SLVS957E June 2009 – April 2016 TPS61300 , TPS61301 , TPS61305
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagrams
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Safety Timer Accuracy
- 8.3.2 LED Failure Modes and Overvoltage Protection
- 8.3.3 Start-Up Sequence
- 8.3.4 Power Good (Flash Ready)
- 8.3.5 LED Temperature Monitoring (TPS61305, TPS61305A, TPS61306)
- 8.3.6 Hot Die Detector
- 8.3.7 NRESET Input: Hardware Enable and Disable
- 8.3.8 ENDCL Input: DC Light Hardware Control
- 8.3.9 Flashlight Blanking (Tx-MASK)
- 8.3.10 Undervoltage Lockout
- 8.3.11 Storage Capacitor Active Cell Balancing
- 8.3.12 RED Light Privacy Indicator
- 8.3.13 White LED Privacy Indicator
- 8.3.14 Storage Capacitor, Precharge Voltage Calibration
- 8.3.15 Storage Capacitor, Adaptive Precharge Voltage
- 8.3.16 Serial Interface Description
- 8.4
Device Functional Modes
- 8.4.1 Down-Mode in Voltage Regulation Mode
- 8.4.2 LED High-Current Regulators, Unused Inputs
- 8.4.3 Power-Save Mode Operation, Efficiency
- 8.4.4 Mode of Operation: DC Light and Flashlight
- 8.4.5 Flash Strobe is Level Sensitive (STT = 0): LED Strobe Follows FLASH_SYNC Input
- 8.4.6 Flash Strobe Is Leading Edge Sensitive (STT = 1): One-Shot LED Strobe
- 8.4.7 Current Limit Operation
- 8.4.8 Hardware Voltage Mode Selection
- 8.4.9 Shutdown
- 8.4.10 Thermal Shutdown
- 8.4.11 F/S-Mode Protocol
- 8.4.12 HS-Mode Protocol
- 8.4.13 TPS6130xx I2C Update Sequence
- 8.5
Register Maps
- 8.5.1 Slave Address Byte
- 8.5.2 Register Address Byte
- 8.5.3 REGISTER1 (TPS61300, TPS61301)
- 8.5.4 REGISTER1 (TPS61305, TPS61305A, TPS61306)
- 8.5.5 REGISTER2 (TPS61300, TPS61301)
- 8.5.6 REGISTER2 (TPS61305, TPS61305A, TPS61306)
- 8.5.7 REGISTER3
- 8.5.8 REGISTER4
- 8.5.9 REGISTER5
- 8.5.10 REGISTER6 (TPS61300, TPS61301)
- 8.5.11 REGISTER6 (TPS61305, TPS61305A)
- 8.5.12 REGISTER7
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2 Typical Applications
- 9.3
System Examples
- 9.3.1 2x 600-mA High-Power White LED Solution Featuring Privacy Indicator
- 9.3.2 White LED Flashlight Driver and Audio Amplifier Power Supply Operating Simultaneously
- 9.3.3 White LED Flashlight Driver and Audio Amplifier Power Supply Operating Simultaneously
- 9.3.4 White LED Flashlight Driver and Audio Amplifier Power Supply Exclusive Operation
- 9.3.5 White LED Flashlight Driver and Auxiliary Lighting Zone Power Supply
- 9.3.6 TPS61300, Typical Application
- 9.3.7 TPS61301, Typical Application
- 9.3.8 TPS61305 Typical Application
- 9.3.9 TPS61306, Typical Application
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- YFF|20
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7 Specifications
7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(1)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voltage range(2) | AVIN, VOUT, SW, LED1, LED2, LED3, SCL, SDA, FLASH_SYNC, ENDCL, NRESET, ENVM, GPIO/PG, HC_SEL, Tx-MASK, TS, BAL | –0.3 | 7 | V |
| Current on GPIO/PG | ±25 | mA | ||
| Power dissipation | Internally limited | |||
| Operating ambient temperature(3), TA | –40 | 85 | °C | |
| Maxium operating junction temperature, TJ(MAX) | 150 | °C | ||
| Storage temperature, Tstg | –65 | 150 | °C | |
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, which do not imply functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under Recommended Operating Conditions. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
(2) All voltage values are with respect to network ground terminal.
(3) In applications where high power dissipation or poor package thermal resistance is present, the maximum ambient temperature may have to be derated. Maximum ambient temperature [TA(MAX)] is dependent on the maximum operating junction temperature [TJ(MAX)], the maximum power dissipation of the device in the application [PD(MAX)], and the junction-to-ambient thermal resistance of the part and package in the application (θJA), as given by the following equation: TA(MAX) = TJ(MAX) – (θJA × PD(MAX))
7.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human-body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001(1) | ±2000 | V |
| Charged-device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101(2) | ±500 | |||
(1) JEDEC document JEP155 states that 500-V HBM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
(2) JEDEC document JEP157 states that 250-V CDM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TJ | Operating junction temperature | –40 | 125 | °C |
7.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | TPS6130xx | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| YFF (DSBGA) | |||
| 20 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 70.9 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 0.4 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 11.4 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 1.9 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 11.2 | °C/W |
(1) For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see the Semiconductor and IC Package Thermal Metrics application report, SPRA953.
