SLVSCN5B june 2014 – may 2023 TPS65262-1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Adjusting the Output Voltage
- 8.3.2 Enable and Adjusting UVLO
- 8.3.3 Soft-Start Time
- 8.3.4 Power-Up Sequencing
- 8.3.5 V7V Low Dropout Regulator and Bootstrap
- 8.3.6 Out-of-Phase Operation
- 8.3.7 Output Overvoltage Protection (OVP)
- 8.3.8 PSM
- 8.3.9 Slope Compensation
- 8.3.10 Overcurrent Protection (OCP)
- 8.3.11 Power Good
- 8.3.12 Thermal Shutdown
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RHB|32
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RHB|32
Orderable Information
8.3.2 Enable and Adjusting UVLO
The EN1, EN2, and EN3 pins provide electrical on and off control of the device. When the EN1, EN2, and EN3 pins' voltage exceeds the threshold voltage, the device starts operation. If each ENx pin voltage is pulled below the threshold voltage, the regulator stops switching and enters low Iq state.
The EN pin has an internal pullup current source, allowing the user to float the EN pin for enabling the device. If an application requires controlling the EN pin, use open-drain or open-collector output logic to interface with the pin.
The device implements internal UVLO circuitry on the VIN pin. The device is disabled when the VIN pin voltage falls below the internal VIN UVLO threshold. The internal VIN UVLO threshold has a hysteresis of 500 mV. If an application requires a higher UVLO threshold on the VIN pin, then the ENx pin can be configured as shown in Figure 8-2. When using the external UVLO function, TI recommends to set the hysteresis to be greater than 500 mV.
The EN pin has a small pullup current, Ip, which sets the default state of the pin to enable when no external components are connected. The pullup current is also used to control the voltage hysteresis for the UVLO function because it increases by Ih after the EN pin crosses the enable threshold. The UVLO thresholds can be calculated using Equation 2 and Equation 3.
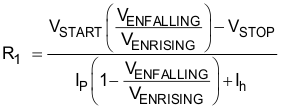
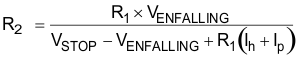
where
- Ih = 3 µA
- Ip = 3.6 µA
- VENRISING = 1.2 V
- VENFALLING = 1.15 V
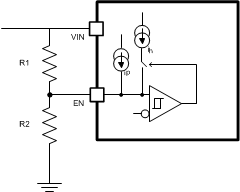 Figure 8-2 Adjustable VIN UVLO
Figure 8-2 Adjustable VIN UVLO