SLVSC26B November 2013 – May 2024 TPS61162A , TPS61163A
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
- 6 Detailed Description
- 7 Application and Implementation
- 8 Device and Documentation Support
- 9 Revision History
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- YFF|9
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.2.2.4 Output Capacitor Selection
The output capacitor is mainly selected to meet the requirement for the output ripple and loop stability. A 1-µF to 2.2-µF capacitor is recommended for the loop stability consideration. This ripple voltage is related to the capacitor’s capacitance and its ESR. Due to its low ESR, Vripple_ESR could be neglected for ceramic capacitors. Assuming a capacitor with zero ESR, the output ripple can be calculated with Equation 7.
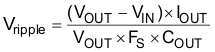
where
- Vripple = peak-to-peak output ripple.
The additional part of ripple caused by the ESR is calculated using Vripple_ESR = IOUT x RESR and can be ignored for ceramic capacitors.
Note that capacitor degradation increases the ripple much. Select the capacitor with 50-V rated voltage to reduce the degradation at the output voltage. If the output ripple is too large, change a capacitor with less degradation effect or with higher rated voltage could be helpful.