SLVSFH6C January 2021 – December 2021 TPS61094
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DSS|12
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DSS|12
Orderable Information
7.3.4 Current Limit Operation
The TPS61094 has the peak current limit in Buck mode and valley current limit in Boost mode. Current limit detection occurs when the high-side MOSFET turns on.
In Buck mode, the TPS61094 has average output current control, so the current limit in Buck mode is hard to reach.
In Boost mode, when the load current is increased such that the inductor current is above the current limit within the whole switching cycle time, the off time is increased to allow the inductor current to decrease to this threshold before the next on time begins (called the frequency foldback mechanism). When the current limit is reached, the output voltage decreases during further load increase.
The maximum continuous output current (IOUT(LC)), before entering current limit (CL) operation, can be defined by Equation 1.

where
- D is the duty cycle.
- ΔIL(P-P) is the inductor ripple current.
The duty cycle can be estimated by Equation 2.
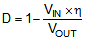
where
- VOUT is the output voltage of the boost converter.
- VIN is the input voltage of the boost converter.
- η is the efficiency of the converter; use 90% for most applications.
The peak-to-peak inductor ripple current is calculated by Equation 3.
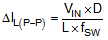
where
- L is the inductance value of the inductor.
- fSW is the switching frequency.
- D is the duty cycle.
- VIN is the input voltage of the boost converter.