SLVSHB5A October 2024 – November 2024 TPS61287
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
-
6 Detailed Description
- 6.1 Overview
- 6.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 6.3 Feature Description
- 7 Application and Implementation
- 8 Device and Documentation Support
- 9 Revision History
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RZP|14
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.2.2.6 Output Capacitor Selection
Typically, a combination of ceramic capacitors and bulk electrolytic capacitors is needed to provide low ESR, high ripple current capacity, and small output voltage ripple.
When input voltage reaches the minimum value , there is the largest output voltage ripple caused by the capacitance. From the required output voltage ripple, use the following equations to calculate the minimum required effective capacitance COUT:
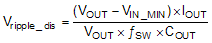
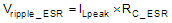
where
- Vripple_dis is output voltage ripple caused by charging and discharging of the output capacitor.
- Vripple_ESR is output voltage ripple caused by ESR of the output capacitor.
- VIN_MIN is the minimum input voltage of boost converter.
- VOUT is the output voltage.
- IOUT is the output current.
- ILpeak is the peak current of the inductor.
- ƒSW is the converter switching frequency.
- RC_ESR is the ESR of the output capacitors.
DC bias effect: High-capacitance ceramic capacitors have a DC bias effect, which has a strong influence on the final effective capacitance. Therefore, the right capacitor value must be chosen carefully. The differences between the rated capacitor value and the effective capacitance result from package size and voltage rating in combination with material. A 10-V rated 0805 capacitor with 10 μF can have an effective capacitance of less than 5 μF at an output voltage of 5 V.