SLVSDU5A April 2018 – November 2019 TPS57112C-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4
Device Functional Modes
- 7.4.1 Adjusting the Output Voltage
- 7.4.2 Enable Functionality and Adjusting Undervoltage Lockout
- 7.4.3 Slow-Start or Tracking Pin
- 7.4.4 Sequencing
- 7.4.5 Constant Switching Frequency and Timing Resistor (RT/CLK Pin)
- 7.4.6 Overcurrent Protection
- 7.4.7 Frequency Shift
- 7.4.8 Reverse Overcurrent Protection
- 7.4.9 Synchronize Using the RT/CLK Pin
- 7.4.10 Power Good (PWRGD Pin)
- 7.4.11 Overvoltage Transient Protection
- 7.4.12 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.4.13 Small-Signal Model for Loop Response
- 7.4.14 Simple Small-Signal Model for Peak-Current-Mode Control
- 7.4.15 Small-Signal Model for Frequency Compensation
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Selecting the Switching Frequency
- 8.2.2.2 Output Inductor Selection
- 8.2.2.3 Output Capacitor
- 8.2.2.4 Input Capacitor
- 8.2.2.5 Slow-Start Capacitor
- 8.2.2.6 Bootstrap Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.2.7 Output Voltage and Feedback Resistor Selection
- 8.2.2.8 Compensation
- 8.2.2.9 Power-Dissipation Estimate
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RTE|16
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RTE|16
Orderable Information
8.2.2.7 Output Voltage and Feedback Resistor Selection
For the example design, the R6 selection is 100 kΩ. Using Equation 32, the calculated value of R7 is 80 kΩ. The nearest standard 1% resistor is 80.5 kΩ.
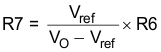
Because of the internal design of the TPS57112C-Q1 device, any given input voltage has a minimum output voltage limit. The output voltage can never be lower than the internal voltage reference of 0.8 V. Above 0.8 V, the output voltage may be limited by the minimum controllable on time. The minimum output voltage in this case is given by Equation 33
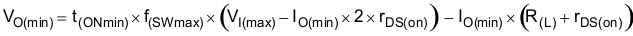
where
- VO(min) = minimum achievable output voltage
- t(ONmin) = minimum controllable on-time (65 ns typical. 120 ns no load)
- f(SWmax) = maximum switching frequency, including tolerance
- VI(max) = maximum input voltage
- IO(min) = minimum load current
- rDS(on) = minimum high-side MOSFET on-resistance (15 mΩ–19 mΩ)
- R(L) = series resistance of output inductor
There is also a maximum achievable output voltage which is limited by the minimum off-time. The maximum output voltage is given by Equation 34
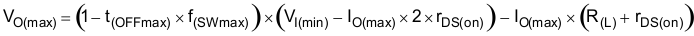
where
- VO(max) = maximum achievable output voltage
- t(OFFmax) = maximum off-time (60 ns typical)
- f(SWmax) = maximum switching frequency, including tolerance
- VI(min) = minimum input voltage
- IO(max) = maximum load current
- rDS(on) = maximum high-side MOSFET on-resistance (19 mΩ–30 mΩ)
- R(L) = series resistance of output inductor