SWCS138F June 2017 – October 2024 TPS650864
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Device Comparison Table
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Electrical Characteristics: Total Current Consumption
- 6.6 Electrical Characteristics: Reference and Monitoring System
- 6.7 Electrical Characteristics: Buck Controllers
- 6.8 Electrical Characteristics: Synchronous Buck Converters
- 6.9 Electrical Characteristics: LDOs
- 6.10 Electrical Characteristics: Load Switches
- 6.11 Digital Signals: I2C Interface
- 6.12 Digital Input Signals (CTLx)
- 6.13 Digital Output Signals (IRQB, GPOx)
- 6.14 Timing Requirements
- 6.15 Switching Characteristics
- 6.16 Typical Characteristics
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3 TPS6508640 Design and Settings
- 7.4 TPS65086401 Design and Settings
- 7.5 TPS6508641 Design and Settings
- 7.6 TPS65086470 Design and Settings
- 7.7 SMPS Voltage Regulators
- 7.8 LDOs and Load Switches
- 7.9 Power Goods (PGOOD or PG) and GPOs
- 7.10 Power Sequencing and VR Control
- 7.11 Device Functional Modes
- 7.12 I2C Interface
- 7.13
Register Maps
- 7.13.1 Register Map Summary
- 7.13.2 DEVICEID1: 1st PMIC Device and Revision ID Register (offset = 00h) [reset = X]
- 7.13.3 DEVICEID2: 2nd PMIC Device and Revision ID Register (offset = 01h) [reset = X]
- 7.13.4 IRQ: PMIC Interrupt Register (offset = 02h) [reset = 0000 0000]
- 7.13.5 IRQ_MASK: PMIC Interrupt Mask Register (offset = 03h) [reset = 1111 1111]
- 7.13.6 PMICSTAT: PMIC Status Register (offset = 04h) [reset = 0000 0000]
- 7.13.7 SHUTDNSRC: PMIC Shut-Down Event Register (offset = 05h) [reset = 0000 0000]
- 7.13.8 BUCK1CTRL: BUCK1 Control Register (offset = 20h) [reset = X]
- 7.13.9 BUCK2CTRL: BUCK2 Control Register (offset = 21h) [reset = X]
- 7.13.10 BUCK3DECAY: BUCK3 Decay Control Register (offset = 22h) [reset = X]
- 7.13.11 BUCK3VID: BUCK3 VID Register (offset = 23h) [reset = X]
- 7.13.12 BUCK3SLPCTRL: BUCK3 Sleep Control VID Register (offset = 24h) [reset = X]
- 7.13.13 BUCK4CTRL: BUCK4 Control Register (offset = 25h) [reset = X]
- 7.13.14 BUCK5CTRL: BUCK5 Control Register (offset = 26h) [reset = X]
- 7.13.15 BUCK6CTRL: BUCK6 Control Register (offset = 27h) [reset = X]
- 7.13.16 LDOA2CTRL: LDOA2 Control Register (offset = 28h) [reset = X]
- 7.13.17 LDOA3CTRL: LDOA3 Control Register (offset = 29h) [reset = X]
- 7.13.18 DISCHCTRL1: 1st Discharge Control Register (offset = 40h) [reset = X]
- 7.13.19 DISCHCTRL2: 2nd Discharge Control Register (offset = 41h) [reset = X]
- 7.13.20 DISCHCTRL3: 3rd Discharge Control Register (offset = 42h) [reset = X]
- 7.13.21 PG_DELAY1: 1st Power Good Delay Register (offset = 43h) [reset = X]
- 7.13.22 FORCESHUTDN: Force Emergency Shutdown Control Register (offset = 91h) [reset = 0000 0000]
- 7.13.23 BUCK1SLPCTRL: BUCK1 Sleep Control Register (offset = 92h) [reset = X]
- 7.13.24 BUCK2SLPCTRL: BUCK2 Sleep Control Register (offset = 93h) [reset = X]
- 7.13.25 BUCK4VID: BUCK4 VID Register (offset = 94h) [reset = X]
- 7.13.26 BUCK4SLPVID: BUCK4 Sleep VID Register (offset = 95h) [reset = X]
- 7.13.27 BUCK5VID: BUCK5 VID Register (offset = 96h) [reset = X]
- 7.13.28 BUCK5SLPVID: BUCK5 Sleep VID Register (offset = 97h) [reset = X]
- 7.13.29 BUCK6VID: BUCK6 VID Register (offset = 98h) [reset = X]
- 7.13.30 BUCK6SLPVID: BUCK6 Sleep VID Register (offset = 99h) [reset = X]
- 7.13.31 LDOA2VID: LDOA2 VID Register (offset = 9Ah) [reset = X]
- 7.13.32 LDOA3VID: LDOA3 VID Register (offset = 9Bh) [reset = X]
- 7.13.33 BUCK123CTRL: BUCK1-3 Control Register (offset = 9Ch) [reset = X]
- 7.13.34 PG_DELAY2: 2nd Power Good Delay Register (offset = 9Dh) [reset = X]
- 7.13.35 SWVTT_DIS: SWVTT Disable Register (offset = 9Fh) [reset = X]
- 7.13.36 I2C_RAIL_EN1: 1st VR Pin Enable Override Register (offset = A0h) [reset = X]
