SLVSFN9A September 2020 – August 2021 TPS65988DK
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Power Supply Requirements and Characteristics
- 6.6 Power Consumption Characteristics
- 6.7 Power Switch Characteristics
- 6.8 Cable Detection Characteristics
- 6.9 USB-PD Baseband Signal Requirements and Characteristics
- 6.10 Thermal Shutdown Characteristics
- 6.11 Oscillator Characteristics
- 6.12 I/O Characteristics
- 6.13 I2C Requirements and Characteristics
- 6.14 SPI Controller Timing Requirements
- 6.15 HPD Timing Requirements
- 6.16 Typical Characteristics
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 USB-PD Physical Layer
- 8.3.2 Power Management
- 8.3.3 Port Power Switches
- 8.3.4 Cable Plug and Orientation Detection
- 8.3.5 Dead Battery Operation
- 8.3.6 ADC
- 8.3.7 DisplayPort HPD
- 8.3.8 Digital Interfaces
- 8.3.9 Digital Core
- 8.3.10 I2C Interfaces
- 8.3.11 SPI Controller Interface
- 8.3.12 Thermal Shutdown
- 8.3.13 Oscillators
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
-
11Layout
- 11.1 Layout Guidelines
- 11.2 Layout Example
- 11.3 Stack-up and Design Rules
- 11.4 Main Component Placement
- 11.5 Super Speed Type-C Connectors
- 11.6 Capacitor Placement
- 11.7 CC1/2 Capacitors & ADCIN1/2 Resistors
- 11.8 CC and SBU Protection Placement
- 11.9 CC Routing
- 11.10 DRAIN1 and DRAIN2 Pad Pours