7.5 Electrical Characteristics
Unless otherwise noted the specification applies for VIN = 3.6 V over an operating junction temperature TJ = –40°C to 125°C; Circuit of (unless otherwise noted). Typical values are for TJ = 25°C.| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SUPPLY CURRENT | |||||||
| VIN | Input voltage range | 2.5 | 5.5 | V | |||
| IQ | Operating quiescent current into AVIN | IOUT = 0 mA, device not switching –40°C ≤ TJ ≤ 85°C |
590 | 700 | μA | ||
| IOUT(DC) = 0 mA, PWM operation VOUT = 4.95 V, voltage regulation mode |
11.3 | mA | |||||
| ISD | Shutdown current | HC_SEL = 0, –40°C ≤ TJ ≤ 85°C | 1 | 5 | μA | ||
| ISTBY | Standby current | HC_SEL = 1, storage capacitor balanced
–40°C ≤ TJ ≤ 85°C |
2 | 12 | μA | ||
| Precharge current | VOUT = 2.3 V, 2.5 V ≤ VIN ≤ 5.5 V | 150 | mA | ||||
| Precharge hysteresis (referred to VOUT) |
40 | 75 | mV | ||||
| VUVLO | Undervoltage lockout threshold (analog circuitry) |
VIN falling | 2.3 | 2.4 | V | ||
| OUTPUT | |||||||
| VOUT | Output voltage range | Current regulation mode | VIN | 5.5 | V | ||
| Voltage regulation mode | 3.825 | 5.7 | |||||
| Internal feedback voltage accuracy | 2.5 V ≤ VIN ≤ 4.8 V, –20°C ≤ TJ ≤ 125°C Boost mode, PWM voltage regulation |
–2% | 2% | ||||
| 0.85 | Power-save mode ripple voltage | IOUT = 10 mA | 0.015 × VOUT | VP–P | |||
| OVP | Output overvoltage protection | VOUT rising, 0000 ≤ OV[3:0] ≤ 0100 | 4.5 | 4.65 | 4.8 | V | |
| VOUT rising, 0101 ≤ OV[3:0] ≤ 1111 | 5.8 | 6 | 6.2 | ||||
| Output overvoltage protection hysteresis | VOUT falling, 0101 ≤ OV[3:0] ≤ 1111 | 0.15 | |||||
| POWER SWITCH | |||||||
| rDS(on) | Switch MOSFET ON-resistance | VOUT = VGS = 3.6 V | 90 | mΩ | |||
| Rectifier MOSFET ON-resistance | VOUT = VGS = 3.6 V | 135 | mΩ | ||||
| Ilkg(SW) | Leakage into SW | VOUT = 0 V, SW = 3.6 V, –40°C ≤ TJ ≤ 85°C | 0.3 | 4 | μA | ||
| Ilim | Rectifier valley current limit (open loop) |
VOUT = 4.95 V, HC_SEL = 0, –20°C ≤ TJ ≤ 85°C PWM operation, relative to selected ILIM |
–15% | 15% | |||
| OSCILLATOR | |||||||
| fOSC | Oscillator frequency | 1.92 | MHz | ||||
| fACC | Oscillator frequency | –10% | 7% | ||||
| THERMAL SHUTDOWN, HOT DIE DETECTOR | |||||||
| Thermal shutdown(1) | 140 | 160 | °C | ||||
| Thermal shutdown hysteresis(1) | 20 | °C | |||||
| Hot die detector accuracy(1) | –8 | 8 | °C | ||||
| LED CURRENT REGULATOR | |||||||
| LED1/3 current accuracy(1) | HC_SEL = 0 | 0.4 V ≤ VLED1/3 ≤ 2 V 00 ≤ DCLC13[1:0] ≤ 11, TJ = 85°C |
–10% | 10% | |||
| 0.4 V ≤ VLED1/3 ≤ 2 V 00 ≤ FC13[1:0] ≤ 11, TJ = 85°C |
–7.5% | 7.5% | |||||
| LED2 current accuracy(1) | 0.4 V ≤ VLED2 ≤ 2 V 000 ≤ DCLC2[2:0] ≤ 111, TJ = 85°C |
–10% | 10% | ||||
| 0.4 V ≤ VLED2 ≤ 2 V 000 ≤ FC2[2:0] ≤ 111, TJ = 85°C |
–7.5% | 7.5% | |||||
| LED1/3 current accuracy(1) | HC_SEL = 1 | 0.4 V ≤ VLED1/3 ≤ 2 V 00 ≤ DCLC13[1:0] ≤ 11, TJ = 85°C |
–10% | 10% | |||
| 0.4 V ≤ VLED1/3 ≤ 2 V 00 ≤ FC13[1:0] ≤ 11, TJ = 85°C |
–10% | 10% | |||||
| LED2 current accuracy(1) | 0.4 V ≤ VLED2 ≤ 2 V 000 ≤ DCLC2[2:0] ≤ 111, TJ = 85°C |
–10% | 10% | ||||
| 0.4 V ≤ VLED1/3 ≤ 2 V 000 ≤ FC2[2:0] ≤ 111, TJ = 85°C |
–10% | 10% | |||||
| LED1/3 current matching(1) | –10% | 10% | |||||
| LED1/2/3 current temperature coefficient | 0.05 | %/°C | |||||
| INDLED current accuracy | 1.5 V ≤ (VIN – VINDLED) ≤ 2.5 V 2.6 mA ≤ IINDLED ≤ 7.9 mA, TJ = 25°C |
–20% | 20% | ||||
| INDLED current temperature coefficient | 0.04 | %/°C | |||||
