VIN = 12 V, VOUT = 3.3 V, TA = 25°C, (unless otherwise noted)
VIN = 12 V, VOUT = 3.3 V, TA = 25°C, (unless otherwise noted) 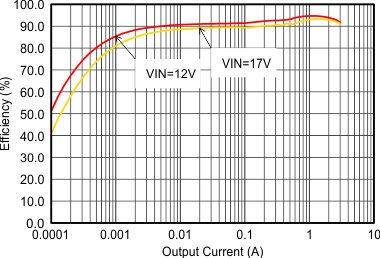 Figure 9-4 Efficiency with 1.25 MHz. VIN = 12 V, VOUT = 3.3 V, TA = 25°C, (unless otherwise noted)
Figure 9-4 Efficiency with 1.25 MHz. VIN = 12 V, VOUT = 3.3 V, TA = 25°C, (unless otherwise noted) 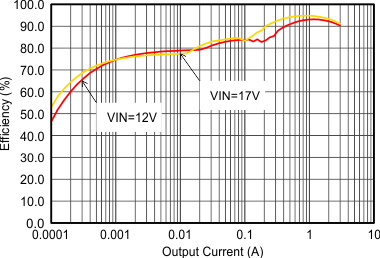 Figure 9-6 Efficiency with 2.5 MHz
Figure 9-6 Efficiency with 2.5 MHz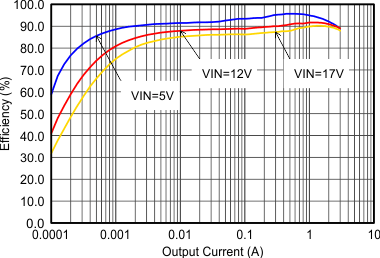 Figure 9-8 Efficiency with 1.25 MHz
Figure 9-8 Efficiency with 1.25 MHz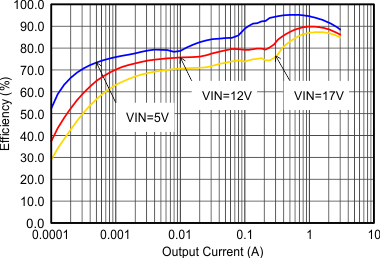 Figure 9-10 Efficiency with 2.5 MHz
