-
TPS720-Q1 350-mA, Ultra-Low VIN, RF Low-Dropout Linear Regulator With BIAS Pin
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
- IMPORTANT NOTICE
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DRV|6
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DRV|6
Orderable Information
TPS720-Q1 350-mA, Ultra-Low VIN, RF Low-Dropout Linear Regulator With BIAS Pin
1 Features
- Qualified for Automotive Applications
- AEC-Q100 Qualified With the Following Results:
- Device Temperature Grade 1: –40°C to +125°C Ambient Operating Temperature Range
- Device HBM ESD Classification Level H2
- Device CDM ESD Classification Level C6
- Input Voltage Range: 1.1 V to 4.5 V
- Output Voltage Range: 0.9 V to 3.6 V
- High-Performance LDO: 350 mA
- Low Quiescent Current: 38 μA
- Excellent Load Transient Response:
±15 mV for ILOAD = 0 mA to 350 mA in 1 μs - Low Noise: 48 μVRMS (10 Hz to 100 kHz)
- 80-dB VIN PSRR (10 Hz to 10 kHz)
- 70-dB VBIAS PSRR (10 Hz to 10 kHz)
- Fast Start-Up Time: 140 μs
- Built-In Soft-Start With Monotonic VOUT Rise and Start-Up Current Limited to 100 mA + ILOAD
- Overcurrent and Thermal Protection
- Low Dropout: 110 mV at ILOAD = 350 mA
- Stable With a 2.2-μF Output Capacitor
- Package: 2.00 mm × 2.00 mm, 6-Pin WSON
2 Applications
- Camera Modules
- FPD Link Power
- Automotive Infotainment
- USB HUB Power
Simplified Schematic

3 Description
The TPS720-Q1 family of dual-rail, low-dropout linear regulators (LDOs) offers outstanding ac performance (PSRR, load and line transient response) and consume a very low quiescent current of 38 μA.
The VBIAS rail that powers the control circuit of the LDO draws very low current (on the order of the LDO quiescent current) and can be connected to any power supply that is equal to or greater than 1.4 V above the output voltage. The main power path is through VIN and can be a lower voltage than VBIAS; this path can be as low as VOUT + VDO, increasing the efficiency of the solution in many power-sensitive applications. For example, VIN can be an output of a high-efficiency, dc-dc, step-down regulator.
The TPS720-Q1 supports a novel feature where the output of the LDO regulates under light loads when the IN pin is left floating. The light-load drive current is sourced from VBIAS under this condition. This feature is particularly useful in power-saving applications where the dc-dc converter connected to the IN pin is disabled but the LDO is still required to regulate the voltage to a light load.
The TPS720-Q1 is stable with ceramic capacitors and uses an advanced BICMOS fabrication process that yields a dropout of 110 mV at a 350-mA output load. The TPS720-Q1 provides a monotonic VOUT rise (overshoot limited to 3%) with VIN inrush current limited to 100 mA + ILOAD with an output capacitor of 2.2 μF.
The TPS720-Q1 uses a precision voltage reference and feedback loop to achieve overall accuracy of 2% over load, line, process, and temperature extremes. The TPS720-Q1 is available in a 6-pin WSON package. This family of devices is fully specified over the temperature range of TJ = –40°C to +125°C.
Device Information(1)
| PART NUMBER | PACKAGE | BODY SIZE (NOM) |
|---|---|---|
| TPS720-Q1 | WSON (6) | 2.00 mm × 2.00 mm |
- For all available packages, see the orderable addendum at the end of the data sheet.
4 Revision History
Changes from * Revision (February 2016) to A Revision
- Changed Output Voltage Range bullet in Features section from "0.9 V to 3.0 V" to "0.9 V to 3.6 V"Go
- Changed maximum value of "output voltage" parameter from 3.0 V to 3.6 V in Recommended Operating Conditions tableGo
- Reformatted Thermal Information table note Go
- Changed maximum value of output voltage parameter from 3.0 V to 3.6 V in Electrical Characteristics table Go
- Changed output voltage range in table note from "0.9 V to 3.0 V" to "0.9 V to 3.3 V" in Device Nomenclature sectionGo
- Changed formatting of Related Documentation section Go
- Added Receiving Notification of Documentation Updates section Go
5 Pin Configuration and Functions

