes low after 2-µs delay. |
| 10, 21 | VIN | P | Power-supply input pins for both integrated power MOSFET pair and the internal LDO. Place the decoupling input capacitors from VIN pins to PGND pins as close as possible. |
| 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18 | PGND | G | Power ground of internal low-side MOSFET. At least six PGND vias are required to be placed as close as possible to the PGND pins. This minimizes parasitic impedance and also lowers thermal resistance. |
| 19 | VCC | I/O | Internal 3-V LDO output. An external bias with 3.3-V or higher voltage can be connected to this pin to save the power losses on the internal LDO. The voltage source on this pin powers both the internal circuitry and gate driver. Requires a 2.2-µF, at least 6.3-V, rating ceramic capacitor from VCC pin to PGND pins as the decoupling capacitor and the placement is required to be as close as possible. |
| 20 | SW | O | Output switching terminal of the power converter. Connect this pin to the output inductor. |
(1) I = Input, O = Output, P = Supply, G = Ground