SLVSFQ7A December 2020 – December 2021 TPS55288-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 VCC Power Supply
- 7.3.2 Operation Mode Setting
- 7.3.3 Input Undervoltage Lockout
- 7.3.4 Enable and Programmable UVLO
- 7.3.5 Soft Start
- 7.3.6 Shutdown and Load Discharge
- 7.3.7 Switching Frequency
- 7.3.8 Switching Frequency Dithering
- 7.3.9 Inductor Current Limit
- 7.3.10 Internal Charge Path
- 7.3.11 Output Voltage Setting
- 7.3.12 Output Current Monitoring and Cable Voltage Droop Compensation
- 7.3.13 Integrated Gate Drivers
- 7.3.14 Output Current Limit
- 7.3.15 Overvoltage Protection
- 7.3.16 Output Short Circuit Protection
- 7.3.17 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6
Register Maps
- 7.6.1 REF Register (Address = 0h, 1h) [reset = 11010010h, 00000000h]
- 7.6.2 IOUT_LIMIT Register (Address = 2h) [reset = 11100100h]
- 7.6.3 VOUT_SR Register (Address = 3h) [reset = 00000001h]
- 7.6.4 VOUT_FS Register (Address = 4h) [reset = 00000011h]
- 7.6.5 CDC Register (Address = 5h) [reset = 11100000h]
- 7.6.6 MODE Register (Address = 6h) [reset = 00100000h]
- 7.6.7 STATUS Register (Address = 7h) [reset = 00000011h]
- 7.6.8 Register Summary
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RPM|26
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RPM|26
Orderable Information
8.2.2.6 Output Capacitor
In boost mode, the output capacitor conducts high ripple current. The output capacitor RMS ripple current is given by Equation 15, where the minimum input voltage and the maximum output voltage correspond to the maximum capacitor current.
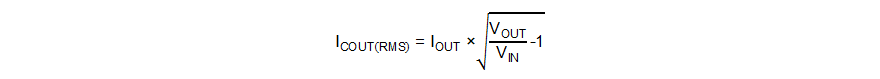
where
- ICOUT(RMS) is the RMS current through the output capacitor
- IOUT is the output current
In this example, the maximum output ripple RMS current is 5.5 A.
The ESR of the output capacitor causes an output voltage ripple given by Equation 16 in boost mode.
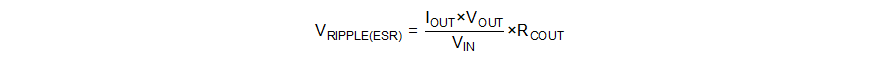
where
- RCOUT is the ESR of the output capacitance
The capacitance also causes a capacitive output voltage ripple given by Equation 17 in boost mode. When input voltage reaches the minimum value and the output voltage reaches the maximum value, there is the largest output voltage ripple caused by the capacitance.
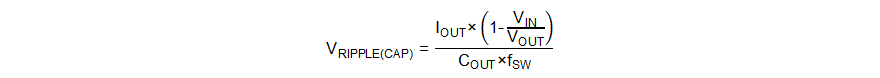
Typically, a combination of ceramic capacitors and bulk electrolytic capacitors is needed to provide low ESR, high ripple current, and small output voltage ripple. From the required output voltage ripple, use Equation 16 and Equation 17 to calculate the minimum required effective capacitance of the COUT.