SLDS222C October 2019 – October 2023 TPS65313-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Device Functional Block Diagram
- 5 Revision History
- 6 Description (continued)
- 7 Device Option Table
- 8 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
9 Specifications
- 9.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 9.2 ESD Ratings
- 9.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 9.4 Thermal Information
- 9.5 Power-On-Reset, Current Consumption, and State Timeout Characteristics
- 9.6 PLL/Oscillator and SYNC_IN Pin Characteristics
- 9.7 Wide-VIN Synchronous Buck Regulator (Wide-VIN BUCK) Characteristics
- 9.8 Low-Voltage Synchronous Buck Regulator (LV BUCK) Characteristics
- 9.9 Synchronous Boost Converter (BOOST) Characteristics
- 9.10 Internal Voltage Regulator (VREG) Characteristics
- 9.11 Voltage Monitors for Regulators Characteristics
- 9.12 External General Purpose Voltage Monitor Characteristics
- 9.13 VIN and VIN_SAFE Under-Voltage and Over-Voltage Warning Characteristics
- 9.14 WAKE Input Characteristics
- 9.15 NRES (nRESET) Output Characteristics
- 9.16 ENDRV/nIRQ Output Characteristics
- 9.17 Analog DIAG_OUT
- 9.18 Digital INPUT/OUTPUT IOs (SPI Interface IOs, DIAG_OUT/SYNC_OUT, MCU_ERROR)
- 9.19 BUCK1, BUCK2, BOOST Thermal Shutdown / Over Temperature Protection Characteristics
- 9.20 PGNDx Loss Detection Characteristics
- 9.21 SPI Timing Requirements
- 9.22 SPI Characteristics
- 9.23 Typical Characteristics
- 10Parameter Measurement Information
-
11Detailed Description
- 11.1 Overview
- 11.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 11.3
Wide-VIN Buck Regulator (BUCK1)
- 11.3.1 Fixed-Frequency Voltage-Mode Step-Down Regulator
- 11.3.2 Operation
- 11.3.3 Voltage Monitoring (Monitoring and Protection)
- 11.3.4 Overcurrent Protection (Monitoring and Protection)
- 11.3.5 Thermal Warning and Shutdown Protection (Monitoring and Protection)
- 11.3.6 Overvoltage Protection (OVP) (Monitoring and Protection)
- 11.3.7 Extreme Overvoltage Protection (EOVP) (Monitoring and Protection)
- 11.4
Low-Voltage Buck Regulator (BUCK2)
- 11.4.1 Fixed-Frequency Peak-Current Mode Step-Down Regulator
- 11.4.2 Operation
- 11.4.3 Output Voltage Monitoring (Monitoring and Protection)
- 11.4.4 Overcurrent Protection (Monitoring and Protection)
- 11.4.5 Thermal Sensor Warning and Thermal Shutdown Protection (Monitoring and Protection)
- 11.4.6 Overvoltage Protection (OVP) (Monitoring and Protection)
- 11.5 Low-Voltage Boost Converter (BOOST)
- 11.6 VREG Regulator
- 11.7
BUCK1, BUCK2, and BOOST Switching Clocks and Synchronization (SYNC_IN) Clock
- 11.7.1 Internal fSW Clock Configuration (fSW Derived from an Internal Oscillator)
- 11.7.2 BUCK1 Switching Clock-Monitor Error (Internal fSW Clock Configuration)
- 11.7.3 BUCK2 Switching Clock-Monitor Error (Internal fSW Clock Configuration)
- 11.7.4 BOOST Switching Clock-Monitor Error (Internal fSW Clock Configuration)
- 11.7.5 External fSW Clock Configuration (fSW Derived from SYNC_IN and PLL Clocks)
- 11.8 BUCK1, BUCK2, and BOOST Switching-Clock Spread-Spectrum Modulation
- 11.9
Monitoring, Protection and Diagnostics Overview
- 11.9.1 Safety Functions and Diagnostic Overview
- 11.9.2 Supply Voltage Monitor (VMON)
- 11.9.3 Clock Monitors
- 11.9.4 Analog Built-In Self-Test
- 11.9.5 Logic Built-In Self-Test
- 11.9.6 Junction Temperature Monitors
- 11.9.7 Current Limit
- 11.9.8 Loss of Ground (GND)
- 11.9.9 Diagnostic Output Pin (DIAG_OUT)
- 11.9.10 Watchdog
- 11.9.11 MCU Error Signal Monitor
- 11.9.12 NRES Driver
- 11.9.13 ENDRV/nIRQ Driver
- 11.9.14 CRC Protection for the Device Configuration Registers
- 11.9.15 CRC Protection for the Device EEPROM Registers
- 11.10 General-Purpose External Supply Voltage Monitors
- 11.11 Analog Wake-up and Failure Latch
- 11.12 Power-Up and Power-Down Sequences
- 11.13 Device Fail-Safe State Controller (Monitoring and Protection)
- 11.14 Wakeup
- 11.15 Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI)
- 11.16 Register Maps
-
12Applications, Implementation, and Layout
- 12.1 Application Information
- 12.2
Typical Application
- 12.2.1 Design Requirements
