SLVSE48C january 2018 – may 2023 TPS65268-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Adjusting the Output Voltage
- 7.3.2 Enable and Adjusting UVLO
- 7.3.3 Soft-Start Time
- 7.3.4 Power-Up Sequencing
- 7.3.5 V7V Low-Dropout Regulator and Bootstrap
- 7.3.6 Out-of-Phase Operation
- 7.3.7 Output Overvoltage Protection (OVP)
- 7.3.8 Slope Compensation
- 7.3.9 Overcurrent Protection
- 7.3.10 Power Good
- 7.3.11 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RHB|32
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RHB|32
Orderable Information
8.2.2.4 Loop Compensation
The TPS65268-Q1 device incorporates a peak current-mode control scheme. The error amplifier is a transconductance amplifier with a gain of 300 µS. A typical type II compensation circuit adequately delivers a phase margin from 40° to 90°. The Cb capacitor adds a high-frequency pole to attenuate high-frequency noise when needed. To calculate the external compensation components, follow these steps:
- Select a switching frequency, fSW, that is appropriate for the application depending on the inductor size, capacitor size, output ripple, EMI, and so forth. Selecting the switching frequency is a trade-off between performance and cost. To achieve a smaller size and lower cost, a higher switching frequency is desired. To optimize efficiency, a lower switching frequency is desired.
- Set up the crossover frequency, fC, which is typically from 1/5 to 1/20 of fSW.
- Use Equation 16 to calculate the value of RC.
Equation 16.
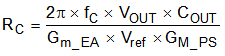
where
- Gm_EA is the error amplifier gain (300 µS).
- Gm_PS is the power stage voltage to current conversion gain (7.4 A/V).
- Use Equation 17 to calculate the value Cc by placing a compensation zero at or before the dominant pole (
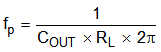 ).
Equation 17.
).
Equation 17.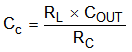
- Optional: Use Equation 18 to calculate the value of CB capacitor to cancel the zero from the ESR associated with CO.
Equation 18.
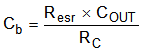
- Optional: Implement type III compensation with the addition of one capacitor, C1. This implementation allows for slightly higher loop bandwidths and higher phase margins. If used, used Equation 19 to calculate the value of C1.
Equation 19.
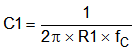
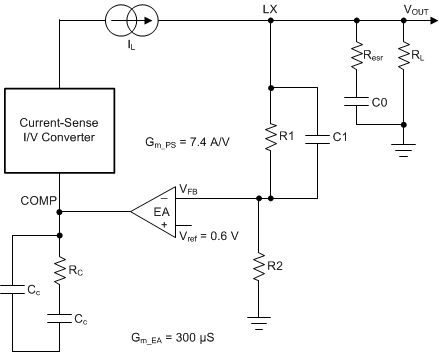 Figure 8-2 DC-DC Loop Compensation
Figure 8-2 DC-DC Loop Compensation