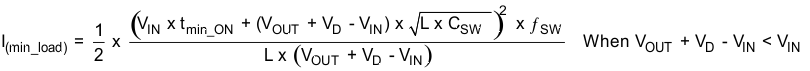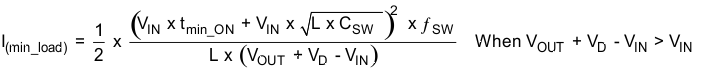SLVS892F December 2008 – April 2019 TPS61175
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Custom Design with WEBENCH Tools
- 8.2.2.2 Determining the Duty Cycle
- 8.2.2.3 Selecting the Inductor
- 8.2.2.4 Computing the Maximum Output Current
- 8.2.2.5 Setting Output Voltage
- 8.2.2.6 Setting the Switching Frequency
- 8.2.2.7 Setting the Soft-Start Time
- 8.2.2.8 Selecting the Schottky Diode
- 8.2.2.9 Selecting the Input and Output Capacitors
- 8.2.2.10 Compensating the Small Signal Control Loop
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|14
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.4.1 Minimum ON Time and Pulse Skipping
Once the PWM switch is turned on, the TPS61175 has minimum ON pulse width of 60 ns. This sets the limit of the minimum duty cycle of the PWM switch, and it is independent of the set switching frequency. When operating conditions result in the TPS61175 having a minimum ON pulse width less than 60 ns, the IC enters pulse-skipping mode. In this mode, the device keeps the power switch off for several switching cycles to keep the output voltage from rising above the regulated voltage. This operation typically occurs in light load condition when the PWM operates in discontinuous mode. Pulse skipping increases the output voltage ripple, see Figure 15.
When setting switching frequency higher than 1.2 MHz, TI recommends using an external synchronous clock as switching frequency to ensure pulse-skipping function works at light load. When using the internal switching frequency above 1.2 MHz, the pulse-skipping operation may not function. When the pulse-skipping function does not work at light load, the TPS61175 always runs in PWM mode with minimum ON pulse width. To keep the output voltage in regulation, a minimum load is required. The minimum load is related to the input voltage, output voltage, switching frequency, external inductor value and the maximum value of the minimum ON pulse width. Use Equation 1 and Equation 2 to calculate the required minimum load at the worst case. The maximum tmin_ON could be estimated to 80 ns. CSW is the total parasite capacitance at the switching node SW pin. It could be estimated to 100 pF.