Figure 9-10 Efficiency with 2.5 MHz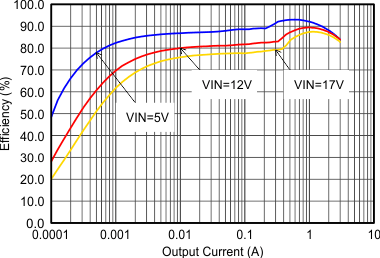 Figure 9-12 Efficiency with 1.25 MHz
Figure 9-12 Efficiency with 1.25 MHz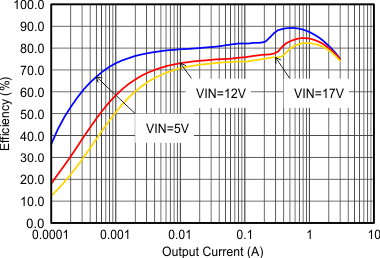 Figure 9-14 Efficiency with 1.25 MHz
Figure 9-14 Efficiency with 1.25 MHz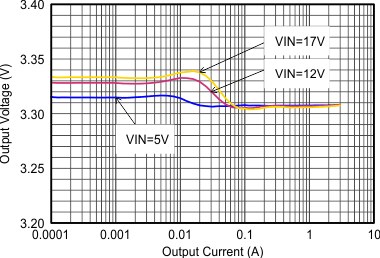 Figure 9-16 Output Voltage Accuracy (Load Regulation)
Figure 9-16 Output Voltage Accuracy (Load Regulation)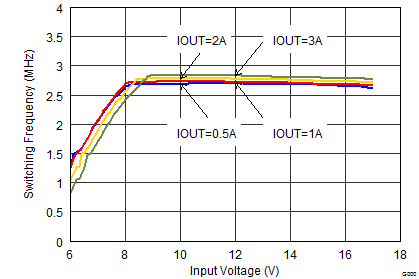 Figure 9-18 Switching Frequency vs Input Voltage
Figure 9-18 Switching Frequency vs Input Voltage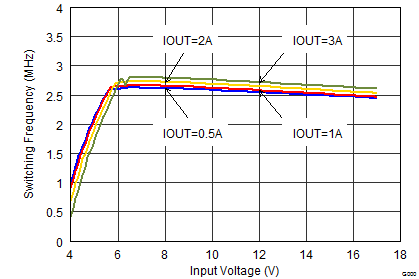 Figure 9-20 Switching Frequency vs Input Voltage
