SLVSE48C january 2018 – may 2023 TPS65268-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Adjusting the Output Voltage
- 7.3.2 Enable and Adjusting UVLO
- 7.3.3 Soft-Start Time
- 7.3.4 Power-Up Sequencing
- 7.3.5 V7V Low-Dropout Regulator and Bootstrap
- 7.3.6 Out-of-Phase Operation
- 7.3.7 Output Overvoltage Protection (OVP)
- 7.3.8 Slope Compensation
- 7.3.9 Overcurrent Protection
- 7.3.10 Power Good
- 7.3.11 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RHB|32
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RHB|32
Orderable Information
8.2.2.1 Output Inductor Selection
Use Equation 7 to calculate the value of the output inductor. LIR is a coefficient that represents the amount of inductor ripple current relative to the maximum output current. The inductor ripple current is filtered by the output capacitor. Therefore, choosing high inductor-ripple currents impacts the selection of the output capacitor because the output capacitor must have a ripple current rating equal to or greater than the inductor ripple current. In general, the inductor ripple value is at the discretion of the designer; however, LIR is normally from 0.1 to 0.3 for the majority of applications. Use Equation 7 to calculate the value of the inductor.

For the output filter inductor, the RMS current and saturation current ratings must not be exceeded. Use Equation 8 and Equation to calculate RMS inductor current (ILrms) and peak inductor current (ILpeak).
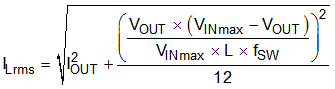
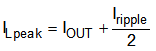
where
The current flowing through the inductor is the inductor ripple current plus the output current. During power up, faults, or transient load conditions, the inductor current can increase above the peak inductor current level calculated in Equation 9. In transient conditions, the inductor current can increase up to the switch current limit of the device. For this reason, the most conservative approach is to specify an inductor with a saturation current rating equal to or greater than the switch current limit rather than the peak inductor current.