| VDO | LED1/2/3 sense voltage | ILED1–3 = full-scale current, HC_SEL = 0 | 400 | mV | |||
| LED1/2/3 sense voltage | ILED1–3 = full-scale current, HC_SEL = 1 | 400 | 450 | ||||
| VOUT dropout voltage | IOUT = –7.5 mA, device not switching | 220 | |||||
| LED1/2/3 input leakage current | VLED1/2/3 = VOUT = 5 V, –40°C ≤ TJ ≤ 85°C | 0.1 | 4 | μA | |||
| INDLED input leakage current | VINDLED = 0 V, –40°C ≤ TJ ≤ 85°C | 0.1 | 1 | μA | |||
| STORAGE CAPACITOR ACTIVE CELL BALANCING | |||||||
| Active cell balancing circuitry quiescent current into VOUT | HC_SEL = 1, storage capacitor balanced –40°C ≤ TJ ≤ 85°C |
1.7 | 6 | μA | |||
| Active cell balancing accuracy | (VOUT – BAL) vs BAL voltage difference Storage capacitor balanced HC_SEL = 1 VOUT = 5.7 V |
–100 | 100 | mV | |||
| BAL output drive capability | VOUT = 4.95 V, Sink and source current | ±10 | ±15 | mA | |||
| Active discharge resistor | HC_SEL = 0, device in shutdown mode VOUT to BAL and BAL to GND |
0.85 | 1.5 | kΩ | |||
| LED TEMPERATURE MONITORING (TPS61305, TPS61035A) | |||||||
| IO(TS) | Temperature Sense Current Source | Thermistor bias current | 23.8 | μA | |||
| TS Resistance (Warning Temperature) | LEDWARN bit = 1, TJ ≥ 25°C | 39 | 44.5 | 50 | kΩ | ||
| TS Resistance (Hot Temperature) | LEDHOT bit = 1, TJ ≥ 25°C | 12.5 | 14.5 | 16.5 | kΩ | ||
| SDA, SCL, GPIO/PG, ENVM, Tx-MASK, ENDCL, NRESET, FLASH_SYNC, HC_SEL | |||||||
| V(IH) | High-level input voltage | 1.2 | V | ||||
| V(IL) | Low-level input voltage | 0.4 | V | ||||
| V(OL) | Low-level output voltage (SDA) | IOL = 8 mA | 0.3 | V | |||
| Low-level output voltage (GPIO) | DIR = 1, IOL = 5 mA | 0.3 | |||||
| V(OH) | High-level output voltage (GPIO) | DIR = 1, GPIOTYPE = 0, IOH = 8 mA | VIN – 0.4 | V | |||
| I(LKG) | Logic input leakage current | Input connected to VIN or GND –40°C ≤ TJ ≤ 85°C |
0.01 | 0.1 | μA | ||
| RPD | ENVM pull-down resistance | ENVM ≤ 0.4 V | 350 | kΩ | |||
| ENDCL, NRESET pull-down resistance | ENDCL, NRESET ≤ 0.4 V | 350 | |||||
| FLASH_SYNC pull-down resistance | FLASH_SYNC ≤ 0.4 V | 350 | |||||
| Tx-MASK pull-down resistance | Tx-MASK ≤ 0.4 V | 350 | |||||
| HC_SEL pull-down resistance | HC_SEL ≤ 0.4 V | 350 | |||||
| C(IN) | SDA input capacitance | SDA = VIN or GND | 9 | pF | |||
| SCL input capacitance | SCL = VIN or GND | 4 | |||||
| GPIO/PG input capacitance | DIR = 0, GPIO/PG = VIN or GND | 9 | |||||
| ENVM input capacitance | ENVM = VIN or GND | 4 | |||||
| ENDCL input capacitance | ENDCL = VIN or GND | 3 | |||||
| HC_SEL input capacitance | HC_SEL = VIN or GND | 3.5 | |||||
| Tx-MASK input capacitance | Tx-MASK = VIN or GND | 4 | |||||
| FLASH_SYNC input capacitance | FLASH_SYNC = VIN or GND | 3 | |||||
| TIMING | |||||||
| tNRESET | Reset pulse width | 10 | μs | ||||
| Start-up time | From shutdown into DC light mode HC_SEL = 0, ILED = 100 mA |
1.4 | ms | ||||
| From shutdown into voltage mode through ENVM, HC_SEL = 0, IOUT = 0 mA | 550 | μs | |||||
| LED current settling time(2) triggered by a rising edge on FLASH_SYNC | MODE_CTRL[1:0] = 10, HC_SEL = 0 ILED2 = from 0 mA to 800 mA |
400 | μs | ||||
| MODE_CTRL[1:0] = 10, HC_SEL = 1 ILED2 = from 0 mA to 1800 mA |
16 | ||||||
| LED current settling time(2) triggered by Tx-MASK | MODE_CTRL[1:0] = 10, HC_SEL = 0 ILED2 = from 800 mA to 350 mA |
15 | μs | ||||
(1) Verified by characterization. Not tested in production.
