SLVSF34B May 2019 – October 2022 TPS65987DDJ
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Power Supply Requirements and Characteristics
- 6.6 Power Consumption Characteristics
- 6.7 Power Switch Characteristics
- 6.8 Cable Detection Characteristics
- 6.9 USB-PD Baseband Signal Requirements and Characteristics
- 6.10 BC1.2 Characteristics
- 6.11 Thermal Shutdown Characteristics
- 6.12 Oscillator Characteristics
- 6.13 I/O Characteristics
- 6.14 I2C Requirements and Characteristics
- 6.15 SPI Controller Timing Requirements
- 6.16 HPD Timing Requirements
- 6.17 Typical Characteristics
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 USB-PD Physical Layer
- 8.3.2 Power Management
- 8.3.3 Port Power Switches
- 8.3.4 Cable Plug and Orientation Detection
- 8.3.5 Dead Battery Operation
- 8.3.6 Battery Charger Detection and Advertisement
- 8.3.7 ADC
- 8.3.8 DisplayPort HPD
- 8.3.9 Digital Interfaces
- 8.3.10 Digital Core
- 8.3.11 I2C Interfaces
- 8.3.12 SPI Controller Interface
- 8.3.13 Thermal Shutdown
- 8.3.14 Oscillators
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Applications
- 9.2.1 Type-C VBUS Design Considerations
- 9.2.2 Notebook Design Supporting PD Charging
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RSH|56
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RSH|56
Orderable Information
5 Pin Configuration and Functions
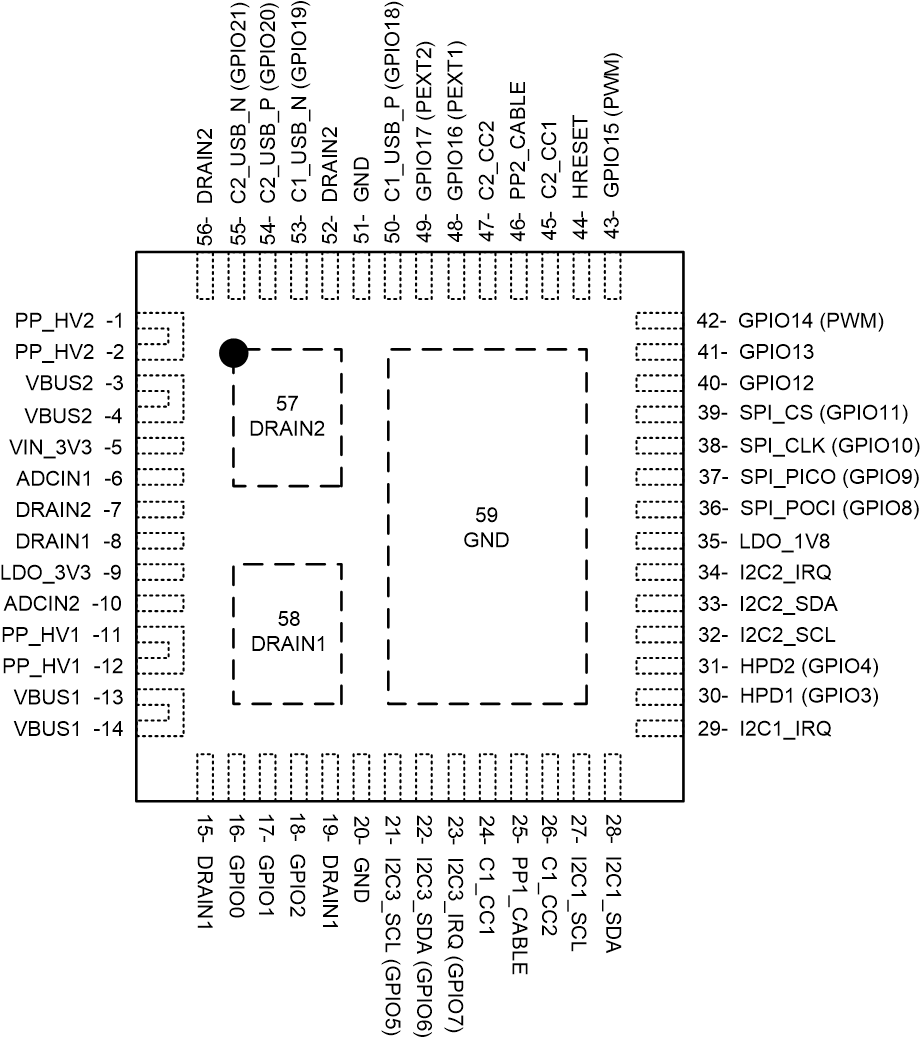 Figure 5-1 RSH Package56-Pin QFNTop View
Figure 5-1 RSH Package56-Pin QFNTop ViewTable 5-1 Pin Functions
| PIN | TYPE(2) | RESET STATE(1) | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | |||
| ADCIN1 | 6 | I | Input | Boot configuration Input. Connect to resistor divider between LDO_3V3 and GND. |
| ADCIN2 | 10 | I | Input | I2C address configuration Input. Connect to resistor divider between LDO_3V3 and GND. |
| C_CC1 | 24 | I/O | High-Z | Output to Type-C CC or VCONN pin . Filter noise with capacitor to GND |
| C_CC2 | 26 | I/O | High-Z | Output to Type-C CC or VCONN pin . Filter noise with capacitor to GND |
| C_USB_N (GPIO19) | 53 | I/O | Input (High-Z) | USB D– connection for BC1.2 support |
| C_USB_P (GPIO18) | 50 | I/O | Input (High-Z) | USB D+ connection for BC1.2 support |
| DRAIN1 | 8, 15, 19, 58 | — | — | Drain of internal power path 1. Connect thermal pad 58 to as big of pad as possible on PCB for best thermal performance. Short the other pins to this thermal pad |
| DRAIN2 | 7, 52, 56, 57 | — | — | Drain of internal power path 2. Connect thermal pad 57 to as big of pad as possible on PCB for best thermal performance. Short the other pins to this thermal pad |
| GND | 20, 45 , 46, 47, 51 | — | — | Unused pin. Tie to GND. |
