SLVS325D March 2001 – February 2018 TPS791
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.3.2 Programming the TPS79101 Adjustable Regulator
The output voltage of the TPS79101 adjustable regulator is programmed using an external resistor divider; see Figure 32. The output voltage is calculated using:
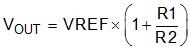
where
- VREF = 1.2246 V typ (the internal reference voltage)
Select resistors R1 and R2 for approximately a 50-µA divider current. Lower value resistors can be used for improved noise performance, but the solution consumes more power. Avoid higher resistor values because leakage current into or out of FB across R1, R2 creates an offset voltage that artificially increases or decreases the feedback voltage and thus erroneously decreases or increases VOUT. The recommended design procedure is to choose R2 = 30.1 kΩ to set the divider current at 50 µA, C1 = 15 pF for stability, and then calculate R1 using:
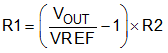
In order to improve the stability of the adjustable version, a small compensation capacitor is suggested to be placed between OUT and FB. For voltages < 1.8 V, the value of this capacitor must be 100 pF. For voltages > 1.8 V, the approximate value of this capacitor can be calculated as:
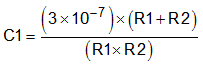
The table in Figure 34 shows the suggested value of this capacitor for several resistor ratios. If this capacitor is not used (such as in a unity-gain configuration) or if an output voltage < 1.8 V is chosen, then the minimum recommended output capacitor is 2.2 µF instead of 1 µF.
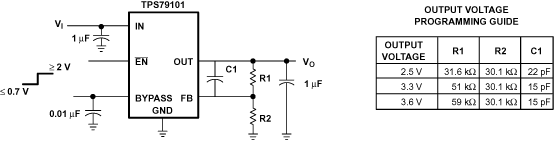 Figure 34. TPS79101 Adjustable LDO Regulator Programming
Figure 34. TPS79101 Adjustable LDO Regulator Programming