Pin Functions
| PIN | I/O | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||
| OUT | 1 | O | Output pin. A 2.2-μF ceramic capacitor is connected from this pin to ground for stability and to provide load transients; see Input and Output Capacitor Requirements |
| NC | 2 | — | No connection. |
| EN | 3 | I | Enable pin. A logic high signal on this pin turns the device on and regulates the voltage from IN to OUT. A logic low on this pin turns the device off. |
| BIAS | 4 | I | Bias supply pin. For better transient performance, TI recommends bypassing this input with a ceramic capacitor to ground; see Input and Output Capacitor Requirements |
| GND | 5 | — | Ground pin. |
| IN | 6 | I | Input pin. This pin can be a maximum of 4.5 V; VIN must not exceed VBIAS. Bypass this input with a ceramic capacitor to ground; see Input and Output Capacitor Requirements. |
6 Specifications
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
at TJ = –40°C to +125°C (unless otherwise noted); all voltages are with respect to GND(1)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VIN(2) | Input voltage (steady-state) | –0.3 | VBIAS or 5(3) | V | |
| VIN_PEAK(4) | Peak transient input | 5.5 | V | ||
| VBIAS | Bias voltage | –0.3 | 6 | V | |
| VEN | Enable voltage | –0.3 | 6 | V | |
| VOUT | Output voltage | –0.3 | 5 | V | |
| IOUT | Peak output current | Internally limited | |||
| Output short-circuit duration | Indefinite | ||||
| PDISS | Total continuous power dissipation | See Thermal Information | |||
| TJ | Operating junction temperature | –55 | 125 | °C | |
| Tstg | Storage temperature | –55 | 150 | °C | |
6.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human-body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001(1) | ±2000 | V |
| Charged-device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101(2) | ±500 | |||
| Machine model (MM) | ±100 | |||
6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
over operating junction temperature range (unless otherwise noted).| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VIN | Input voltage (steady-state) | 1.1 | VBIAS or 4.5(1) | V | |
| VBIAS | Bias voltage | 2.6 or VOUT + 1.4(2) | 5.5 | V | |
| VOUT | Output voltage | 0.9 | 3.6 | V | |
| IOUT | Peak output current | 0 | 350 | mA | |
| VEN | Enable voltage | 0 | 5.5 | V | |
| CIN | Input capacitance | 1 | µF | ||
| CBIAS | Bias capacitance | 0.1 | µF | ||
| COUT(3) | Output capacitance | 2.2 | µF | ||
6.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | TPS720-Q1 | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| DRV (WSON) | |||
| 6 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 66.5 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 86.2 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 36.1 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 1.7 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 36.6 | °C/W |
| RθJC(bot) | Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance | 7.4 | °C/W |
6.5 Electrical Characteristics
over operating temperature range (TJ = –40°C to +125°C), VBIAS = (VOUT + 1.4 V ) or 2.6 V (whichever is greater), VIN ≥ VOUT + 0.5 V, IOUT = 1 mA, VEN = 1.1 V, and COUT = 2.2 μF (unless otherwise noted); typical values are at TJ = 25°C| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VIN | Input voltage | 1.1(1) | VBIAS or 4.5(2) | V | ||||
| VBIAS | Bias voltage | 2.6 | 5.5 | V | ||||