| GPIO0 | 16 | I/O | Input (High-Z) | General Purpose Digital I/O 0. Float pin when unused. GPIO0 is asserted low during the TPS65987DDJ boot process. Once device configuration and patches are loaded GPIO0 is released |
| GPIO1 | 17 | I/O | Input (High-Z) | General Purpose Digital I/O 1. Ground pin with a 1-MΩ resistor when unused in the application |
| GPIO2 | 18 | I/O | Input (High-Z) | General Purpose Digital I/O 2. Float pin when unused |
| GPIO3 (HPD) | 30 | I/O | Input (High-Z) | General Purpose Digital I/O 3. Configured as Hot Plug Detect (HPD) TX and RX when DisplayPort alternate mode is enabled. Float pin when unused |
| GPIO4 | 31 | I/O | Input (High-Z) | General Purpose Digital I/O 4. Float pin when unused |
| I2C3_SCL (GPIO5) | 21 | I/O | Input (High-Z) | I2C port 3 serial clock. Open-drain output. Tie pin to I/O voltage through a 10-kΩ resistance when used. Float pin when unused |
| I2C3_SDA (GPIO6) | 22 | I/O | Input (High-Z) | I2C port 3 serial data. Open-drain output. Tie pin to I/O voltage through a 10-kΩ resistance when used. Float pin when unused |
| I2C3_IRQ (GPIO7) | 23 | I/O | Input (High-Z) | I2C port 3 interrupt detection (port 3 operates as an I2C Master Only). Active low detection. Connect to the I2C slave's interrupt line to detect when the slave issues an interrupt. Float pin when unused |
| GPIO12 | 40 | I/O | Input (High-Z) | General Purpose Digital I/O 12. Float pin when unused |
| GPIO13 | 41 | I/O | Input (High-Z) | General Purpose Digital I/O 13. Float pin when unused |
| GPIO14 (PWM) | 42 | I/O | Input (High-Z) | General Purpose Digital I/O 14. May also function as a PWM output. Float pin when unused |
| GPIO15 (PWM) | 43 | I/O | Input (High-Z) | General Purpose Digital I/O 15. May also function as a PWM output. Float pin when unused |
| GPIO16 (PP_EXT1) | 48 | I/O | Input (High-Z) | General Purpose Digital I/O 16. May also function as single wire enable signal for external power path 1. Pull-down with external resistor when used for external path control. Float pin when unused |
| GPIO17 (PP_EXT2) | 49 | I/O | Input (High-Z) | General Purpose Digital I/O 17. May also function as single wire enable signal for external power path 2. Pull-down with external resistor when used for external path control. Float pin when unused |
| GPIO20 | 54 | I/O | Input (High-Z) | General Purpose Digital I/O 20. Float pin when unused |
| GPIO21 | 55 | I/O | Input (High-Z) | General Purpose Digital I/O 21. Float pin when unused |
| HRESET | 44 | I/O | Input | Active high hardware reset input. Will reinitialize all device settings. Ground pin when HRESET functionality will not be used |
| I2C1_IRQ | 29 | O | High-Z | I2C port 1 interrupt. Active low. Implement externally as an open drain with a pull-up resistance. Float pin when unused |