Figure 9-20 Switching Frequency vs Input Voltage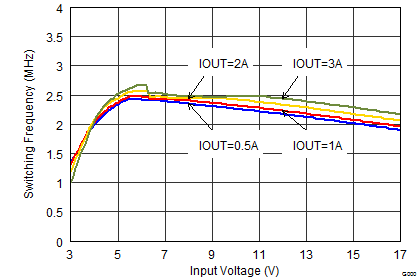 Figure 9-22 Switching Frequency vs Input Voltage
Figure 9-22 Switching Frequency vs Input Voltage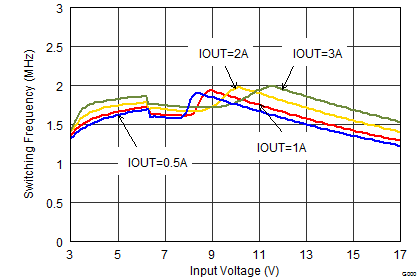 Figure 9-24 Switching Frequency vs Input Voltage
Figure 9-24 Switching Frequency vs Input Voltage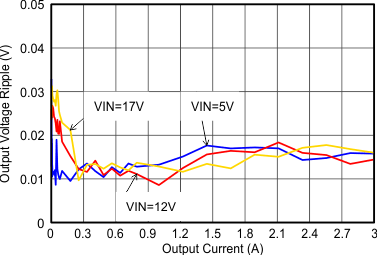 Figure 9-26 Output Voltage Ripple
Figure 9-26 Output Voltage Ripple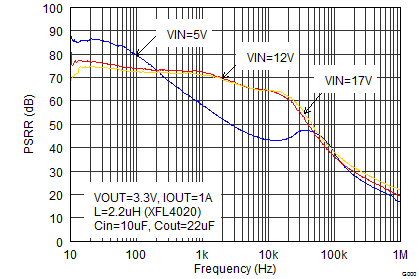 Figure 9-28 Power Supply Rejection Ratio
Figure 9-28 Power Supply Rejection Ratio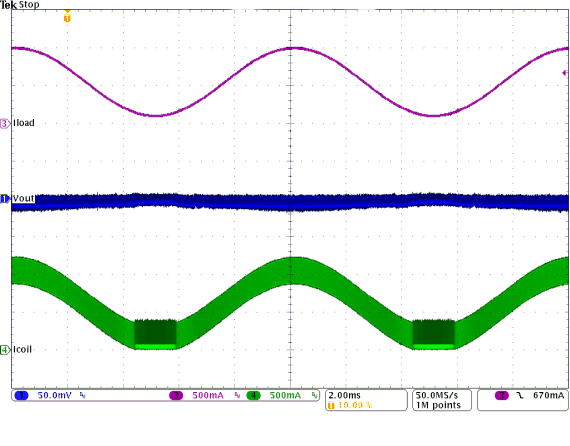
| VIN = 12 | VOUT = 3.3 V with 50 mV/Div |
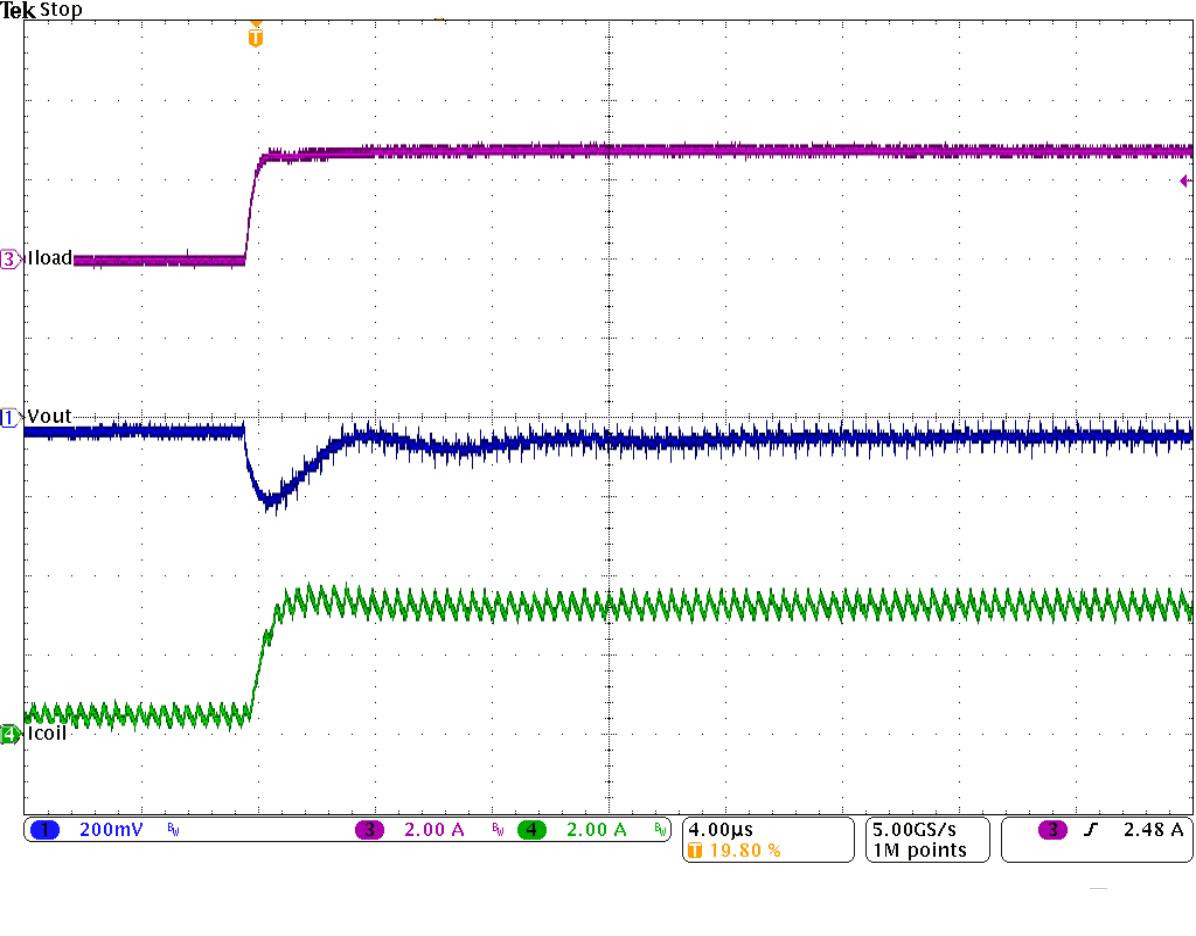 Figure 9-32 Load Transient Response of Figure 9-31, Rising Edge
