SLVSH62 November 2023 TPS61033-Q1 , TPS610333-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Device Comparison Table
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Undervoltage Lockout
- 7.3.2 Enable and Soft Start
- 7.3.3 Setting the Output Voltage
- 7.3.4 Current Limit Operation
- 7.3.5 Pass-Through Operation
- 7.3.6 Power Good Indicator
- 7.3.7 Implement Output Discharge by PG function
- 7.3.8 Spread Spectrum Frequency Modulation
- 7.3.9 Overvoltage Protection
- 7.3.10 Output Short-to-Ground Protection
- 7.3.11 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Revision History
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DRL|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.2.2.2 Inductor Selection
Because the selection of the inductor affects steady-state operation, transient behavior, and loop stability. The inductor is the most important component in power regulator design. There are three important inductor specifications, inductor value, saturation current, and dc resistance (DCR).
The TPS61033-Q1 is designed to work with inductor values between 0.37 µH and 2.9 µH. Follow Equation 6 to Equation 8 to calculate the inductor peak current for the application. To calculate the current in the worst case, use the minimum input voltage, maximum output voltage, and maximum load current of the application. To have enough design margins, choose the inductor value with –30% tolerances, and low power-conversion efficiency for the calculation.
In a boost regulator, the inductor dc current can be calculated by Equation 6.
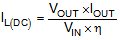
where
- VOUT is the output voltage of the boost converter
- IOUT is the output current of the boost converter
- VIN is the input voltage of the boost converter
- η is the power conversion efficiency, use 90% for most applications
The inductor ripple current is calculated by Equation 7.
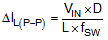
where
- D is the duty cycle, which can be calculated by Equation 3
- L is the inductance value of the inductor
- fSW is the switching frequency
- VIN is the input voltage of the boost converter
Therefore, the inductor peak current is calculated by Equation 8.
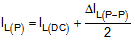
Normally, it is advisable to work with an inductor peak-to-peak current of less than 40% of the average inductor current for maximum output current. A smaller ripple from a larger valued inductor reduces the magnetic hysteresis losses in the inductor and EMI. But in the same way, load transient response time is increased. The saturation current of the inductor must be higher than the calculated peak inductor current. Table 8-2 lists the recommended inductors for the TPS61033-Q1.
| PART NUMBER(1) | L (µH) | DCR MAX (mΩ) | SATURATION CURRENT (A) | SIZE (LxWxH) | VENDOR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XGL4020-471MEC | 0.47 | 5.1 | 6.1 | 4 x 4 x 2.1 | Coilcraft |
XGL4020-102MEC | 1 | 9.0 | 3.8 | 4 x 4 x 2.1 | Coilcraft |