SNVSA40B October 2014 – June 2024 TPS61169
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
- 6 Detailed Description
- 7 Application and Implementation
- 8 Device and Documentation Support
- 9 Revision History
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DCK|5
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.2.2.3 Output Capacitor Selection
The output capacitor is mainly selected to meet the requirement for the output ripple and loop stability. This ripple voltage is related to capacitor capacitance and its equivalent series resistance (ESR). Assuming a capacitor with zero ESR, the minimum capacitance needed for a given ripple can be calculated with Equation 6:
Equation 6. 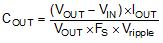
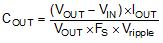
where
- Vripple = peak-to-peak output ripple
The additional part of the ripple caused by ESR is calculated using: Vripple_ESR = IOUT × RESR
Due to its low ESR, Vripple_ESR could be neglected for ceramic capacitors, a 1µF to 4.7µF capacitor is recommended for typical application.