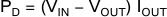SBVS188E march 2012 – may 2023 TPS7A16-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2 Typical Applications
- 8.3 Power Supply Recommendations
- 8.4 Layout
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DGN|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DGN|8
Orderable Information
8.4.1.2 Power Dissipation
The ability to remove heat from the die is different for each package type, presenting different considerations in the PCB layout. The PCB area around the device that is free of other components moves the heat from the device to the ambient air. Using heavier copper increases the effectiveness of removing heat from the device. The addition of plated through-holes to heat dissipating layers also improves the heat sink effectiveness.
Power dissipation depends on input voltage and load conditions. Power dissipation (PD) is equal to the product of the output current times the voltage drop across the output pass element, as shown in Equation 2: