SLVSCZ5B July 2016 – October 2018 TPS61230A
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Applications
- 8.2.1 TPS61230A 2.5-V to 4.5-V Input, 5-V Output Converter
- 8.2.2 Systems Example - TPS61230A with Feed Forward Capacitor for Best Transient Response
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RNS|7
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.2.1.2.2.1 Inductor Selection
A boost converter requires two main passive components for storing energy during the conversion, an inductor and an output capacitor. It is advisable to select an inductor with a saturation current rating higher than the possible peak current flowing through the power FETs. The inductor peak current varies as a function of the load, the input and output voltages and is estimated using Equation 5.
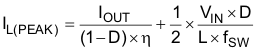
Where
η = Power conversion estimated efficiency
Selecting an inductor with the insufficient saturation performance can lead to the excessive peak current in the converter. This could eventually harm the device and reduce reliability. It's recommended to choose the saturation current for the inductor 20%~30% higher than the IL(PEAK), from Equation 5. The following inductors are recommended to be used in designs.
Table 5. List of Inductors
| INDUCTANCE [µH] | CURRENT RATING [A] | DC RESISTANCE [mΩ] | PART NUMBER | MANUFACTURER |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.0 | 9.0 | 12 | 744 383 560 10 | Wurth |
| 1.0 | 5.1 | 10.8 | XFL4020-102MEB | Coilcraft |