- 7.13.37 I2C_RAIL_EN2/GPOCTRL: 2nd VR Pin Enable Override and GPO Control Register (offset = A1h) [reset = X]
- 7.13.38 PWR_FAULT_MASK1: 1st VR Power Fault Mask Register (offset = A2h) [reset = X]
- 7.13.39 PWR_FAULT_MASK2: 2nd VR Power Fault Mask Register (offset = A3h) [reset = X]
- 7.13.40 GPO1PG_CTRL1: 1st GPO1 PG Control Register (offset = A4h) [reset = X]
- 7.13.41 GPO1PG_CTRL2: 2nd GPO1 PG Control Register (offset = A5h) [reset = X]
- 7.13.42 GPO4PG_CTRL1: 1st GPO4 PG Control Register (offset = A6h) [reset = X]
- 7.13.43 GPO4PG_CTRL2: 2nd GPO4 PG Control Register (offset = A7h) [reset = X]
- 7.13.44 GPO2PG_CTRL1: 1st GPO2 PG Control Register (offset = A8h) [reset = X]
- 7.13.45 GPO2PG_CTRL2: 2nd GPO2 PG Control Register (offset = A9h) [reset = X]
- 7.13.46 GPO3PG_CTRL1: 1st GPO3 PG Control Register (offset = AAh) [reset = X]
- 7.13.47 GPO3PG_CTRL2: 2nd GPO3 PG Control Register (offset = ABh) [reset = X]
- 7.13.48 MISCSYSPG Register (offset = ACh) [reset = X]
- 7.13.49 LDOA1_SWB2_CTRL: LDOA1 and SWB2 Control Register (offset = AEh) [reset = X]
- 7.13.50 PG_STATUS1: 1st Power Good Status Register (offset = B0h) [reset = 0000 0000]
- 7.13.51 PG_STATUS2: 2nd Power Good Status Register (offset = B1h) [reset = 0000 0000]
- 7.13.52 PWR_FAULT_STATUS1: 1st Power Fault Status Register (offset = B2h) [reset = 0000 0000]
- 7.13.53 PWR_FAULT_STATUS2: 2nd Power Fault Status Register (offset = B3h) [reset = 0000 0000]
- 7.13.54 TEMPCRIT: Temperature Fault Status Register (offset = B4h) [reset = 0000 0000]
- 7.13.55 TEMPHOT: Temperature Hot Status Register (offset = B5h) [reset = 0000 0000]
- 7.13.56 OC_STATUS: Overcurrent Fault Status Register (offset = B6h) [reset = 0000 0000]
-
8 Applications, Implementation, and Layout
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2 Typical Application
- 8.3 Power Supply Coupling and Bulk Capacitors
- 8.4 Do's and Don'ts
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Revision History
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RSK|64
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RSK|64
Orderable Information
7.7.2 Converter Overview
The PMIC synchronous step-down DCDC converters include a unique hysteretic PWM controller scheme which enables a high switching frequency converter, excellent transient and AC load regulation as well as operation with cost-competitive external components. The converter topology supports forced PWM mode as well as power-save mode operation. Power-save mode operation, or PFM mode, reduces the quiescent current consumption and ensures high conversion efficiency at light loads by skipping switch pulses. In forced PWM mode, the device operates on a quasi-fixed frequency, avoids pulse skipping, and allows filtering of the switch noise by external filter components. The PMIC device offers fixed output voltage options featuring smallest solution size by using only three external components per converter.
A significant advantage of PMIC compared to other hysteretic PWM controller topologies is its excellent AC load transient regulation capability. When the output voltage falls below the threshold of the error comparator, a switch pulse is initiated, and the high-side switch is turned on. The high-side switch remains turned on until a minimum ON-time of tONmin expires and the output voltage trips the threshold of the error comparator or the inductor current reaches the high-side switch current limit. When the high-side switch turns off, the low-side switch rectifier is turned on and the inductor current ramps down until the high-side switch turns on again or the inductor current reaches zero. In forced PWM mode operation, negative inductor current is allowed to enable continuous conduction mode even at no load condition.
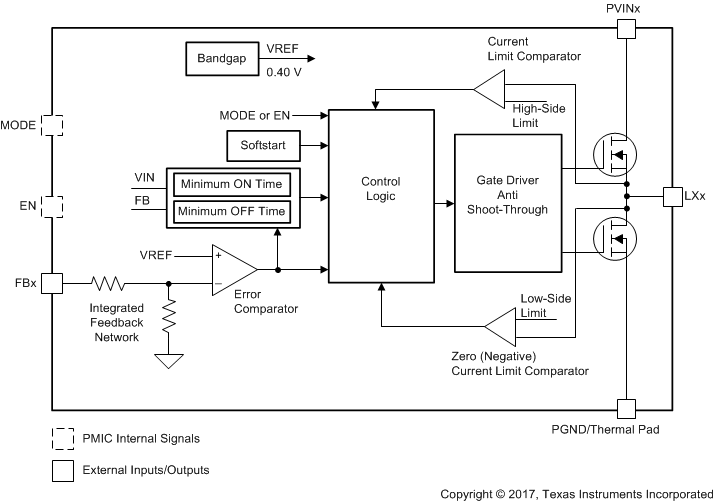 Figure 7-18 Converter Block Diagram
Figure 7-18 Converter Block Diagram