(2) Settling time to ±15% of the target value.
7.6 Timing Requirements
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| f(SCL) | SCL clock frequency | Standard mode | 100 | kHz | |
| Fast mode | 400 | ||||
| High-speed mode (write operation), CB – 100 pF maximum |
3.4 | MHz | |||
| High-speed mode (read operation), CB – 100 pF maximum |
3.4 | ||||
| High-speed mode (write operation), CB – 400 pF maximum |
1.7 | ||||
| High-speed mode (read operation), CB – 400 pF maximum |
1.7 | ||||
| tBUF | Bus free time between a STOP and START condition | Standard mode | 4.7 | µs | |
| Fast mode | 1.3 | ||||
| tHD, tSTA | Hold time (repeated) START condition | Standard mode | 4 | µs | |
| Fast mode | 600 | ns | |||
| High-speed mode | 160 | ||||
| tLOW | LOW period of the SCL clock | Standard mode | 4.7 | µs | |
| Fast mode | 1.3 | ||||
| High-speed mode, CB – 100 pF maximum | 160 | ns | |||
| High-speed mode, CB – 400 pF maximum | 320 | ||||
| tHIGH | HIGH period of the SCL clock | Standard mode | 4 | µs | |
| Fast mode | 600 | ns | |||
| High-speed mode, CB – 100 pF maximum | 60 | ||||
| High-speed mode, CB – 400 pF maximum | 120 | ||||
| tSU, tSTA | Setup time for a repeated START condition | Standard mode | 4.7 | µs | |
| Fast mode | 600 | ns | |||
| High-speed mode | 160 | ||||
| tSU, tDAT | Data setup time | Standard mode | 250 | ns | |
| Fast mode | 100 | ||||
| High-speed mode | 10 | ||||
| tHD, tDAT | Data hold time | Standard mode | 0 | 3.45 | µs |
| Fast mode | 0 | 0.9 | |||
| High-speed mode, CB – 100 pF maximum | 0 | 70 | ns | ||
| High-speed mode, CB – 400 pF maximum | 0 | 150 | |||
