SLVSD86B december 2015 – may 2023 TPS65265
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Adjusting the Output Voltage
- 8.3.2 Mix PGOOD, PG_DLY Functions
- 8.3.3 Enable and Adjusting UVLO
- 8.3.4 Soft-Start Time
- 8.3.5 Power-Up Sequencing
- 8.3.6 V7V Low Dropout Regulator and Bootstrap
- 8.3.7 Out of Phase Operation
- 8.3.8 Output Overvoltage Protection (OVP)
- 8.3.9 PSM
- 8.3.10 Slope Compensation
- 8.3.11 Overcurrent Protection
- 8.3.12 Adjustable Switching Frequency
- 8.3.13 Thermal Shutdown
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RHB|32
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RHB|32
Orderable Information
6 Pin Configuration and Functions
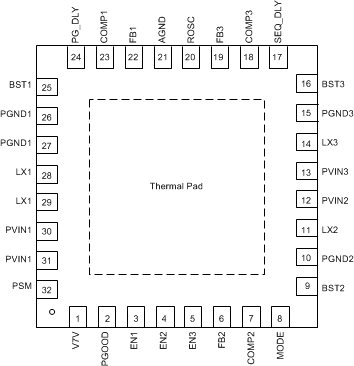
There is no electric signal down bonded to thermal pad inside IC. Exposed thermal pad must be soldered to PCB for optimal thermal performance.
Figure 6-1 RHB Package32-Lead Plastic QFNTop ViewTable 6-1 Pin Functions
| PIN | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|
| NO. | NAME | |
| 1 | V7V | Internal LDO for gate driver and internal controller. Connect a 10-µF capacitor from the pin to power ground |
| 2 | PGOOD | An open drain output, asserts low if output voltage of any buck beyond regulation range due to thermal shutdown, over-current, under-voltage or ENx shut down. |
| 3 | EN1 | Enable for buck1. Float to enable. Can use this pin to adjust the input undervoltage lockout (UVLO) of buck1 with a resistor divider. |
| 4 | EN2 | Enable for buck2. Float to enable. Can use this pin to adjust the input UVLO of buck2 with a resistor divider. |
| 5 | EN3 | Enable for buck3. Float to enable. Can use this pin to adjust the input UVLO of buck3 with a resistor divider. |
| 6 | FB2 | Feedback Kelvin sensing pin for buck2 output voltage. Connect this pin to buck2 resistor divider. |
| 7 | COMP2 | Error amplifier output and Loop compensation pin for buck2. Connect a series resistor and capacitor to compensate the control loop of buck2 with peak current PWM mode. |
| 8 | MODE | When floating, Buck1/2/3 are controlled separate by EN1/2/3. When tied to HIGH or tied to GND, an automatic power-up/power-down sequence is provided according to states of EN1, EN2 and EN3 pins. |
| 9 | BST2 | Boot strapped supply to the high side floating gate driver in buck2. Connect a capacitor (recommend 47nF) from BST2 pin to LX2 pin. |
| 10 | PGND2 | Power ground connection of buck2. Connect PGND2 pin as close as practical to the (-) terminal of PVIN2 input ceramic capacitor. |
| 11 | LX2 | Switching node connection to the inductor and bootstrap capacitor for buck2. The voltage swing at this pin is from a diode voltage below the ground up to PVIN2 voltage. |
| 12 | PVIN2 | Input power supply for buck2. Connect PVIN2 pin as close as practical to the (+) terminal of an input ceramic capacitor (suggest 10 µF). |
| 13 | PVIN3 | Input power supply for buck3. Connect PVIN3 pin as close as practical to the (+) terminal of an input ceramic capacitor (suggest 10 µF). |
| 14 | LX3 | Switching node connection to the inductor and bootstrap capacitor for buck3. The voltage swing at this pin is from a diode voltage below the ground up to PVIN3 voltage. |
| 15 | PGND3 | Power ground connection of buck3. Connect PGND3 pin as close as practical to the (-) terminal of PVIN3 input ceramic capacitor. |
| 16 | BST3 | Boot strapped supply to the high side floating gate driver in buck3. Connect a capacitor (recommend 47nF) from BST3 pin to LX3 pin. |
| 17 | SEQ_DLY | Delay time programmable between bucks at automatic power sequencing mode. Connect an external capacitor to set the interval delay time. |
| 18 | COMP3 | Error amplifier output and Loop compensation pin for buck3. Connect a series resistor and capacitor to compensate the control loop of buck3 with peak current PWM mode. |
| 19 | FB3 | Feedback Kelvin sensing pin for buck3 output voltage. Connect this pin to buck3 resistor divider. |
| 20 | ROSC | Oscillator frequency programmable pin. Connect an external resistor to set the switching frequency. |
| 21 | AGND | Analog ground common to buck controllers and other analog circuits. |
| 22 | FB1 | Feedback Kelvin sensing pin for buck1 output voltage. Connect this pin to buck1 resistor divider. |
| 23 | COMP1 | Error amplifier output and Loop compensation pin for buck1. Connect a series resistor and capacitor to compensate the control loop of buck1 with peak current PWM mode. |
| 24 | PG_DLY | PGOOD delay programmable pin. Connect an external capacitor to set the delay time. |
| 25 | BST1 | Boot strapped supply to the high side floating gate driver in buck1. Connect a capacitor (recommend 47nF) from BST1 pin to LX1 pin. |
| 26, 27 | PGND1 | Power ground connection of Buck1. Connect PGND1 pin as close as practical to the (-) terminal of PVIN1 input ceramic capacitor. |
| 28, 29 | LX1 | Switching node connection to the inductor and bootstrap capacitor for buck1. The voltage swing at this pin is from a diode voltage below the ground up to PVIN1 voltage. |
| 30, 31 | PVIN1 | Input power supply for buck1. Connect PVIN1 pin as close as practical to the (+) terminal of an input ceramic capacitor (suggest 22 µF). |
| 32 | PSM | Ties to HIGH or leaves floating, PSM mode; Ties to GND, FCCM mode. |
| PAD | There is no electric signal down bonded to thermal pad inside IC. Exposed thermal pad must be soldered to PCB for optimal thermal performance. | |