Figure 9-32 Load Transient Response of Figure 9-31, Rising Edge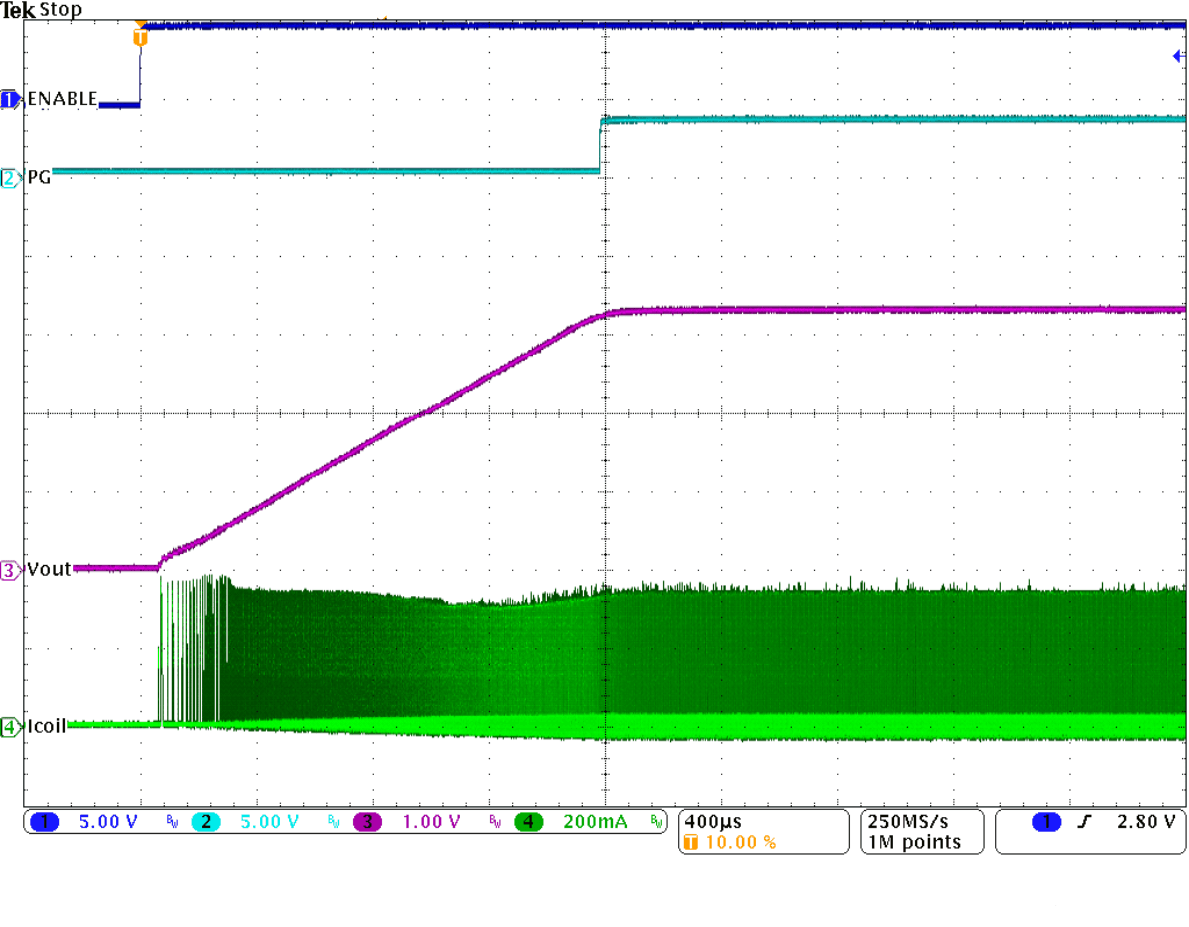 Figure 9-34 Start-Up Into 100
mA
Figure 9-34 Start-Up Into 100
mA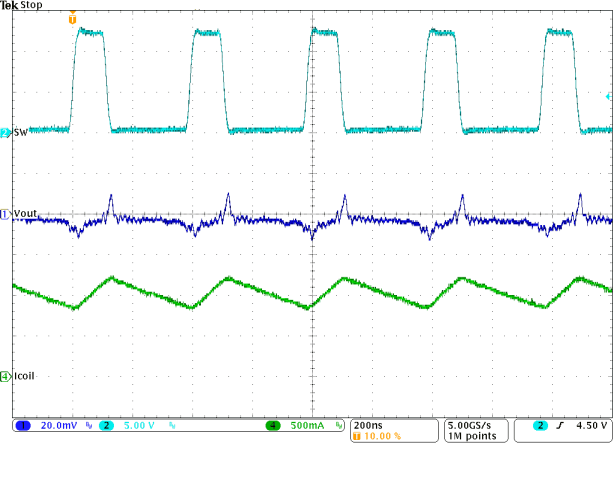 Figure 9-36 Typical Operation In PWM Mode
Figure 9-36 Typical Operation In PWM Mode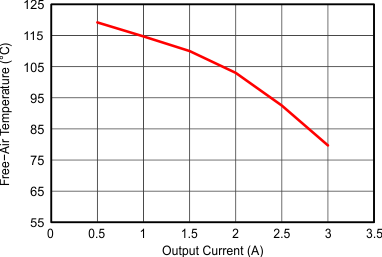
| FSW = 2.5 MHz | | TPS62130EVM |
| L = 2.2 µH (XFL4020) |
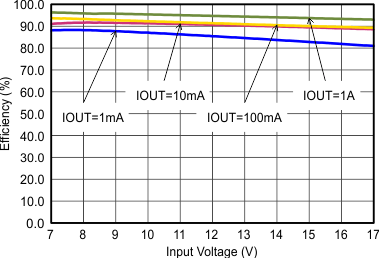 Figure 9-5 Efficiency with 1.25 MHz
Figure 9-5 Efficiency with 1.25 MHz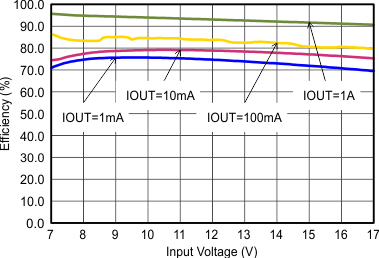 Figure 9-7 Efficiency with 2.5 MHz
Figure 9-7 Efficiency with 2.5 MHz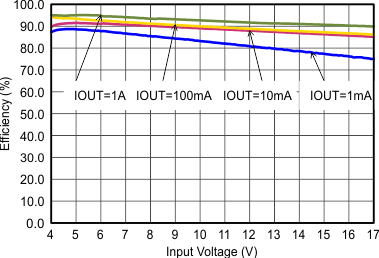 Figure 9-9 Efficiency with 1.25 MHz