| VOUT(4) | Output voltage(3) | 0.9 | 3.6 | V | ||||
| Output accuracy | Over VBIAS, VIN, IOUT, TJ = –40°C to +125°C | VOUT + 1.4 V ≤ VBIAS ≤ 5.5 V, VOUT + 0.5 V ≤ VIN ≤ 4.5 V, 0 mA ≤ IOUT ≤ 350 mA |
–2% | 2% | ||||
| Over VBIAS, VIN, IOUT, TJ = –40°C to +125°C | VOUT + 1.4 V ≤ VBIAS ≤ 5.5 V, VOUT + 0.5 V ≤ VIN ≤ 4.5 V, 0 mA ≤ IOUT ≤ 350 mA, VOUT < 1.2 V |
–25 | 25 | mV | ||||
| VIN floating | VOUT + 1.4 V ≤ VBIAS ≤ 5.5 V, 0 μA ≤ IOUT ≤ 500 μA |
±1% | ||||||
| ΔVOUT/ΔVIN | VIN line regulation | VIN = (VOUT + 0.5 V) to 4.5 V, IOUT = 1 mA | 16 | μV/V | ||||
| ΔVOUT/ΔVBIAS | VBIAS line regulation | VBIAS = (VOUT + 1.4 V) or 2.6 V (whichever is greater) to 5.5 V, IOUT = 1 mA | 16 | μV/V | ||||
| VIN line transient | ΔVIN = 400 mV, tRISE = tFALL = 1 μs | ±200 | μV | |||||
| VBIAS line transient | ΔVBIAS = 600 mV, tRISE = tFALL = 1 μs | ±0.8 | mV | |||||
| ΔVOUT/ΔIOUT | Load regulation | 0 mA ≤ IOUT ≤ 350 mA (no load to full load) | –15 | μV/mA | ||||
| Load transient | 0 mA ≤ IOUT ≤ 350 mA, tRISE = tFALL = 1 μs | ±15 | mV | |||||
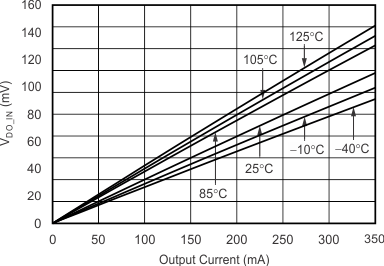
| VDO_IN | VIN dropout voltage(5) | VIN = VOUT(NOM) – 0.1 V, (VBIAS – VOUT(NOM)) = 1.4 V, IOUT = 350 mA |
110 | 200 | mV | |||
| VDO_BIAS | VBIAS dropout voltage(6) | VIN = VOUT(NOM) + 0.3 V, IOUT = 350 mA | 1.09 | 1.4 | V | |||
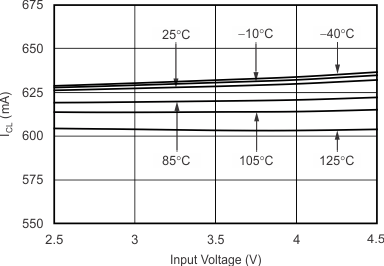
| ICL | Output current limit | VOUT = 0.9 × VOUT(NOM) | 420 | 600 | 800 | mA | ||
| IGND | Ground pin current | IOUT = 100 μA | 38 | μA | ||||
| IOUT = 0 mA to 350 mA | 54 | 80 | ||||||
| ISHDN | Shutdown current (IGND) | VEN ≤ 0.4 V | 0.5 | 2.5 | μA | |||
| PSRR | VIN power-supply rejection ratio | VIN – VOUT ≥ 0.5 V, VBIAS = VOUT + 1.4 V, IOUT = 350 mA |
f = 10 Hz | 85 | dB | |||
| f = 100 Hz | 85 | |||||||
| f = 1 kHz | 85 | |||||||
| f = 10 kHz | 80 | |||||||
| f = 100 kHz | 70 | |||||||
| f = 1 MHz | 50 | |||||||
| PSRR | VBIAS power-supply rejection ratio | VIN – VOUT ≥ 0.5 V, VBIAS = VOUT + 1.4 V, IOUT = 350 mA |
f = 10 Hz | 80 | dB | |||
| f = 100 Hz | 80 | |||||||
| f = 1 kHz | 75 | |||||||
| f = 10 kHz | 65 | |||||||
| f = 100 kHz | 55 | |||||||
| f = 1 MHz | 35 | |||||||
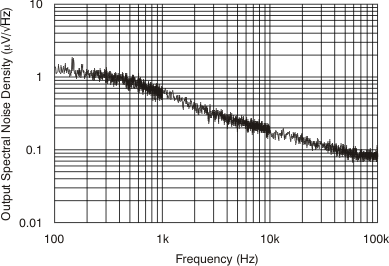
| VN | Output noise voltage | Bandwidth = 10 Hz to 100 kHz, VBIAS ≥ 2.6 V, VIN = VOUT + 0.5 V |
48 | μVRMS | ||||
| IVIN_INRUSH | Inrush current on VIN | VBIAS = (VOUT +1.4 V) or 2.6 V (whichever is greater), VIN = VOUT + 0.5 V | 100 + ILOAD | mA | ||||
| VEN(HI) | Enable pin high (enabled) | 1.1 | V | |||||
| VEN(LO) | Enable pin low (disabled) | 0 | 0.4 | V | ||||
| IEN | Enable pin current | VEN = 5.5 V, VIN = 4.5 V, VBIAS = 5.5 V | 1 | µA | ||||
| UVLO | Undervoltage lockout | VBIAS rising | 2.35 | 2.45 | 2.59 | V | ||
| UVLO hysteresis | VBIAS falling | 150 | mV | |||||
| TSD | Thermal shutdown temperature | Shutdown, temperature increasing | 160 | °C | ||||
| Reset, temperature decreasing | 140 | |||||||
| TJ | Operating junction temperature | –40 | 125 | °C | ||||
6.6 Timing Requirements
| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tSTR | Start-up time | VOUT = 95%, VOUT (NOM), IOUT = 350 mA, COUT = 2.2 μF | 140 | µs | ||
6.7 Typical Characteristics
over operating temperature range (TJ = –40°C to +125°C), VBIAS = (VOUT + 1.4 V) or 2.6 V (whichever is greater), VIN = VOUT + 0.5 V, IOUT = 1 mA, VEN = 1.1 V, and COUT = 2.2 μF (unless otherwise noted); typical values are at TJ = 25°C
| IOUT = 0 mA |