| tRCL | Rise time of SCL signal | Standard mode | 20 + 0.1 CB | 1000 | ns |
| Fast mode | 20 + 0.1 CB | 300 | |||
| High-speed mode, CB – 100 pF maximum | 10 | 40 | |||
| High-speed mode, CB – 400 pF maximum | 20 | 80 | |||
| tRCL1 | Rise time of SCL signal after a repeated START condition and after an acknowledge BIT | Standard mode | 20 + 0.1 CB | 1000 | ns |
| Fast mode | 20 + 0.1 CB | 300 | |||
| High-speed mode, CB – 100 pF maximum | 10 | 80 | |||
| High-speed mode, CB – 400 pF maximum | 20 | 160 | |||
| tFCL | Fall time of SCL signal | Standard mode | 20 + 0.1 CB | 300 | ns |
| Fast mode | 20 + 0.1 CB | 300 | |||
| High-speed mode, CB – 100 pF maximum | 10 | 40 | |||
| High-speed mode, CB – 400 pF maximum | 20 | 80 | |||
| tRDA | Rise time of SDA signal | Standard mode | 20 + 0.1 CB | 1000 | ns |
| Fast mode | 20 + 0.1 CB | 300 | |||
| High-speed mode, CB – 100 pF maximum | 10 | 80 | |||
| High-speed mode, CB – 400 pF maximum | 20 | 160 | |||
| tFDA | Fall time of SDA signal | Standard mode | 20 + 0.1 CB | 300 | ns |
| Fast mode | 20 + 0.1 CB | 300 | |||
| High-speed mode, CB – 100 pF maximum | 10 | 80 | |||
| High-speed mode, CB – 400 pF maximum | 20 | 160 | |||
| tSU, tSTO | Setup time for STOP condition | Standard mode | 4 | µs | |
| Fast mode | 600 | ns | |||
| High-speed mode | 160 | ||||
| CB | Capacitive load for SDA and SCL | 400 | pF | ||
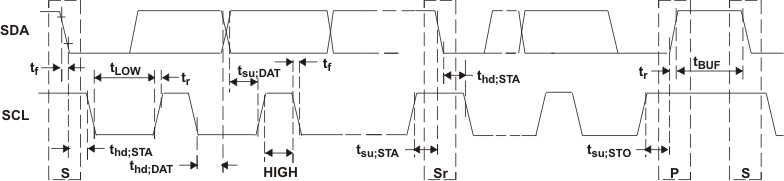 Figure 1. Serial Interface Timing for F/S-Mode
Figure 1. Serial Interface Timing for F/S-Mode
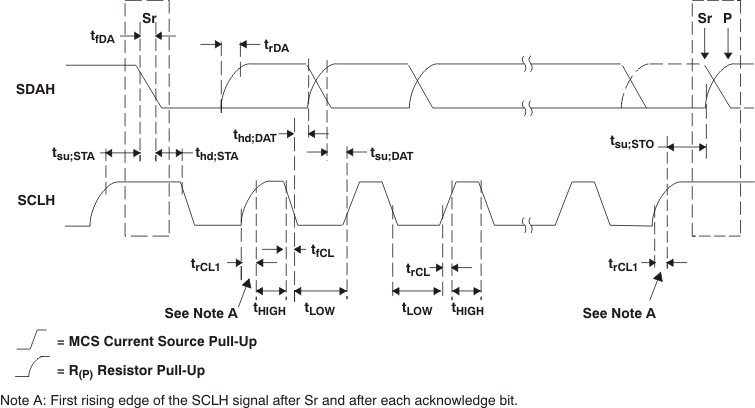 Figure 2. Serial Interface Timing for HS-Mode
