SLVS497F SEPTEMBER 2003 – June 2016 TPS65140 , TPS65141 , TPS65145
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1
Boost Converter Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1.1 Inductor Selection
- 8.2.2.1.2 Output Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.2.1.3 Input Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.2.1.4 Rectifier Diode Selection
- 8.2.2.1.5 Converter Loop Design and Stability
- 8.2.2.1.6 Design Procedure Quick Steps
- 8.2.2.1.7 Setting the Output Voltage and Selecting the Feedforward Capacitor
- 8.2.2.1.8 Compensation
- 8.2.2.1.9 Negative Charge Pump
- 8.2.2.1.10 Positive Charge Pump
- 8.2.2.1.11 Linear Regulator Controller
- 8.2.2.1
Boost Converter Design Procedure
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 8.3 System Examples
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RGE|24
- PWP|24
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
10 Layout
10.1 Layout Guidelines
For all switching power supplies, the layout is an important step in the design, especially at high-peak currents and switching frequencies. If the layout is not carefully designed, the regulator might show stability and EMI problems. TI recommends the following PCB layout guidelines for the TPS6514x devices:
- Connect PGND and AGND together on the same ground plane.
- Connect all capacitor grounds and PGND together on a common ground plane.
- Place the input filter capacitor as close as possible to the input pin of the IC.
- Route first the traces carrying high-switching currents with wide and short traces.
- Isolate analog signal paths from power paths.
- If vias are necessary, try to use more than one in parallel to decrease parasitics, especially for power traces.
- Solder the thermal pad to the PCB for good thermal performance
10.2 Layout Example
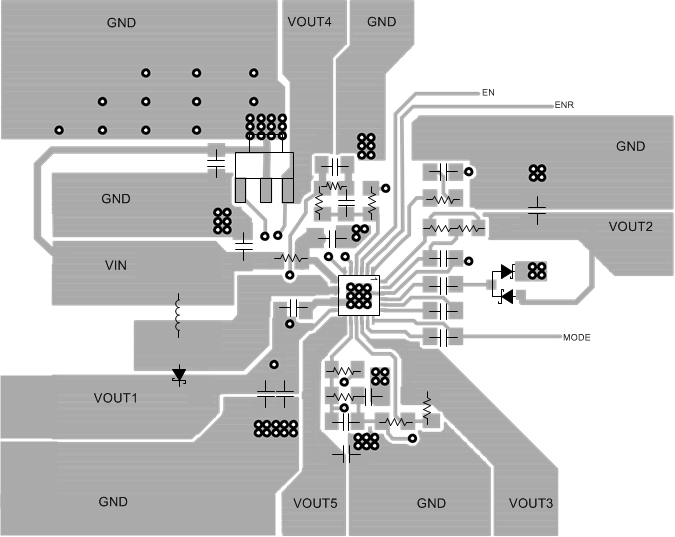 Figure 26. PCB Layout Example
Figure 26. PCB Layout Example
10.3 Thermal Considerations
An influential component of the thermal performance of a package is board design. To take full advantage of the heat dissipation abilities of the PowerPAD or VQFN package with exposed thermal die, a board that acts similar to a heatsink and allows for the use of an exposed (and solderable) deep downset pad must be used. For further information, see Texas Instruments application notes PowerPAD Thermally Enhanced Package and Power Pad Made Easy. For the VQFN package, see the application report QFN/SON PCB Attachement. Especially for the VQFN package, it is required to solder down the thermal pad to achieve the required thermal resistance.