| IOUT = 0 mA |






| IOUT = 350 mA |

| VIN = 2.3 V | VOUT = 1.8 V | VBIAS = 3.2 V to 3.8 V |
| VBIAS slew rate = 600 m/μs | IOUT = 350 mA | |

| IOUT = 350 mA |

| IOUT = 350 mA |


| VBIAS = 3.2 V |

| VOUT = VOUT(NOM) – 0.1 V | IOUT = 350 mA | |

| IOUT = 1 mA | ||

| IOUT = 350 mA |


| VIN – VOUT = 0.5 V, VBIAS – VOUT = 1.4 V |

| VIN – VOUT = 0.5 V | VBIAS – VOUT = 1.4 V |
| VIN = 2.1 to 2.5 V | VOUT = 1.8 V | VBIAS = 3.2 V |
| VIN slew rate = 1 V/μs | IOUT = 350 mA |

| VIN = 2.3 V | VOUT = 1.8 V | VBIAS = 3.2 V |
| tRISE = 1 μs |
7 Detailed Description
7.1 Overview
The TPS720-Q1 family of LDO regulators uses innovative circuitry to achieve ultra-wide bandwidth and high loop gain, resulting in extremely high PSRR (up to 1 MHz) at very low headroom (VIN – VOUT). The implementation of the BIAS pin on the TPS720-Q1 vastly improves efficiency of low VOUT applications by allowing the use of a pre-regulated, low-voltage input supply. The TPS720-Q1 supports a novel feature where the output of the LDO regulates under light loads (< 500 μA) when the IN pin is left floating. The light-load drive current is sourced from VBIAS under this condition. This feature is particularly useful in power-saving applications where the dc-dc converter connected to the IN pin is disabled but the LDO is still required to regulate the voltage to a light load. These features, combined with low noise, low ground pin current, and ultra-small packaging, make this device ideal for portable applications. This family of regulators offers sub-band-gap output voltages, current limit, and thermal protection, and is fully specified from –40°C to +125°C.
7.2 Functional Block Diagram

7.3 Feature Description
7.3.1 Internal Current Limit
The TPS720-Q1 internal current limits help protect the regulator during fault conditions. During current limit, the output sources a fixed amount of current that is largely independent of output voltage. In such a case, the output voltage is not regulated, and is VOUT = ILIMIT × RLOAD. The NMOS pass transistor dissipates (VIN – VOUT) × IOUT until thermal shutdown is triggered and the device is turned off. When the device cools down, the internal thermal shutdown circuit turns the device back on. If the fault condition continues, the device cycles between current limit and thermal shutdown; see Thermal Considerations for more details.
The NMOS pass element in the TPS720-Q1 has a built-in body diode that conducts current when the voltage at OUT exceeds the voltage at IN. This current is not limited, so if extended reverse voltage operation is anticipated, TI recommends external limiting to 5% of rated output current.
7.3.2 Inrush Current Limit
The TPS720-Q1 family of LDO regulators implements a novel inrush current limit circuit architecture: the current drawn through the IN pin is limited to a finite value. This IINRUSHLIMIT charges the output to the final voltage. All current drawn through VIN charges the output capacitance when the load is disconnected. Equation 1 shows the inrush current limit performed by the circuit.