Figure 9-9 Efficiency with 1.25 MHz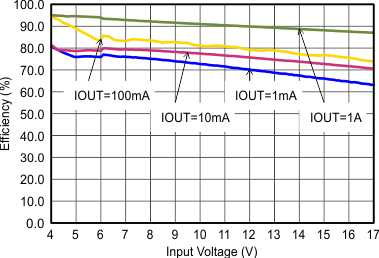 Figure 9-11 Efficiency with 2.5 MHz
Figure 9-11 Efficiency with 2.5 MHz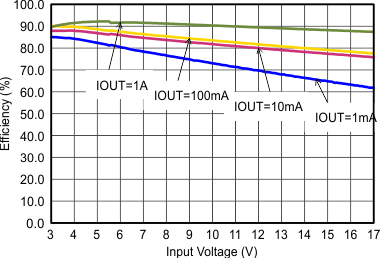 Figure 9-13 Efficiency with 1.25 MHz
Figure 9-13 Efficiency with 1.25 MHz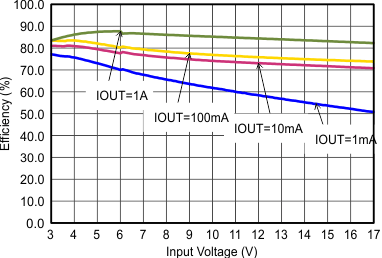 Figure 9-15 Efficiency with 1.25 MHz
Figure 9-15 Efficiency with 1.25 MHz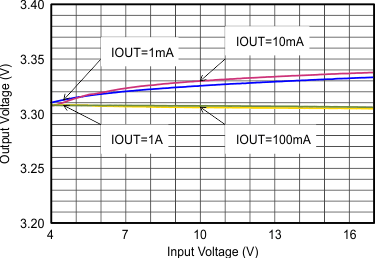 Figure 9-17 Output Voltage Accuracy (Line Regulation)
Figure 9-17 Output Voltage Accuracy (Line Regulation)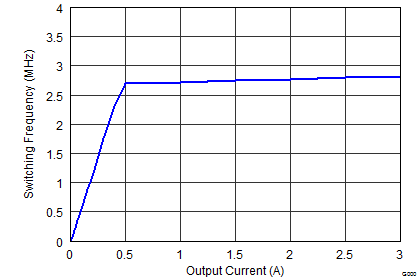 Figure 9-19 Switching Frequency vs Output Current
