SLVSB07A July 2011 – March 2018 TPS61256A
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Package Summary
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- YFF|9
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.7.2 Current Limit Operation
The TPS61256A device employs a valley current limit sensing scheme. Current limit detection occurs during the off-time by sensing of the voltage drop across the synchronous rectifier.
The output voltage is reduced as the power stage of the device operates in a constant current mode. The maximum continuous output current (IOUT(CL)), before entering current limit (CL) operation, can be defined by Equation 1.
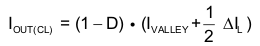
The duty cycle (D) can be estimated by Equation 2
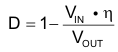
and the peak-to-peak current ripple (ΔIL) is calculated by Equation 3
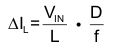
The output current, IOUT(DC), is the average of the rectifier ripple current waveform. When the load current is increased such that the lower peak is above the current limit threshold, the off-time is increased to allow the current to decrease to this threshold before the next on-time begins (so called frequency fold-back mechanism). When the current limit is reached the output voltage decreases during further load increase.
illustrates the inductor and rectifier current waveforms during current limit operation.
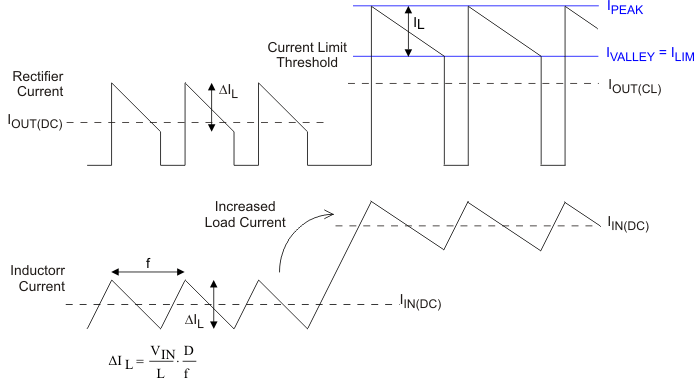 Figure 13. Inductor/Rectifier Currents In Current Limit Operation
Figure 13. Inductor/Rectifier Currents In Current Limit Operation