- 11.11 VBUS Routing
- 11.12 Completed Layout
- 11.13 Power Dissipation
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RSH|56
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RSH|56
Orderable Information
11.11 VBUS Routing
When higher current are required in the system and there are space constraints it is recommended to stack power planes to help carry the higher currents. These are mostly used at the Type-C connector where most of the room will be reserved for SSTX/RX, USB2, SBU and CC signals. Table 11-3 summarizes the recommended widths for various VBUS currents.
Table 11-3 Recommended Trace Width for VBUS Currents
| VBUS Current | Trace Width (0.5 oz Copper) | Trace Width (1 oz Copper) |
|---|---|---|
| 1.5 A | 50 mil | 30 mil |
| 3 A | 100 mil | 60 mil |
| 5 A | 240 mil | 120 mil |
The figures below show the SSTXRX1, Power1, Power2 and SSTXRX2 layers and the VBUS routing for the two ports.
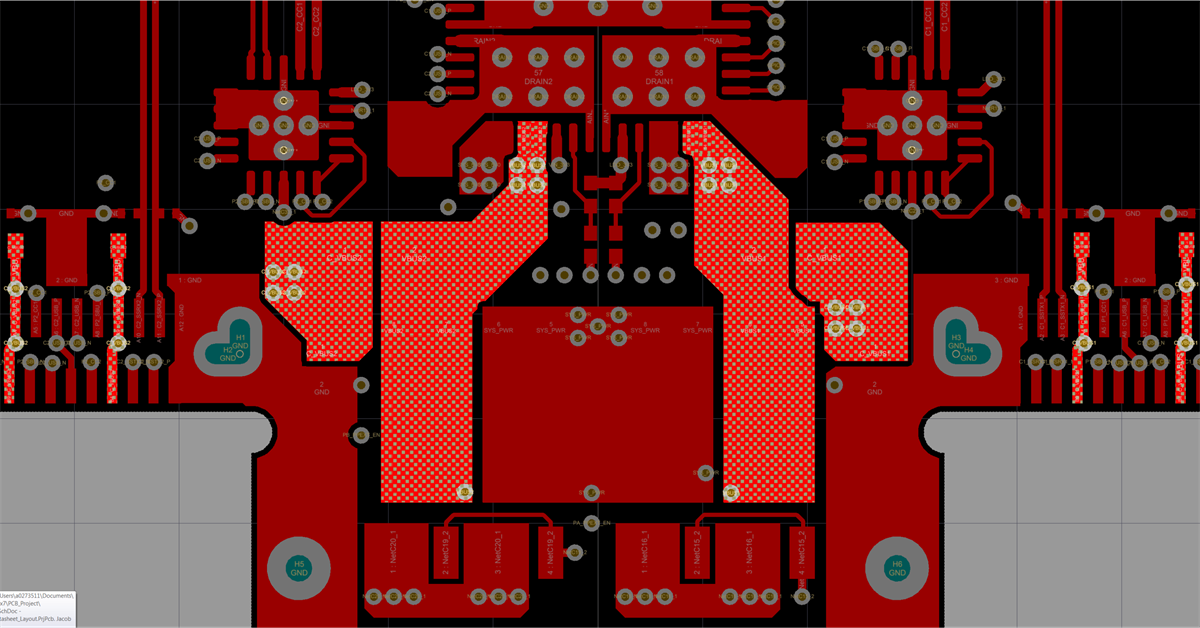 Figure 11-17 VBUS Routing Top Layer
Figure 11-17 VBUS Routing Top Layer Figure 11-19 VBUS Routing Power 2
Figure 11-19 VBUS Routing Power 2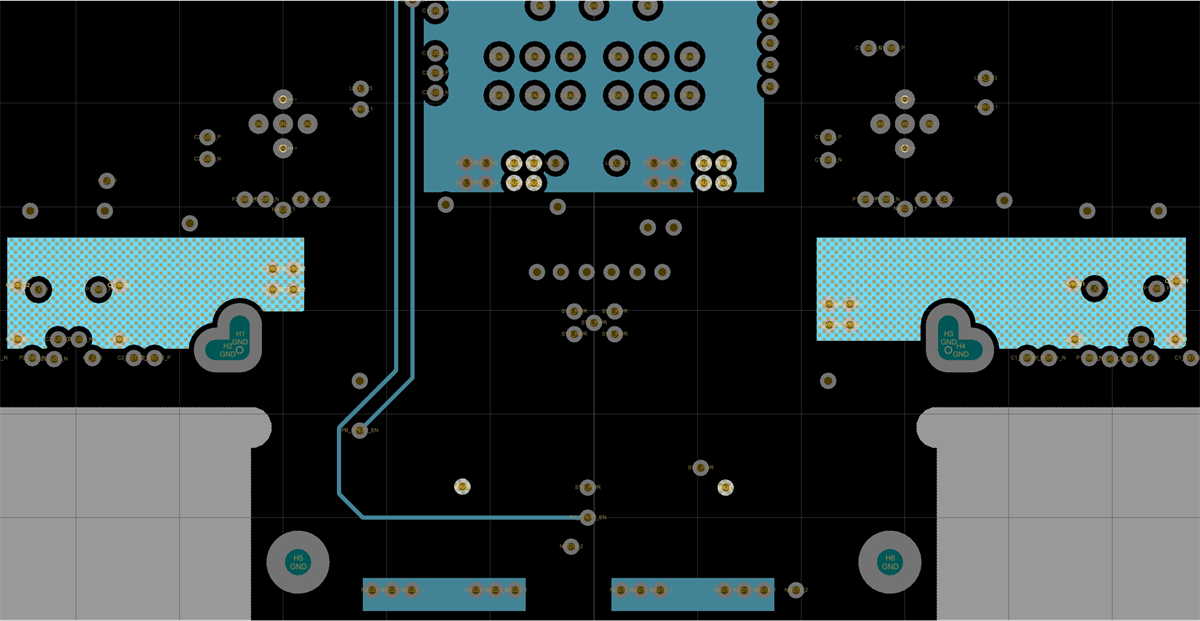 Figure 11-18 VBUS Routing Power 1
Figure 11-18 VBUS Routing Power 1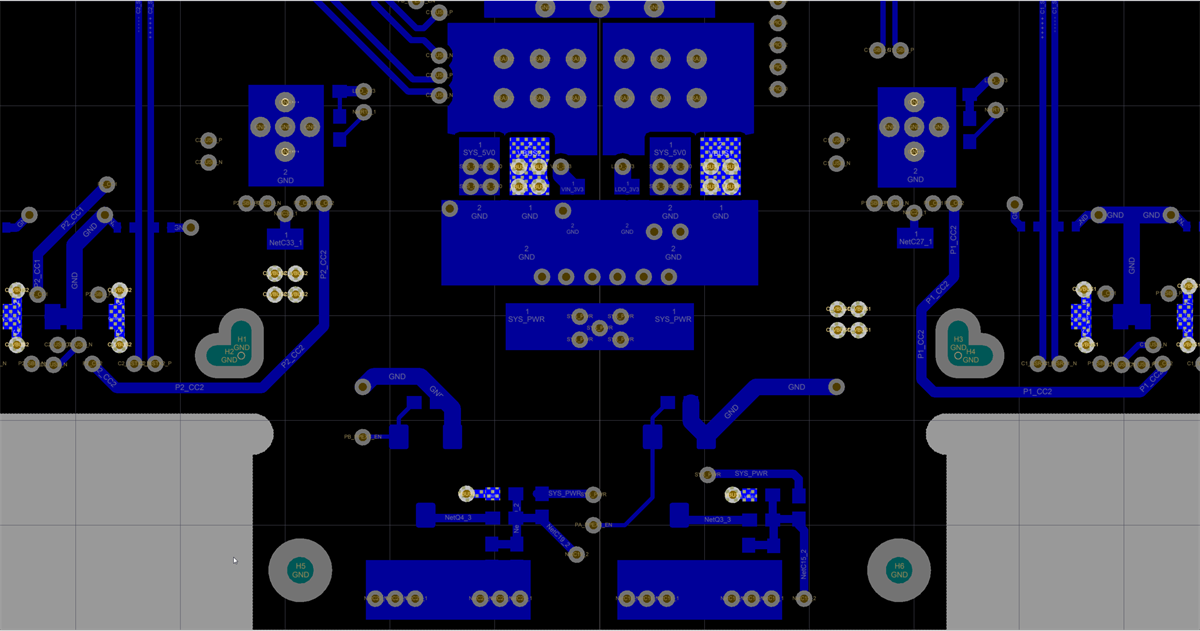 Figure 11-20 VBUS Routing Bottom Layer
Figure 11-20 VBUS Routing Bottom Layer