- 12.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 12.2.2.1 Selecting the BUCK1, BUCK2, and BOOST Output Voltages
- 12.2.2.2 Selecting the BUCK1, BUCK2, and BOOST Inductors
- 12.2.2.3 Selecting the BUCK1 and BUCK2 Output Capacitors
- 12.2.2.4 Selecting the BOOST Output Capacitors
- 12.2.2.5 Input Filter Capacitor Selection for BUCK1, BUCK2, and BOOST
- 12.2.2.6 Input Filter Capacitors on AVIN and VIN_SAFE Pins
- 12.2.2.7 Bootstrap Capacitor Selection
- 12.2.2.8 Internal Linear Regulator (VREG) Output Capacitor Selection
- 12.2.2.9 EXTSUP Pin
- 12.2.2.10 WAKE Input Pin
- 12.2.2.11 VIO Supply Pin
- 12.2.2.12 External General-Purpose Voltage Monitor Input Pins (EXT_VSENSE1 and EXT_VSENSE2)
- 12.2.2.13 SYNC_IN Pin
- 12.2.2.14 MCU_ERR Pin
- 12.2.2.15 NRES Pin
- 12.2.2.16 ENDRV/nIRQ Pin
- 12.2.2.17 DIAG_OUT Pin
- 12.2.2.18 SPI Pins (NCS,SCK, SDI, SDO)
- 12.2.2.19 PBKGx, AGND, DGND, and PGNDx Pins
- 12.2.2.20 Calculations for Power Dissipation and Junction Temperature
- 12.2.3 Application Curves
- 12.2.4 Layout
- 12.3 Power Supply Coupling and Bulk Capacitors
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RWG|40
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
11.5.2 Overcurrent Protection (Monitoring and Protection)
The currents through the high-side (HS) power MOSFET and the low-side (LS) power MOSFET are continuously monitored to protect the internal MOSFETs from damage. Cycle-by-cycle currents through the HS MOSFET and LS MOSFET are compared against the IHS_ LIMIT_BOOST and ILS_ LIMIT_BOOST current limits, respectively.
As load current increases to greater than the maximum IBOOST_LOAD current defined in Section 9.9, the HS MOSFET current exceeds the IHS_LIMIT_BOOST current limit. Consequently, an overload event is detected and the BOOST_HS_OVC status bit is set in the SAFETY_BOOST_STAT1 register. However, the regulator does not shut down. If the load current continues to increase, the LS MOSFET current exceeds the short-circuit current limit (ILS_LIMIT_BOOST). The LS MOSFET is turned off immediately and the HS MOSFET is turned on until the inductor current decreases to less than the overload threshold (IHS_ LIMIT_BOOST). The BOOST converter is then disabled and the BOOST_SCG status bit is set in the SAFETY_BOOST_STAT1 register. The BOOST_EN control bit is cleared and the device goes into the SAFE state, where the device error counter increments and the ENDRV/nIRQ pin is driven low. If the BOOT_UV_RST_EN bit is set to 1b (BOOST UV event configured as RESET state condition), as the VBOOST voltage rail is discharged to less than its UV-threshold level, the device goes into the RESET state.
The HS MOSFET is also protected by detection circuitry for a cycle-by-cycle sink-current limit. This detection circuitry protects the HS MOSFET from excessive reverse current caused by switching the PH3 pin to the VSUP2 supply pin. If the HS sinking current exceeds the ICL_HS_SINK_BOOST sink-current limit, an event is detected and the BOOST_HS_SINK_OVC SPI status bit is set in the SAFETY_BOOST_STAT1 register. If the event occurs for more than 20 µs (typical), the BOOST converter is turned off. The inductor current continues to flow to the supply (VBUCK1 voltage rail) through the body diode of the LS MOSFET. The device response after detection of a HS sink-current limit is identical to that of a short-circuit event.
The HS sink current-limit event can also be detected when the regulator is enabled while its output has not been discharged to less than the voltage level defined by the VBOOST_RESTART_LEVEL level. Therefore, the HS sink current-limit event is masked when the BOOST converter is enabled until it the output voltage ramps to greater than its UV-threshold level.
After receiving an interrupt, the MCU can try to enable the BOOST converter again by sending command to set the BOOST_EN control bit. If a current-limit condition is still present, the BOOST converter is switched off again and the device error counter increments.
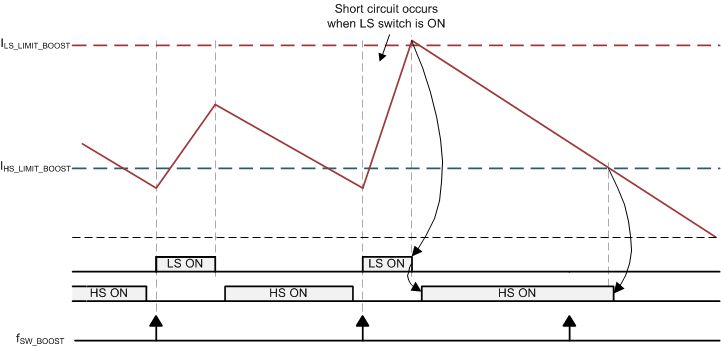
- When the BOOST load current continues to increase to greater than the IBOOST_LOAD maximum value, an UV event can occur.