Figure 2. Serial Interface Timing for HS-Mode
7.7 Typical Characteristics
| TABLE OF GRAPHS | FIGURE NO. | |
|---|---|---|
| LED Power Efficiency | vs Input Voltage | Figure 3, Figure 4 |
| DC Input Current | vs Input Voltage | Figure 5 |
| LED Current | vs LED Pin Headroom Voltage | Figure 6, Figure 7, Figure 8 |
| LED Current | vs LED Current Digital Code | Figure 9, Figure 10, Figure 11, Figure 12 |
| INDLED Current | vs LED Pin Headroom Voltage | Figure 13 |
| Voltage Mode Efficiency | vs Output Current | Figure 14, Figure 15 |
| DC Output Voltage | vs Output Current | Figure 16, Figure 17 |
| Maximum Output Current | vs Input Voltage | Figure 18 |
| DC preCharge Current | vs Differential Input-Output Voltage | Figure 19, Figure 20 |
| Valley Current Limit | Figure 21, Figure 22 | |
| Balancing Current | vs Balance Pin Voltage | Figure 23 |
| Supply Current | vs Input Voltage | Figure 24 |
| Standby Current | vs Ambient Temperature | Figure 25 |
| Temperature Detection Threshold | Figure 26, Figure 27 | |
| Junction Temperature | vs Port Voltage | Figure 28 |
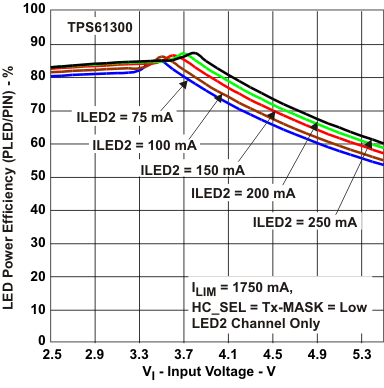 Figure 3. LED Power Efficiency vs Input Voltage
Figure 3. LED Power Efficiency vs Input Voltage
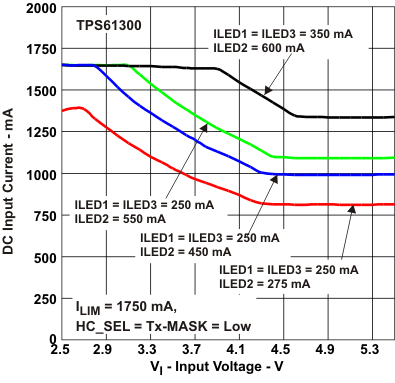 Figure 5. DC Input Current vs Input Voltage
Figure 5. DC Input Current vs Input Voltage
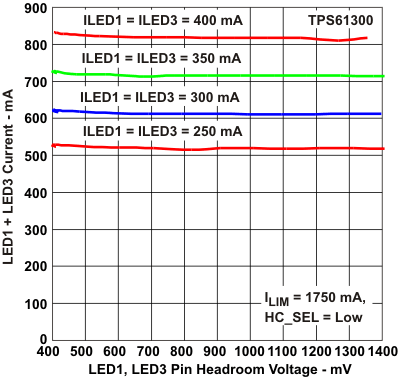 Figure 7. LED1+LED3 Current vs
Figure 7. LED1+LED3 Current vsLED1+LED3 Pin Headroom Voltage (HC_SEL = 0)
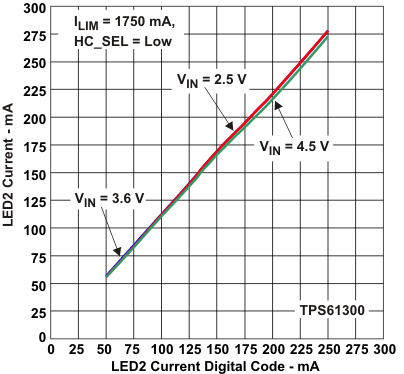 Figure 9. LED2 Current vs
