SLVSEE7B June 2018 – January 2021 TPS61372
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Custom Design With WEBENCH® Tools
- 8.2.2.2 Setting the Output Voltage
- 8.2.2.3 Selecting the Inductor
- 8.2.2.4 Selecting the Output Capacitors
- 8.2.2.5 Selecting the Input Capacitors
- 8.2.2.6 Loop Stability and Compensation
- 8.2.2.7 Loop Compensation Design Steps
- 8.2.2.8 Selecting the Bootstrap Capacitor
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- YKB|16
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.2.2.2 Setting the Output Voltage
The output voltage of the TPS61372 is externally adjustable using a resistor divider network. The relationship between the output voltage and the resistor divider is given by Equation 1.
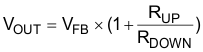
where
- VOUT is the output voltage
- RUP is the top divider resistor
- RDOWN is the bottom divider resistor
Choose RDOWN to be approximately 100 kΩ. Slightly increasing or decreasing RDOWN can result in closer output voltage matching when using standard value resistors. In this design, RDOWN = 100 kΩ and RUP = 1.909 MΩ (1 MΩ + 909 kΩ) , resulting in an output voltage of 12 V.
For the best accuracy, TI recommends RDOWN to be around 100 kΩ to ensure that the current following through RDOWN is at least 100 times larger than FB pin leakage current. Changing RDOWN towards the lower value increases the robustness against noise injection. Changing RDOWN towards the higher values reduces the quiescent current for achieving higher efficiency at the light load currents.