| I2C1_SCL | 27 | I/O | High-Z | I2C port 1 serial clock. Open-drain output. Tie pin to I/O voltage through a 10-kΩ resistance when used or unused |
| I2C1_SDA | 28 | I/O | High-Z | I2C port 1 serial data. Open-drain output. Tie pin to I/O voltage through a 10-kΩ resistance when used or unused |
| I2C2_IRQ | 34 | O | High-Z | I2C port 2 interrupt. Active low. Implement externally as an open drain with a pull-up resistance. Float pin when unused |
| I2C2_SCL | 32 | I/O | High-Z | I2C port 2 serial clock. Open-drain output. Tie pin to I/O voltage through a 10-kΩ resistance when used or unused |
| I2C2_SDA | 33 | I/O | High-Z | I2C port 2 serial data. Open-drain output. Tie pin to I/O voltage through a 10-kΩ resistance when used or unused |
| LDO_1V8 | 35 | PWR | — | Output of the 1.8-V LDO for internal circuitry. Bypass with capacitor to GND |
| LDO_3V3 | 9 | PWR | — | Output of the VBUS to 3.3-V LDO or connected to VIN_3V3 by a switch. Main internal supply rail. Used to power external flash memory. Bypass with capacitor to GND |
| PP_CABLE | 25 | PWR | — | 5-V supply input for port 1 C_CC pins. Bypass with capacitor to GND |
| PP_HV1 | 11, 12 | PWR | — | System side of first VBUS power switch. Bypass with capacitor to ground. Tie to ground when unused |
| PP_HV2 | 1, 2 | PWR | — | System side of second VBUS power switch. Bypass with capacitor to ground. Tie to ground when unused |
| SPI_CLK | 38 | I/O | Input | SPI serial clock. Ground pin when unused |
| SPI_POCI | 36 | I/O | Input | SPI serial controller input from peripheral. Ground pin when unused |
| SPI_PICO | 37 | I/O | Input | SPI serial controller output to peripheral. Ground pin when unused |
| SPI_CS | 39 | I/O | Input | SPI chip select. Ground pin when unused |
| VBUS1 | 13, 14 | PWR | — | Port side of first VBUS power switch. Bypass with capacitor to ground. Tie to VBUS2 |
| VBUS2 | 3, 4 | PWR | — | Port side of second VBUS power switch. Bypass with capacitor to ground. Tie to VBUS1 |
| VIN_3V3 | 5 | PWR | — | Supply for core circuitry and I/O. Bypass with capacitor to GND |
| Thermal Pad (PPAD) | 59 | GND | — | Ground reference for the device as well as thermal pad used to conduct heat from the device. This connection serves two purposes. The first purpose is to provide an electrical ground connection for the device. The second purpose is to provide a low thermal-impedance path from the device die to the PCB. This pad must be connected to a ground plane |
(1) Reset State indicates the state of a given pin immediately
following power application, prior to any configuration from firmware.
(2) I = input, O = output, I/O = bidirectional, GND = ground, PWR =
power, NC = no connect