Assuming a COUT of 2.2 μF with the load disconnected (that is, ILOAD = 0), the IINRUSHLIMIT is calculated to be 100 mA. The inrush current charges the LDO output capacitor. If the output of the LDO regulates to 1.3 V, then the LDO charges the output capacitor to the final output value in approximately 28.6 μs.
Another consideration is when a load is connected to the output of an LDO. The TPS720-Q1 inrush current limit circuit employs a technique that supplies not only the IINRUSHLIMIT, but the additional current required by the load. If ILOAD = 350 mA, then IINRUSHLIMIT calculates to be approximately 450 mA (from Equation 1).
7.3.3 Shutdown
The enable pin (EN) is active high and is compatible with standard and low-voltage, TTL-CMOS levels. When shutdown capability is not required, EN can be connected to the IN pin.
7.3.4 Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO)
The TPS720-Q1 uses an undervoltage lockout circuit on the BIAS pin to keep the output shut off until the internal circuitry is operating properly. The UVLO circuit has a deglitch feature that typically ignores undershoot transients on the input if these transients are less than 50 μs in duration.
7.4 Device Functional Modes
Driving the EN pin over 1.1 V turns on the regulator. Driving the EN pin below 0.4 V causes the regulator to enter shutdown mode. In shutdown, the current consumption of the device is typically reduced to 500 nA.
8 Application and Implementation
NOTE
Information in the following applications sections is not part of the TI component specification, and TI does not warrant its accuracy or completeness. TI’s customers are responsible for determining suitability of components for their purposes. Customers should validate and test their design implementation to confirm system functionality.
8.1 Application Information
8.1.1 Input and Output Capacitor Requirements
Although a capacitor is not required for stability on the IN pin, good analog design practice is to connect a 0.1-μF to 1-μF low equivalent series resistance (ESR) capacitor across the IN pin input supply near the regulator. This capacitor counteracts reactive input sources and improves transient response, noise rejection, and ripple rejection. A higher-value capacitor may be necessary if large, fast rise-time load transients are anticipated, or if the device is located far from the power source. If source impedance is not sufficiently low, a 0.1-μF input capacitor may be necessary to ensure stability.
The BIAS pin does not require an input capacitor because BIAS does not source high currents. However, if source impedance is not sufficiently low, TI recommends a small 0.1-µF bypass capacitor.
The TPS720-Q1 is designed to be stable with standard ceramic capacitors with values of 2.2 μF or larger at the output. X5R- and X7R-type capacitors are best because they have minimal variation in value and ESR over temperature. Maximum ESR must be less than 250 mΩ.
8.1.2 Output Regulation With the IN Pin Floating
The TPS720-Q1 supports a novel feature where the output of the LDO regulates under light loads when the IN pin is left floating. Under normal conditions when the IN pin is connected to a power source, the BIAS pin draws only tens of milliamperes. However, when the IN pin is floating, an innovative circuit allows a maximum current of 500 μA to be drawn by the load through the BIAS pin and maintains the output in regulation. This feature is particularly useful in power-saving applications where a dc-dc converter connected to the IN pin is disabled, but the LDO is required to regulate the output voltage to a light load.
Figure 25 shows an application example where a microcontroller is not turned off (to maintain the state of the internal memory), but where the regulated supply (shown as the TPS62xxx) is turned off to reduce power. In this case, the TPS720-Q1 BIAS pin provides sufficient load current to maintain a regulated voltage to the microcontroller.
 Figure 25. Floating IN Pin Regulation Example
Figure 25. Floating IN Pin Regulation Example
8.1.3 Dropout Voltage
The TPS720-Q1 uses a NMOS pass transistor to achieve low dropout. When (VIN – VOUT) is less than the dropout voltage (VDO), the NMOS pass device is in the linear region of operation and the input-to-output resistance is the RDS(ON) of the NMOS pass element. VDO approximately scales with output current because the NMOS device behaves like a resistor in dropout.
PSRR and transient response are degraded when (VIN – VOUT) approaches dropout. This effect is shown in Figure 19.
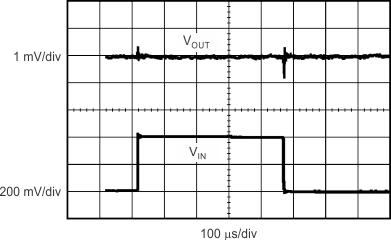
8.1.4 Transient Response
Increasing the size of the output capacitor reduces overshoot and undershoot magnitude but increases duration of the transient response.
8.1.5 Minimum Load
The TPS720-Q1 is stable with no output load. Although some LDOs suffer from low loop gain at very light output loads, the TPS720-Q1 employs an innovative, low-current mode circuit under very light or no-load conditions which improves output voltage regulation performance.
8.2 Typical Application
 Figure 26. Typical Application Schematic
Figure 26. Typical Application Schematic
8.2.1 Design Requirements
Table 1 lists the parameters for this design example.
Table 1. Design Parameters
| DESIGN PARAMETER | EXAMPLE VALUE |
|---|---|
| VIN | 2.3 V |
| VBIAS | 3.2 V |
| VOUT | 1.8 V |
| IOUT | 10-mA typical, 350-mA peak |
8.2.2 Detailed Design Procedures
TI recommends selecting the minimum component size; a small size solution for this design example is desired. Set CIN = 1 µF, C BIAS = 100 nF, and COUT = 2.2 µF.
8.2.3 Application Curves

| IOUT = 350 mA |

9 Power Supply Recommendations
The input supply and bias supply for the LDO must be within the recommended operating conditions and must provide adequate headroom for the device to have a regulated output. The minimum capacitor requirements must be met, and if the input supply is noisy, additional input capacitors with low ESR can improve transient performance.