Figure 9. LED2 Current vsLED2 Current Digital Code (HC_SEL = 0)
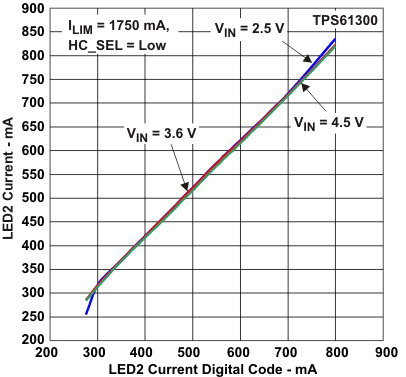 Figure 11. LED2 Current vs
Figure 11. LED2 Current vsLED2 Current Digital Code (HC_SEL = 0)
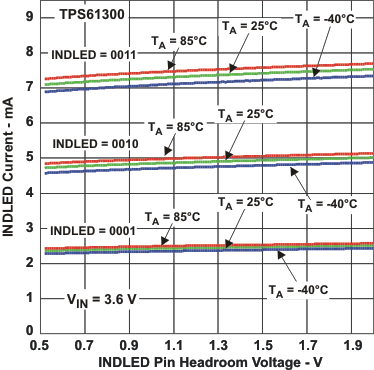 Figure 13. INDLED Current vs
Figure 13. INDLED Current vsINDLED Pin Headroom Voltage
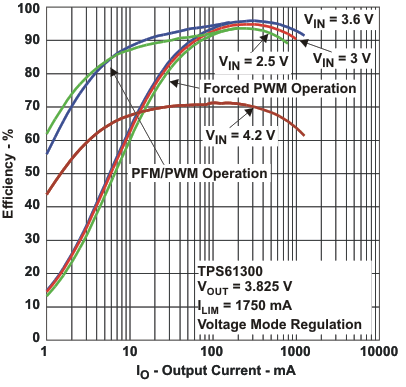 Figure 15. Efficiency vs Output Current
Figure 15. Efficiency vs Output Current
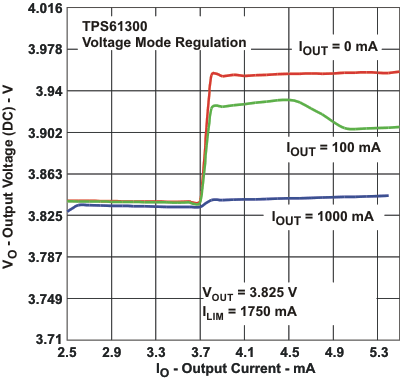 Figure 17. DC Output Voltage vs Load Current
Figure 17. DC Output Voltage vs Load Current
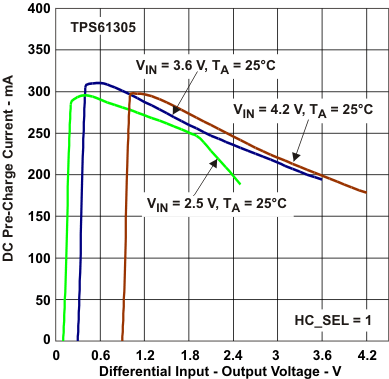 Figure 19. DC Precharge Current vs Differential Input‑Output Voltage (HC_SEL = 1)
Figure 19. DC Precharge Current vs Differential Input‑Output Voltage (HC_SEL = 1)
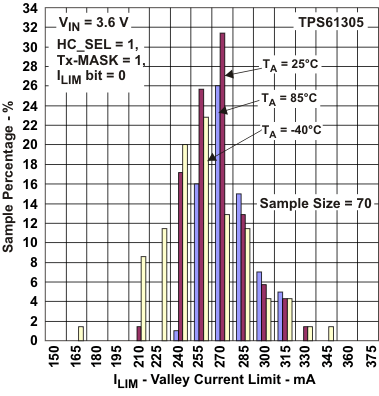 Figure 21. Valley Current Limit (HC_SEL = 1)
Figure 21. Valley Current Limit (HC_SEL = 1)
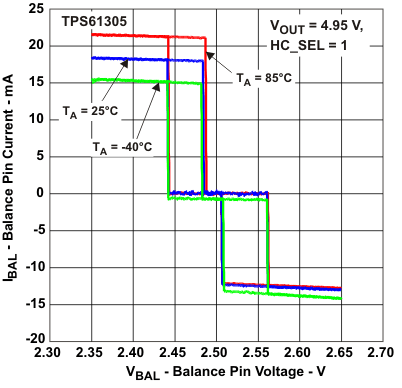 Figure 23. Balancing Current vs Balance Pin Voltage
Figure 23. Balancing Current vs Balance Pin Voltage
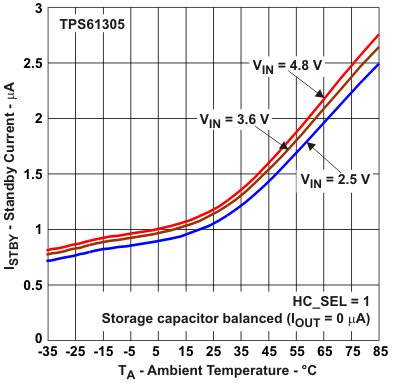 Figure 25. Standby Current vs Ambient Temperature (HC_SEL = 1)
Figure 25. Standby Current vs Ambient Temperature (HC_SEL = 1)
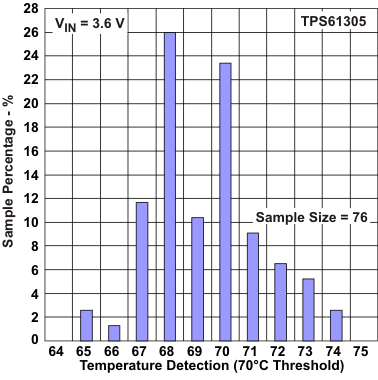 Figure 27. Temperature Detection Threshold
Figure 27. Temperature Detection Threshold
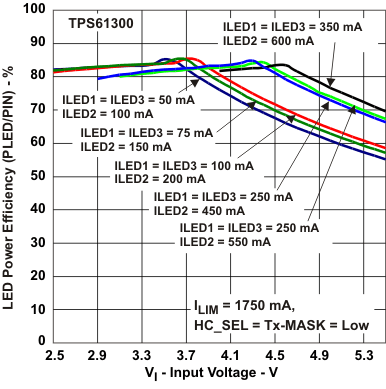 Figure 4. LED Power Efficiency vs Input Voltage
Figure 4. LED Power Efficiency vs Input Voltage
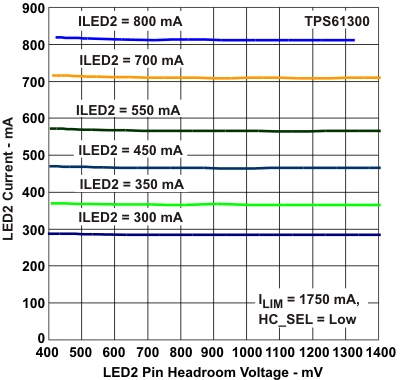 Figure 6. LED2 Current vs LED2 Pin Headroom Voltage
