SLVSCM8D May 2015 – August 2021 TPS61088
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RHL|20
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RHL|20
Orderable Information
8.2.2.8 Loop Stability
The TPS61088 requires external compensation, which allows the loop response to be optimized for each application. The COMP pin is the output of the internal error amplifier. An external compensation network comprised of resistor R5, ceramic capacitors C5 and C8 is connected to the COMP pin.
The power stage small signal loop response of constant off-time (COT) with peak current control can be modeled by Equation 13.
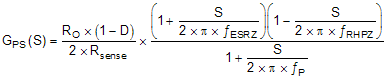
where
- D is the switching duty cycle
- RO is the output load resistance
- Rsense is the equivalent internal current sense resistor, which is 0.08 Ω
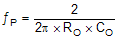
where
- CO is output capacitor
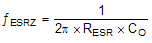
where
- RESR is the equivalent series resistance of the output capacitor
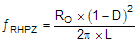
The COMP pin is the output of the internal transconductance amplifier. Equation 17 shows the small signal transfer function of compensation network.
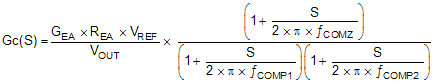
where
- GEA is the transconductance of the amplifier
- REA is the output resistance of the amplifier
- VREF is the reference voltage at the FB pin
- VOUT is the output voltage
- ƒCOMP1, ƒCOMP2 are the poles' frequency of the compensation network
- ƒCOMZ is the zero's frequency of the compensation network
The next step is to choose the loop crossover frequency, ƒC. The higher in frequency that the loop gain stays above zero before crossing over, the faster the loop response is. It is generally accepted that the loop gain cross over no higher than the lower of either 1/10 of the switching frequency, ƒSW, or 1/5 of the RHPZ frequency, ƒRHPZ.
Then set the value of R5, C5, and C8 (in Figure 8-1) by following these equations.
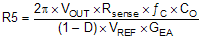
where
- ƒC is the selected crossover frequency
The value of C5 can be set by Equation 19.
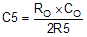
The value of C8 can be set by Equation 20.
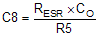
If the calculated value of C8 is less than 10 pF, it can be left open.
Designing the loop for greater than 45° of phase margin and greater than 10-dB gain margin eliminates output voltage ringing during the line and load transient.