Figure 9-19 Switching Frequency vs Output Current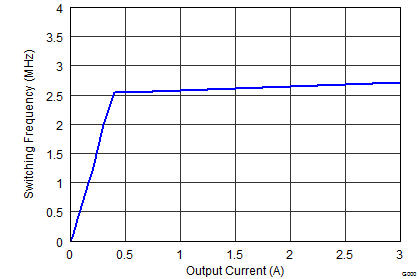 Figure 9-21 Switching Frequency vs Output Current,
Figure 9-21 Switching Frequency vs Output Current,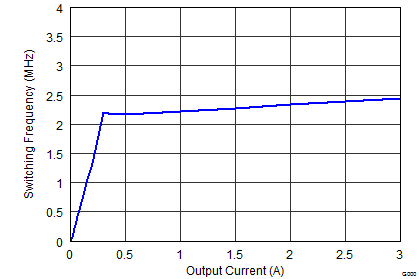 Figure 9-23 Switching Frequency vs Output Current
Figure 9-23 Switching Frequency vs Output Current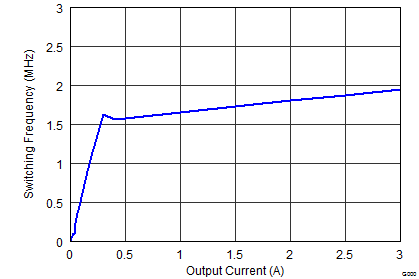 Figure 9-25 Switching Frequency vs Output Current
Figure 9-25 Switching Frequency vs Output Current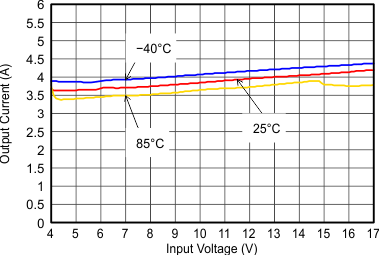 Figure 9-27 Maximum Output Current
Figure 9-27 Maximum Output Current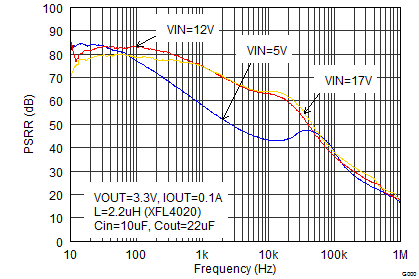 Figure 9-29 Power Supply Rejection Ratio
Figure 9-29 Power Supply Rejection Ratio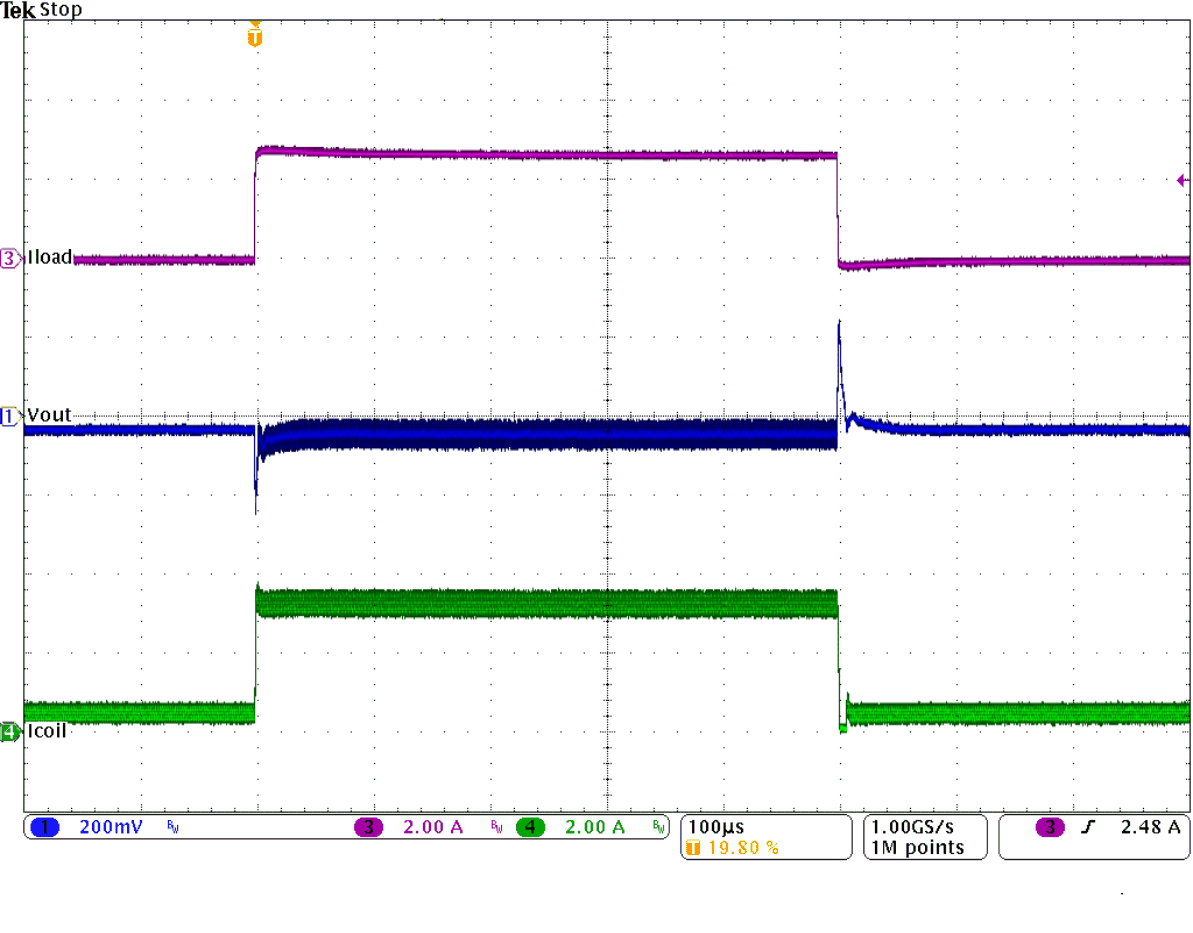 Figure 9-31 Load Transient Response