Figure 6. LED2 Current vs LED2 Pin Headroom Voltage(HC_SEL = 0)
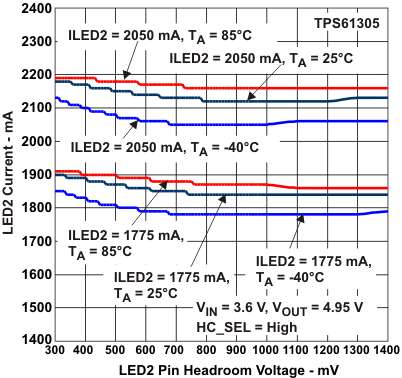 Figure 8. LED2 Current vs
Figure 8. LED2 Current vsLED2 Pin Headroom Voltage (HC_SEL = 1)
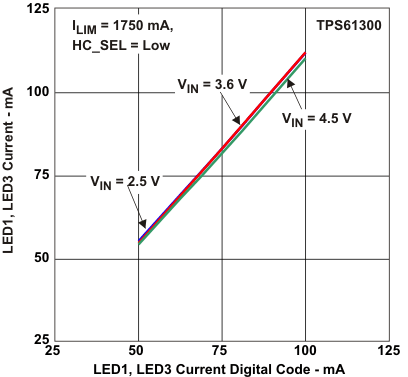 Figure 10. LED1, LED3 Current vs
Figure 10. LED1, LED3 Current vsLED1, LED3 Current Digital Code (HC_SEL = 0)
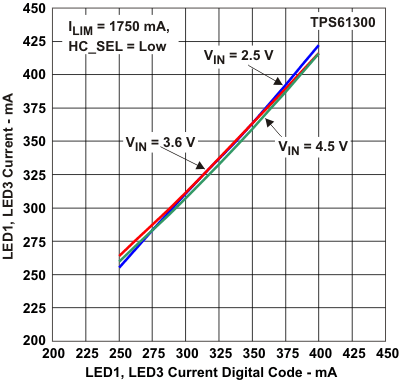 Figure 12. LED1, LED3 Current vs
Figure 12. LED1, LED3 Current vsLED1, LED3 Current Digital Code (HC_SEL = 0)
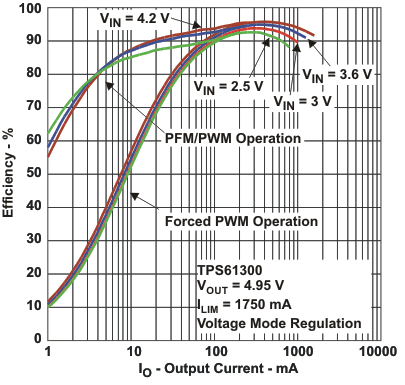 Figure 14. Efficiency vs Output Current
Figure 14. Efficiency vs Output Current
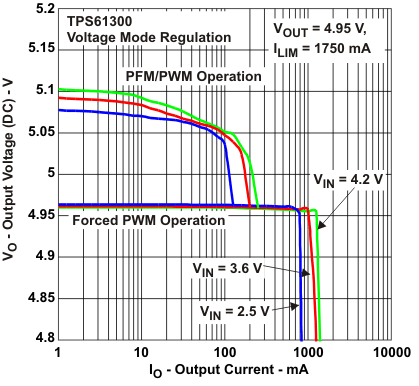 Figure 16. DC Output Voltage vs Load Current
Figure 16. DC Output Voltage vs Load Current
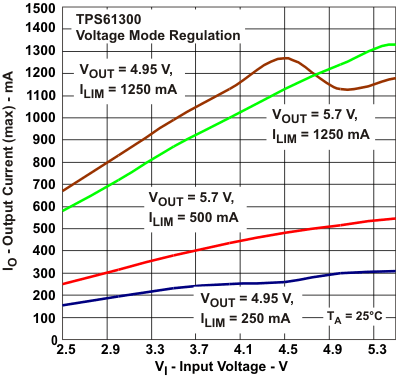 Figure 18. Maximum Output Current vs Input Voltage
Figure 18. Maximum Output Current vs Input Voltage
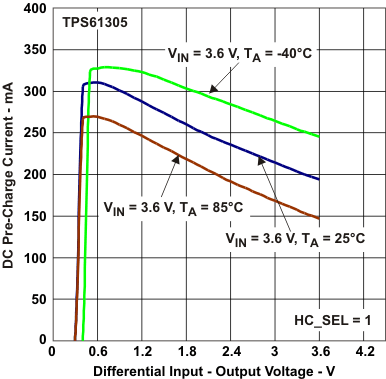 Figure 20. DC Precharge Current vs Differential Input‑Output Voltage (HC_SEL = 1)
Figure 20. DC Precharge Current vs Differential Input‑Output Voltage (HC_SEL = 1)
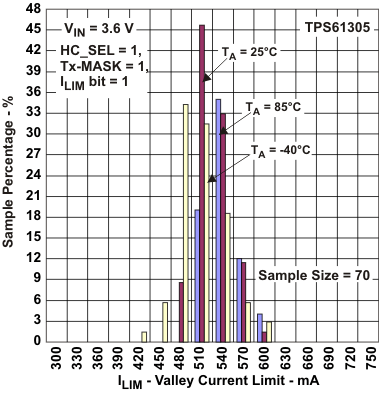 Figure 22. Valley Current Limit (HC_SEL = 1)
Figure 22. Valley Current Limit (HC_SEL = 1)
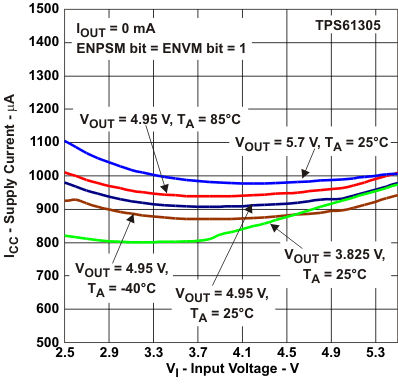 Figure 24. Supply Current vs Input Voltage
Figure 24. Supply Current vs Input Voltage
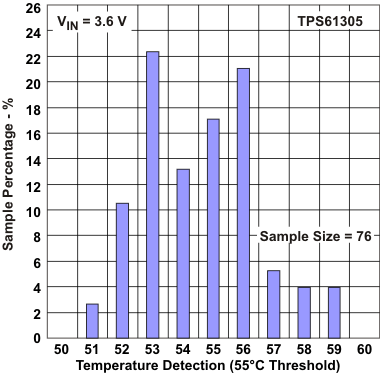 Figure 26. Temperature Detection Threshold
Figure 26. Temperature Detection Threshold
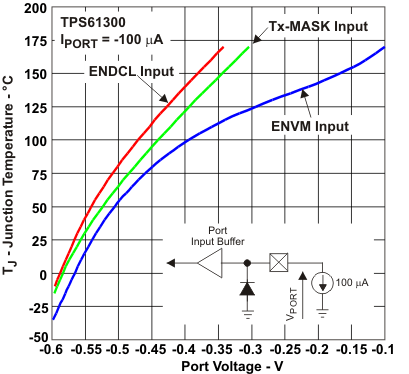 Figure 28. Junction Temperature vs Port Voltage
Figure 28. Junction Temperature vs Port Voltage