Figure 9-31 Load Transient Response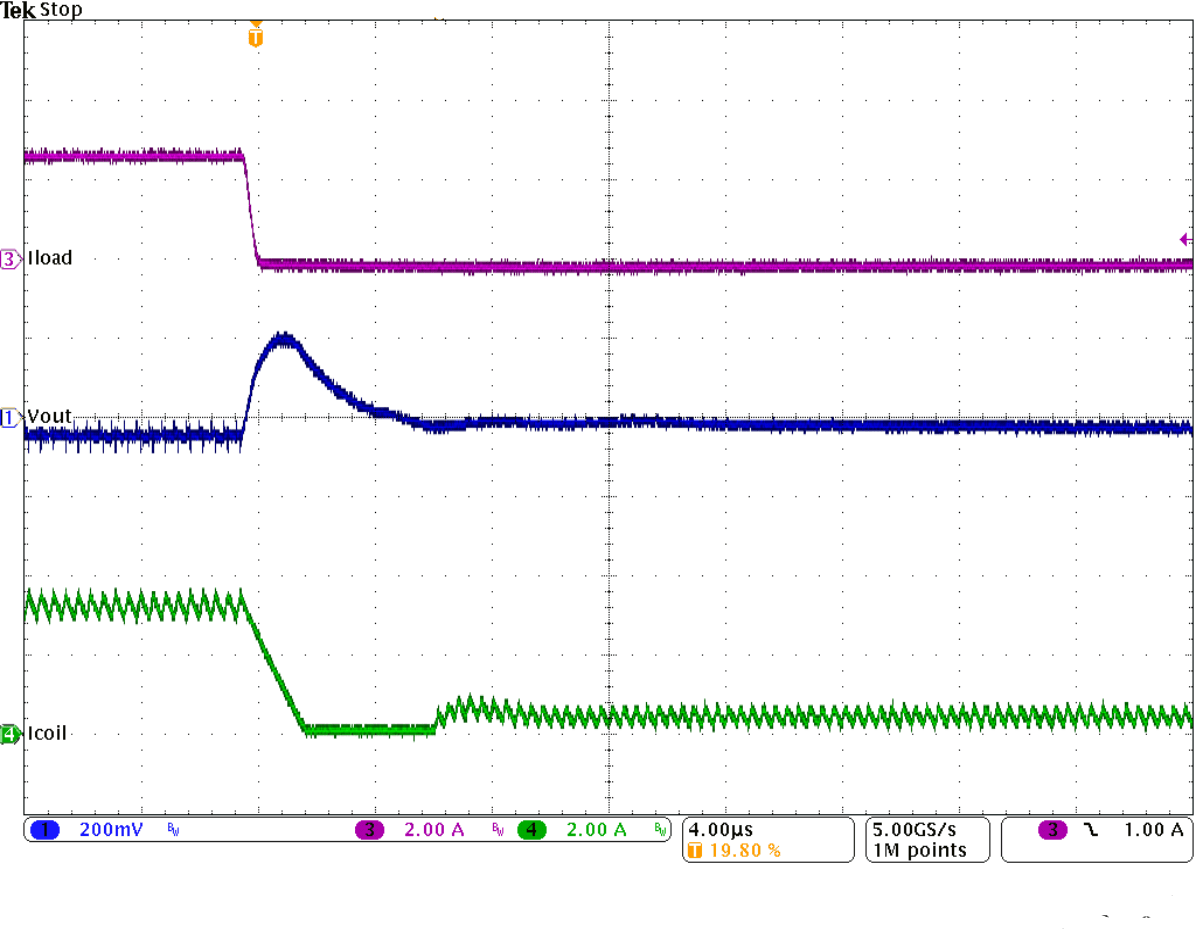 Figure 9-33 Load Transient Response of Figure 9-31, Falling Edge
Figure 9-33 Load Transient Response of Figure 9-31, Falling Edge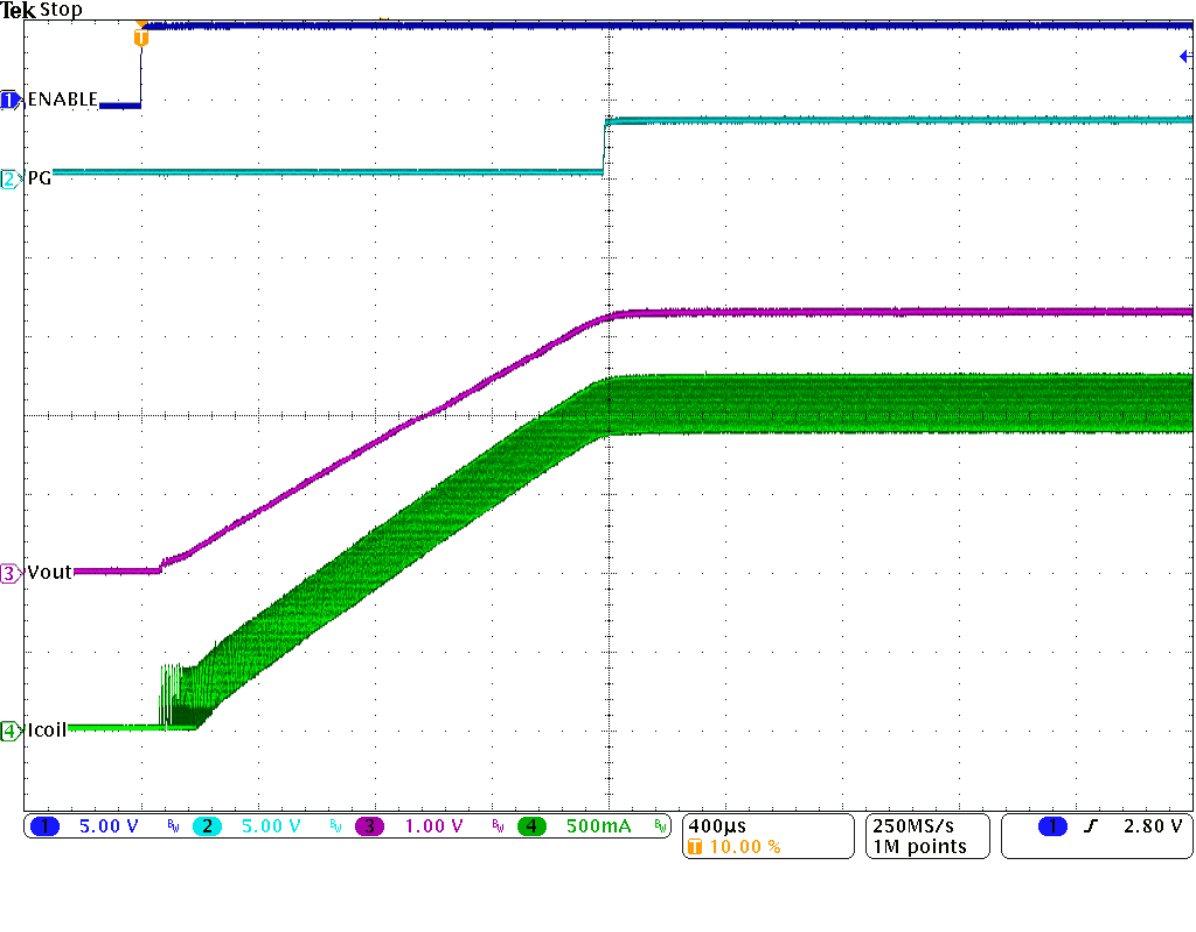 Figure 9-35 Start-Up Into 3 A
Figure 9-35 Start-Up Into 3 A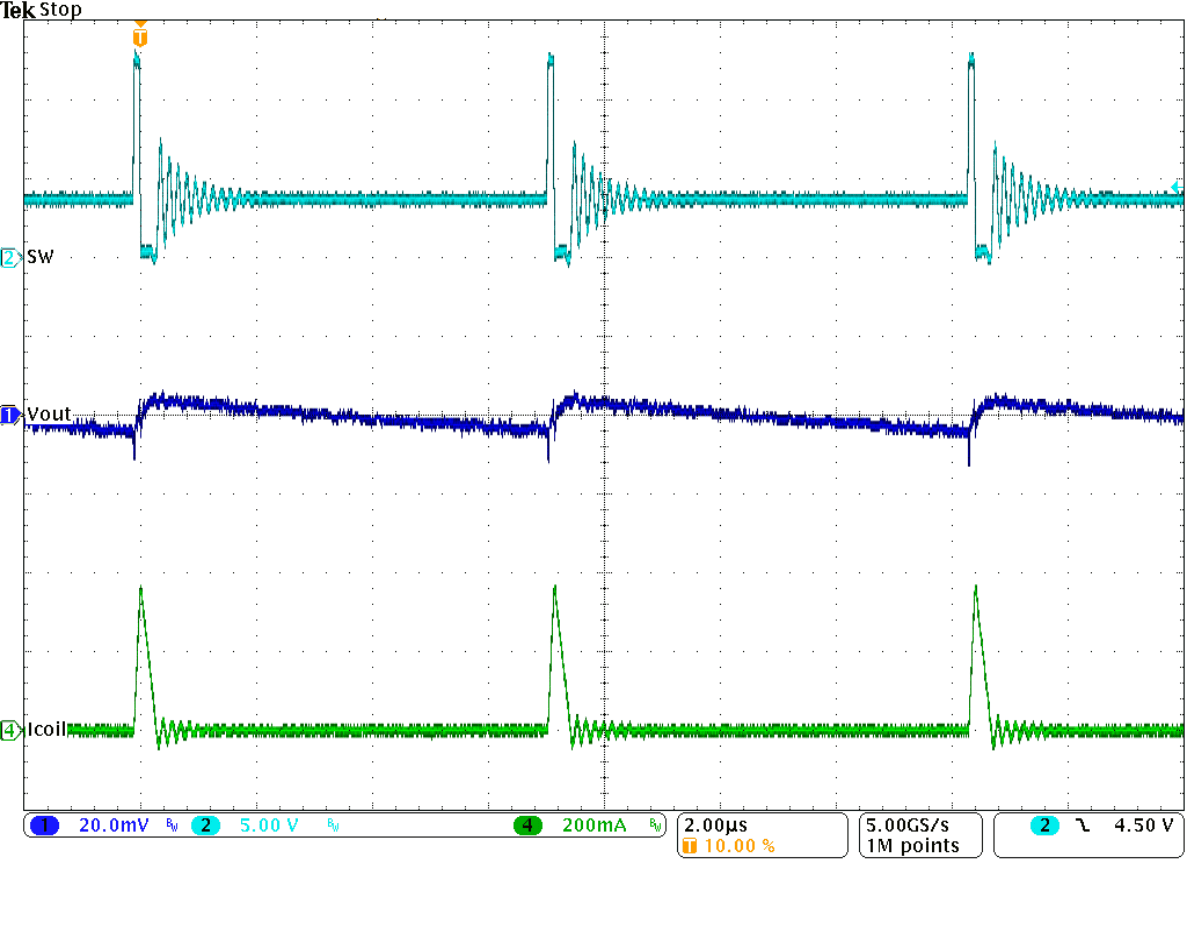 Figure 9-37 Typical Operation In Power Save Mode
Figure 9-37 Typical Operation In Power Save Mode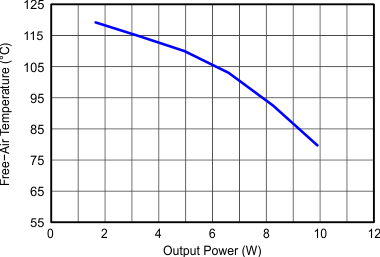
| FSW = 2.5 MHz | | TPS62130EVM |
| L = 2.2 µH (XFL4020) |







 Figure 9-16 Output Voltage Accuracy (Load Regulation)
Figure 9-16 Output Voltage Accuracy (Load Regulation)



 Figure 9-26 Output Voltage Ripple
Figure 9-26 Output Voltage Ripple

 Figure 9-32 Load Transient Response of Figure 9-31, Rising Edge
Figure 9-32 Load Transient Response of Figure 9-31, Rising Edge Figure 9-34 Start-Up Into 100
mA
Figure 9-34 Start-Up Into 100
mA







 Figure 9-17 Output Voltage Accuracy (Line Regulation)
Figure 9-17 Output Voltage Accuracy (Line Regulation)



 Figure 9-27 Maximum Output Current
Figure 9-27 Maximum Output Current

 Figure 9-33 Load Transient Response of Figure 9-31, Falling Edge
Figure 9-33 Load Transient Response of Figure 9-31, Falling Edge Figure 9-35 Start-Up Into 3 A
Figure 9-35 Start-Up Into 3 A
